A) \[-2,1,4\]
B) \[0,2,4\]
C) \[0,1,4\]
D) \[-2,2,4\]
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
We have \[|{{x}^{2}}-x-6|=x+2\] ?(i) or \[|(x-3)(x+2)|=x+2\] Case I: When \[-2\le x\]or \[x\ge 3\] From Eq. (i) \[{{x}^{2}}-x-6=x+2\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[{{x}^{2}}-2x-8=0\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[(x-4)(x+2)=0\Rightarrow x=-2,4\] Case II: When \[-2<x<3\] From Eq. (i) \[-({{x}^{2}}-x-6)=x+2\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[-{{x}^{2}}+x+6=x+2\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[-{{x}^{2}}=-4\Rightarrow x=\pm \,2\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[x=2\](\[\because \,x=-2\]not lies in the interval) Hence, the roots are \[\{-2,\text{ }2,\text{ }4\}\] Alternate Solution: Case I: When\[-2\le x\]or \[x\ge 3\] Let \[y={{x}^{2}}-x-6=x+2\] Now, \[y={{x}^{2}}-x-6\] \[\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+\frac{1}{4} \right)=y+6+\frac{1}{4}\]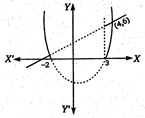 \[{{\left( x-\frac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=y+\frac{25}{4}\] and \[y=x+2\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{y}{2}-\frac{x}{2}=1\] Case II: When \[-2<x<3\] Let \[y=-({{x}^{2}}-x-6)=x+2\] Now, \[y=-({{x}^{2}}-x-6)\]
\[{{\left( x-\frac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=y+\frac{25}{4}\] and \[y=x+2\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{y}{2}-\frac{x}{2}=1\] Case II: When \[-2<x<3\] Let \[y=-({{x}^{2}}-x-6)=x+2\] Now, \[y=-({{x}^{2}}-x-6)\] 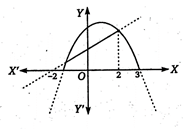 \[-\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+\frac{1}{4} \right)=y-6-\frac{1}{4}\] \[{{\left( x-\frac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=-\left( y-\frac{25}{4} \right)\] and \[y=x+2\] It is clear from die above two figures that the curve will intersect the line^ in three different points i.e., \[\{-2,\text{ }2,\text{ }4\}\].
\[-\left( {{x}^{2}}-x+\frac{1}{4} \right)=y-6-\frac{1}{4}\] \[{{\left( x-\frac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=-\left( y-\frac{25}{4} \right)\] and \[y=x+2\] It is clear from die above two figures that the curve will intersect the line^ in three different points i.e., \[\{-2,\text{ }2,\text{ }4\}\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
