A) 2
B) 1
C) -2
D) 3
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
Let the equation of\[AB\]be\[\frac{xb}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\]. Since, the line AB touches the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-4y+4=0\] \[\therefore \] \[\frac{\left| \frac{2}{a}+\frac{2}{b}=1 \right|}{\sqrt{\frac{1}{{{a}^{2}}}+\frac{1}{{{b}^{2}}}}}=2\] [Since, \[O(0,\,\,0)\]and\[C(2,\,\,2)\]lie on the same side of\[AB\], therefore\[\frac{2}{a}+\frac{2}{b}-1<0\]]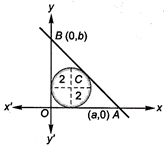 \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{-(2b+2a-ab)}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=2\] \[\Rightarrow \,\,\,2a-2b-ab+2\,\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=0\] ?(i) Since, \[\Delta \,\,OAB\]is a right angled triangle. So, its circumcentre is the midpoint of\[AB\]. \[\therefore \] \[h=\frac{a}{2}\] and \[k=\frac{b}{2}\] ? (ii) \[\Rightarrow \] \[a=2h\]and\[b=2k\] From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get \[4h+4k-4hk+2\sqrt{4{{h}^{2}}+4{{k}^{2}}}=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[h+k-hk+\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=0\] So, the locus of\[P(h,\,\,k)\]is \[x+y-xy+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}=0\] But the locus of the circumcentre is given to be \[x+y-xy+k\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}=0\] \[\therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,k=1\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{-(2b+2a-ab)}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=2\] \[\Rightarrow \,\,\,2a-2b-ab+2\,\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=0\] ?(i) Since, \[\Delta \,\,OAB\]is a right angled triangle. So, its circumcentre is the midpoint of\[AB\]. \[\therefore \] \[h=\frac{a}{2}\] and \[k=\frac{b}{2}\] ? (ii) \[\Rightarrow \] \[a=2h\]and\[b=2k\] From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get \[4h+4k-4hk+2\sqrt{4{{h}^{2}}+4{{k}^{2}}}=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[h+k-hk+\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=0\] So, the locus of\[P(h,\,\,k)\]is \[x+y-xy+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}=0\] But the locus of the circumcentre is given to be \[x+y-xy+k\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}=0\] \[\therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,k=1\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
