Answer:
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The diagram of electric motor is shown below
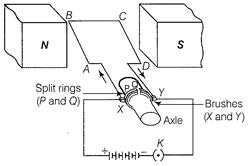 (2)
Principle It works on the principle of magnetic effect of current. When a current-carrying conductor is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field, it experiences a force. (1)
Working Consider at the beginning, the arms AB and CD are perpendicular to the direction of applied magnetic field.
(a) Initially, let the current in the coil flows along the path ABCD. Then, according to the Fleming's left-hand rule, a downward force acts on the arm AB pushes it downwards and an upward force on arm CD pushes it upwards. These forces cause the coil to rotate in anti-clockwise direction about its own axis.
(b) After completing half rotation, the position of split rings interchanges due to which direction of current in the coil gets reversed and current flows along the path DCBA. Again according to Fleming's left-hand rule, the force acting on the arms AB and CD also get reversed. This makes the coil to rotate and complete the next half cycle of rotation in the same direction.
Thus, the interchanging of split rings at each half turn, makes the coil to rotate continuously in the same direction as long as the current is passing through it.
(2)
Principle It works on the principle of magnetic effect of current. When a current-carrying conductor is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field, it experiences a force. (1)
Working Consider at the beginning, the arms AB and CD are perpendicular to the direction of applied magnetic field.
(a) Initially, let the current in the coil flows along the path ABCD. Then, according to the Fleming's left-hand rule, a downward force acts on the arm AB pushes it downwards and an upward force on arm CD pushes it upwards. These forces cause the coil to rotate in anti-clockwise direction about its own axis.
(b) After completing half rotation, the position of split rings interchanges due to which direction of current in the coil gets reversed and current flows along the path DCBA. Again according to Fleming's left-hand rule, the force acting on the arms AB and CD also get reversed. This makes the coil to rotate and complete the next half cycle of rotation in the same direction.
Thus, the interchanging of split rings at each half turn, makes the coil to rotate continuously in the same direction as long as the current is passing through it. 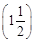 Function of split ring It reverses the direction of current in the armature coil. (1/2)
Or
A current induces in a solenoid if a bar magnet is moved relative to it. This is the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Function of split ring It reverses the direction of current in the armature coil. (1/2)
Or
A current induces in a solenoid if a bar magnet is moved relative to it. This is the principle of electromagnetic induction. 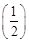 (i) When a bar magnet is pushed into a coil of insulated copper wire, a current is induced momentarily in the coil. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily in a particular direction.
(ii) When the bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil of the insulated copper wire, a current is again induced momentarily in the coil in the opposite direction. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily in the opposite direction.
(iii) When a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil no current will be induced in the coil. Hence, galvanometer will show no deflection.
(i) When a bar magnet is pushed into a coil of insulated copper wire, a current is induced momentarily in the coil. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily in a particular direction.
(ii) When the bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil of the insulated copper wire, a current is again induced momentarily in the coil in the opposite direction. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily in the opposite direction.
(iii) When a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil no current will be induced in the coil. Hence, galvanometer will show no deflection. 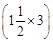
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
