A) \[\frac{1}{2}x\]
B) \[2{{x}^{2}}\]
C) \[2x\]
D) \[\frac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
Since family of all circles touching x-axis at the origin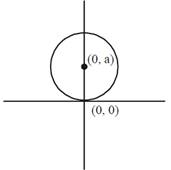 \[\therefore \]Eqn is \[{{(x)}^{2}}+{{(y-a)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]where (0, a) is the centre of circle. \[\Rightarrow \]\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}-2ay={{a}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2ay=0\] ...(1) Differentiate both side w.r.t 'x', we get \[2x+2y\frac{dy}{dx}-2a\frac{dy}{dx}=0\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[x+y\frac{dy}{dx}-a\frac{dy}{dx}=0\Rightarrow \frac{x+y\frac{dy}{dx}}{dy}=a\]\[\Rightarrow \] Put value of 'a' in eqn (1), we get \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2y\left[ \frac{y\frac{dy}{dx}+x}{\frac{dy}{dx}} \right]=0\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[({{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}})\frac{dy}{dx}-2{{y}^{2}}\frac{dy}{dx}-2xy=0\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[({{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2{{y}^{2}})\frac{dy}{dx}=2xy\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[({{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}})\frac{dy}{dx}=2xy\equiv g(x)y\] Hence, g(x) = 2x
\[\therefore \]Eqn is \[{{(x)}^{2}}+{{(y-a)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]where (0, a) is the centre of circle. \[\Rightarrow \]\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}-2ay={{a}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2ay=0\] ...(1) Differentiate both side w.r.t 'x', we get \[2x+2y\frac{dy}{dx}-2a\frac{dy}{dx}=0\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[x+y\frac{dy}{dx}-a\frac{dy}{dx}=0\Rightarrow \frac{x+y\frac{dy}{dx}}{dy}=a\]\[\Rightarrow \] Put value of 'a' in eqn (1), we get \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2y\left[ \frac{y\frac{dy}{dx}+x}{\frac{dy}{dx}} \right]=0\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[({{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}})\frac{dy}{dx}-2{{y}^{2}}\frac{dy}{dx}-2xy=0\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[({{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2{{y}^{2}})\frac{dy}{dx}=2xy\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[({{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}})\frac{dy}{dx}=2xy\equiv g(x)y\] Hence, g(x) = 2x
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
