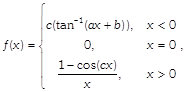 \[(c\ne 0)\] is differentiable at \[x=0,\]then locus of the point \[(b+c,a)\] is
\[(c\ne 0)\] is differentiable at \[x=0,\]then locus of the point \[(b+c,a)\] is
A) \[{{x}^{2}}=y\]
B) \[{{y}^{2}}=2x\]
C) \[x=2y\]
D) \[y=2x\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
[c]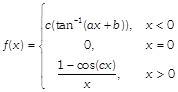 \[f(x)\] is continuous at \[x=0\] \[\therefore \,\,\,\,c{{\tan }^{-1}}(b)=0=\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{1-\cos (cx)}{x}\] \[\therefore \,\,c{{\tan }^{-1}}(b)=0\] \[\therefore \,\,b=0\] Also, R.H.D. \[f'({{0}^{+}})=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{\frac{1-\cos (ch)}{h}-0}{h}\] \[=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{1-\cos \,ch}{{{h}^{2}}.{{c}^{2}}}.{{c}^{2}}=\frac{{{c}^{2}}}{2}\] L.H.D. \[=f'({{0}^{-}})=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{c{{\tan }^{-1}}(-ah)-0}{-h}=ac\] It is given that \[f(x)\] is differentiable at\[x=0\]. So, \[\frac{{{c}^{2}}}{2}=ac\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\Rightarrow c=2a\] \[\therefore \,\,\,\,(b+c,a)\equiv (c,a)\] Locus of \[(c,a)\] is\[x=2y\].
\[f(x)\] is continuous at \[x=0\] \[\therefore \,\,\,\,c{{\tan }^{-1}}(b)=0=\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{1-\cos (cx)}{x}\] \[\therefore \,\,c{{\tan }^{-1}}(b)=0\] \[\therefore \,\,b=0\] Also, R.H.D. \[f'({{0}^{+}})=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{\frac{1-\cos (ch)}{h}-0}{h}\] \[=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{1-\cos \,ch}{{{h}^{2}}.{{c}^{2}}}.{{c}^{2}}=\frac{{{c}^{2}}}{2}\] L.H.D. \[=f'({{0}^{-}})=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{c{{\tan }^{-1}}(-ah)-0}{-h}=ac\] It is given that \[f(x)\] is differentiable at\[x=0\]. So, \[\frac{{{c}^{2}}}{2}=ac\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\Rightarrow c=2a\] \[\therefore \,\,\,\,(b+c,a)\equiv (c,a)\] Locus of \[(c,a)\] is\[x=2y\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
