A) total internal reflection
B) Interference
C) refraction with angle of refraction\[90{}^\circ \]
D) None of the above
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
Let the critical angle for air glass pair of media is given by c. Therefore, \[\mu =\frac{1}{\sin C},\sqrt{2}=\frac{1}{\sin C}\Rightarrow C=45{}^\circ \] By geometry, angle of incidence at hypotenuse surface of transparent right-angled isosceles prism is\[45{}^\circ \]. Therefore, \[i=c=45{}^\circ \] Thus, total internal reflection doesnt occur as\[i\]is not\[>c\]. And. angle of refraction is\[90{}^\circ \].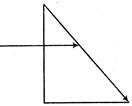
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
