A) \[3\pi -8:\pi +8\]
B) \[\pi -3:3\pi +3\]
C) \[3\pi -4:\pi +4\]
D) \[\pi -2:3\pi +2\]
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
Let I be the smaller portion and II be the greater portion of the given figure then,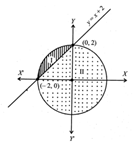 Area of \[I=\int\limits_{-2}^{0}{{}}\left[ \sqrt{4-{{x}^{2}}}-\left( x+2 \right) \right]dx\] \[=\left[ \frac{x}{2}\sqrt{4-{{x}^{2}}}+\frac{4}{2}{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \frac{x}{2} \right)_{-2}^{0} \right]-\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+2x \right]_{-2}^{0}\] \[=\left[ 2{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right) \right]-\left[ -\frac{4}{2}+4 \right]=2\times \frac{\pi }{2}-2=\pi -2\] Now, area of II = Area of circle - area of I. \[=4\pi -(\pi -2)\] \[=3\pi +2\] Hence, required ratio \[\text{=}\frac{\text{area}\,\text{of}\,\text{I}}{\text{area}\,\text{of}\,\text{II}}=\frac{\pi -2}{3\pi +2}\]
Area of \[I=\int\limits_{-2}^{0}{{}}\left[ \sqrt{4-{{x}^{2}}}-\left( x+2 \right) \right]dx\] \[=\left[ \frac{x}{2}\sqrt{4-{{x}^{2}}}+\frac{4}{2}{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \frac{x}{2} \right)_{-2}^{0} \right]-\left[ \frac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+2x \right]_{-2}^{0}\] \[=\left[ 2{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right) \right]-\left[ -\frac{4}{2}+4 \right]=2\times \frac{\pi }{2}-2=\pi -2\] Now, area of II = Area of circle - area of I. \[=4\pi -(\pi -2)\] \[=3\pi +2\] Hence, required ratio \[\text{=}\frac{\text{area}\,\text{of}\,\text{I}}{\text{area}\,\text{of}\,\text{II}}=\frac{\pi -2}{3\pi +2}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
