A) NADPH only
B) NADH only
C) FADH only
D) FADH and NADH.
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
: The pentose phosphate pathway is primarily an anabolic pathway that utilizes the 6 carbons of glucose to generate 5 carbon sugars and reducing equivalents. However, this pathway does oxidize glucose and under certain conditions can completely oxidize glucose to\[C{{O}_{2}}\]and water. The primary functions of this pathway are: 1. To generate reducing equivalents, in the form of NADPH, for reductive biosynthesis reactions within cells. 2. To provide the cell with ribose-5-phosphate (R5P) for the synthesis of the nucleotides and nucleic acids. 3. Although not a significant function of the PPP it can operate to metabolize dietary pentose sugars derived from the digestion of nucleic acids as well as to rearrange the carbon skeletons of dietary carbohydrates into glycolytic/gluconeogenic intermedia. The pentose phosphate pathway has both an oxidative and a non-oxidative arm. The oxidation steps, utilizing glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) as the substrate, occur at the beginning of the pathway and are the reactions that generate NADPH. The reactions catalyzed by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase generate one mole of NADPH each for every mole of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) that enters the PPP. Oxidative Stage of Pentose Phosphate Pathway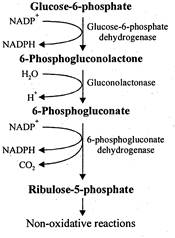 Oxidative pentose phosphate pathway generates NADPH for reductive synthesis such as fatty acid, amino acids via glutamate dehydrogenase, or reduced glutathione in erythrocytes and steroid biosynthesis. It is active in liver, adipose tissue, adrenal cortex, thyroid, erythrocytes, testes and lactating mammary glands. It occurs inside the cytoplasm.
Oxidative pentose phosphate pathway generates NADPH for reductive synthesis such as fatty acid, amino acids via glutamate dehydrogenase, or reduced glutathione in erythrocytes and steroid biosynthesis. It is active in liver, adipose tissue, adrenal cortex, thyroid, erythrocytes, testes and lactating mammary glands. It occurs inside the cytoplasm.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
