| The absolute refractive indices of glass and water are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is \[2\times {{10}^{8}}\,m/s,\] calculate the speed of light in |
| (i) vacuum, (ii) water. |
| Two elements 'F' and 'Q' belong to the same period of the modern periodic table and are in Group-1 and Group-2 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form: |
| (a) The number of electrons in their atoms |
| (b) The sizes of their atoms |
| (c) Their metallic characters |
| (d) Their tendencies to lose electrons |
| (e) The formula of their oxides |
| (f) The formula of their chlorides |
| Explain with an example for each, how the following provides evidences in favour of evolution in organisms: |
| (a) Homologous organs |
| (b) Analogous organs |
| (c) Fossils |
| Explain the following: |
| (a) Speciation |
| (b) Natural Selection |
| (a) Name the human male reproductive organ that produces sperms and also secretes a hormone. Write the functions of the secreted hormone. |
| (b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where |
| (i) fertilisation takes place, |
| (ii) implantation of the fertilised egg occurs. |
| Explain how the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother's body. |
| How do Mendel's experiments show that the |
| (a) traits may be dominant or recessive, |
| (b) traits are inherited independently? |
| What is meant by power of a lens? Define its S.I. unit. |
| You have two lenses A and B of focal lengths \[+\mathbf{10}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\]and \[\mathbf{10}\text{ }\mathbf{cm}\]respectively. State the nature and power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will form a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 8 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. |
| One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. |
| A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image. |
| Write the importance of ciliary muscles in the human eye. Name the defect of vision that arises due to gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles in old age. What type of lenses are required by the persons suffering from this defect to see the objects clearly? |
| Akshay, sitting in the last row in his class, could not see clearly the words written on the blackboard. When the teacher noticed it, he announced if any student sitting in the front row could volunteer to exchange his seat with Akshay. Salman immediately agreed to exchange his seat with Akshay. He could now see the words written on the blackboard clearly. The teacher thought it fit to send the message to Akshay?s parents advising them to get his eyesight checked. In the context of the above event, answer the following questions: |
| (a) Which defect of vision is Akshay suffering from? Which type of lens is used to correct this defect? |
| (b) State the values displayed by the teacher and Salman. |
| (c) In your opinion, in what way can Akshay express his gratitude towards the teacher and Salman? |
| What do we observe on pouring acetic acid on red blue litmus papers? |
| (a) Red litmus remains red and blue litmus turns red. |
| (b) Red litmus turns blue and blue litmus remains blue. |
| (c) Red litmus turns blue and blue litmus turns red. |
| (d) Red litmus becomes colourless and blue litmus remains blue. |
| While preparing soap a small quantity of common salt is generally added to the reaction mixture of vegetable oil and sodium hydroxide. Which one of the following may be the purpose of adding common salt? |
| (a) To reduce the basic nature of the soap |
| (b) To make the soap neutral |
| (c) To enhance the cleansing power of the soap |
| (d) To favour the precipitation of the soap |
| A student takes about 4 mL of distilled water in four test tubes marked V, Q, R and S. He then dissolves in each test tube an equal amount of one salt in one test tube, in namely sodium sulphate in P, potassium sulphate in Q, calcium sulphate in R and magnesium sulphate in S. After that he adds an equal amount of soap solution in each test tube. On shaking each of these test tubes well, he observes a good amount of lather (foam) in the test tubes marked |
| (a) P and Q (b) Q and R |
| (c) P, Q and S (d) P, R and S |
| A student was asked to observe and identify the various parts of an embryo of a red kidney bean seed. He identified the parts and listed them as under: |
| I. Tegmen II. Testa |
| III. Cotyledon IV. Radicle |
| V. Plumule |
| The correctly identified parts among these are |
| (a) I, II and III |
| (b) II, III and IV |
| (c) III, IV and V |
| (d) I, III, IV and V |
| Given below is the list of vegetables available in the market. Select from these the two vegetables having homologous structures: |
| Potato, sweet potato, ginger, radish, tomato, carrot, okra (Lady's finger) |
| (a) Potato and sweet potato |
| (b) Radish and carrot |
| (c) Okra and sweet potato |
| (d) Potato and tomato |
| A student obtains a sharp image of the distant window (W) of the school laboratory on the screen (S) using the given concave mirror (M) to determine its focal length. Which of the following distance should he measure to get the focal length of the mirror? |
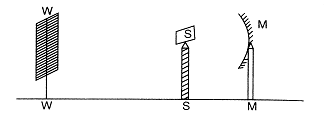 |
| (a) MW (b) MS |
| (c) SW (d) MW-MS |
| A student used a device (X) to obtain/focus the image of a well illuminated distant building on a screen (S) as shown below in the diagram. Select the correct statement about the device (X). |
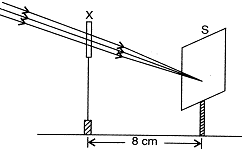 |
| (a) This device is a concave lens of focal length 8 cm. |
| (b) This device is a convex mirror of focal length 8 cm. |
| (c) This device is a convex lens of focal length 4 cm. |
| (d) This device is a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. |
| A student traces the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for the different values of angle of incidence. He observes all possible precautions at each step of the experiment. At the end of the experiment, on analysing the measurements, which of the following conclusions is he likely to draw? |
| (a) \[\angle i=\angle e<\angle r\] |
| (b) \[\angle i<\angle e<\angle r\] |
| (c) \[\angle i>\angle e<\angle r\] |
| (d) \[\angle i=\angle e>\angle r\] |
| A student traces the path of a ray of light through a triangular glass prism for different values of angle of incidence. On analysing the ray diagrams, which one of the following conclusions is he likely to draw? |
| (a) The emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray. |
| (b) The emergent ray bends at an angle to the direction of the incident ray. |
| (c) The emergent ray and the refracted ray are at right angles to each other. |
| (d) The emergent ray is perpendicular to the incident ray. |
| Students were asked to observe the permanent slides showing different stages of budding in yeast under high power of a microscope. |
| (a) Which adjustment screw (coarse/fine) were you asked to move to focus the slides? |
| (b) Draw three diagrams in correct sequence showing budding in yeast. |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
