A) \[\left( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}},\,\,1 \right)\]
B) \[\left( 1,\,\,\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\]
C) \[\left( \frac{1}{2},\,\,\frac{1}{2} \right)\]
D) \[\left( \frac{1}{2},\,\,\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\]
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
Equation of tangent to ellipse at given point is \[x\left( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)+2y\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)=1\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[x+\sqrt{2}y=\sqrt{2}\] ? (i)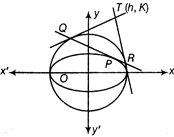 Now,\[QR\]is chord of contact of circle\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=1\]with respect to point\[T(h,\,\,K)\]. then, \[QR\equiv hx+Ky=1\] ... (ii) Equations (I) and (Ii) represent same straight line, then comparing ratio of coefficients we have \[\frac{h}{1}=\frac{K}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\] Hence;\[(h,\,\,K)\equiv \left( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}},\,\,1 \right)\]
Now,\[QR\]is chord of contact of circle\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=1\]with respect to point\[T(h,\,\,K)\]. then, \[QR\equiv hx+Ky=1\] ... (ii) Equations (I) and (Ii) represent same straight line, then comparing ratio of coefficients we have \[\frac{h}{1}=\frac{K}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\] Hence;\[(h,\,\,K)\equiv \left( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}},\,\,1 \right)\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
