A) \[f(x)\] is discontinuous at \[x=a\]
B) \[f(x)\] is not differentiable at \[x=a\]
C) \[f(x)\] is differentiable at \[x\ge a\]
D) \[f(x)\] is continuous at all \[x<a\]
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
Given, \[f(x)=\left\{ \begin{matrix} 2a-x & in & -a<x<a \\ 3x-2a & in & a\le x \\ \end{matrix} \right.\] At \[x=a\] LHL= \[\underset{x\to {{a}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f(x)\] \[=\underset{x\to a}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\,2a-x=a\] RHL \[=\underset{x\to {{a}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f(x)\] \[=\underset{x\to a}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\,3x-2a=a\] and \[f(a)=3(a)-2a=a\] \[\therefore \] LHL = RHL =\[f(a)\] Hence, it is continuous at \[x=a\] Again, at \[x=a\] LHD \[=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{lim}}\,\frac{f(a-h)-f(a)}{-h}\] \[=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{lim}}\,\frac{2a-(a-h)-a}{-h}=\frac{h}{-h}=-1\] and RHD \[=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{f(a+h)-f(a)}{h}\] \[=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{3(a+h)-2a-a}{h}=3\] \[\therefore \] \[LHD\ne RHD\] Hence, it is not differentiable at \[x=a\]. Alternate Solution Let \[y=f(x)=\left\{ \begin{matrix} 2a-x & in & -a<x<a \\ 3x-2a & in & a\le x \\ \end{matrix} \right.\]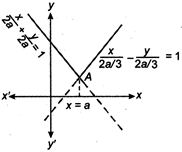 It is clear from the graph that \[f(x)\] is continuous everywhere it is also differentiable everywhere except a point A at \[x=a\]
It is clear from the graph that \[f(x)\] is continuous everywhere it is also differentiable everywhere except a point A at \[x=a\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
