A) \[\frac{1}{2}\]
B) \[\frac{1}{16}\]
C) \[\frac{1}{4}\]
D) 1
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
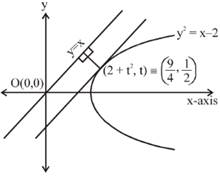 we have, \[{{\left. 2y.\frac{dy}{dx}=1\Rightarrow \frac{dy}{dx} \right]}_{P(2+{{t}^{2}},t)}}=\frac{1}{2t}=1\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[t=\frac{1}{2}\] \[\therefore \] \[P\left( \frac{9}{4},\frac{1}{2} \right)\] So, shortest distance \[=\frac{\left| \frac{9}{4}-\frac{2}{4} \right|}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{7}{4\sqrt{2}}\] \[\frac{dy}{dx}+\left( \frac{2x}{{{x}^{2}}+1} \right)y=\frac{1}{{{({{x}^{2}}+1)}^{2}}}\] (Linear differential equation) \[\therefore \]\[I.F.={{e}^{\ell n\left( {{x}^{2}}+1 \right)}}=({{x}^{2}}+1)\] So, general solution is \[y.({{x}^{2}}+1)=ta{{n}^{-1}}x+c\] As\[y(0)=0\Rightarrow c=0\] \[\therefore \]\[y(x)=\frac{{{\tan }^{-1}}x}{{{x}^{2}}+1}\] As,\[\sqrt{a}.y\,(1)=\frac{\pi }{32}\]\[\Rightarrow \]\[\sqrt{a}=\frac{1}{4}\Rightarrow a=\frac{1}{16}\]
we have, \[{{\left. 2y.\frac{dy}{dx}=1\Rightarrow \frac{dy}{dx} \right]}_{P(2+{{t}^{2}},t)}}=\frac{1}{2t}=1\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[t=\frac{1}{2}\] \[\therefore \] \[P\left( \frac{9}{4},\frac{1}{2} \right)\] So, shortest distance \[=\frac{\left| \frac{9}{4}-\frac{2}{4} \right|}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{7}{4\sqrt{2}}\] \[\frac{dy}{dx}+\left( \frac{2x}{{{x}^{2}}+1} \right)y=\frac{1}{{{({{x}^{2}}+1)}^{2}}}\] (Linear differential equation) \[\therefore \]\[I.F.={{e}^{\ell n\left( {{x}^{2}}+1 \right)}}=({{x}^{2}}+1)\] So, general solution is \[y.({{x}^{2}}+1)=ta{{n}^{-1}}x+c\] As\[y(0)=0\Rightarrow c=0\] \[\therefore \]\[y(x)=\frac{{{\tan }^{-1}}x}{{{x}^{2}}+1}\] As,\[\sqrt{a}.y\,(1)=\frac{\pi }{32}\]\[\Rightarrow \]\[\sqrt{a}=\frac{1}{4}\Rightarrow a=\frac{1}{16}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
