| (i) If X and Y are complementary goods. |
| (ii) If X and Y are substitute goods. |
Answer:
Excess Demand It refers to a situation when Demand\[({{D}_{X}})>\] Supply\[({{S}_{X}})\]corresponding to a given price X. Excess Supply It refers to a situation when\[{{D}_{X}}<{{S}_{X}}\], corresponding to a given price of X. Following demand and supply schedule illustrates the situations:
Effects of Excess Demand on Price of the Commodity In a situation of excess demand, consumers are willing to buy greater amount of a commodity than what the producers are willing to sell. Accordingly, price of the commodity will be pushed up. This causes expansion of supply and contraction of demand. This process will continue till demand of a commodity equals its supply and the equilibrium struck in the market. The market will reach the point of equilibrium at a higher price than that price at which there was excess demand. In the schedule given above, there is excess demand when price is Rs. 4\[({{D}_{X}}=80,{{S}_{X}}=40)\]. Because of this, price will rise to Rs.6, which is the equilibrium price. After equilibrium struck\[({{D}_{X}}={{S}_{X}}=60),{{P}_{X}}\]=Rs.6. Effects of Excess Supply on Price of the Commodity In a situation of excess supply, producer are willing to sell greater amount of a commodity than what the consumers are willing to buy. Accordingly, price of the commodity will be pushed down. This will cause contraction of supply and expansion of demand. This process will continue till demand of a commodity equals its supply, and the equilibrium is struck in the market. The market will reach the point of equilibrium at a lower price than price at which there was excess supply. In the given schedule, there is excess supply when price is Rs. 8, \[({{S}_{X}}=80,{{D}_{X}}=40)\]. Because of excess supply, price falls to Rs.6, which is the equilibrium price. After equilibrium is struck\[({{S}_{X}}={{D}_{X}}=60),\,\,{{P}_{X}}=Rs.\,\,60\]
\[{{P}_{X}}\](Rs.)
Supply\[({{S}_{X}})\]
Demand\[({{D}_{X}})\]
Excess Supply (Units) \[({{S}_{X}}-{{D}_{X}})\]
Excess Demand (Units) \[({{D}_{X}}-{{S}_{X}})\]
10
100
20
80
?
8
80
40
40
?
6
60
60
?
?
4
40
80
?
40
2
20
100
?
80
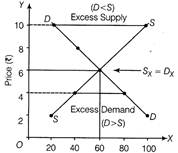 Quantity (units) Diagram Showing Excess Demand and Excess Supply Or (i) In case of complementary goods, when the price of X falls, demand for commodity Y increases. As a result, demand curve of commodity Y will shift towards right but supply curve remains constant.
Quantity (units) Diagram Showing Excess Demand and Excess Supply Or (i) In case of complementary goods, when the price of X falls, demand for commodity Y increases. As a result, demand curve of commodity Y will shift towards right but supply curve remains constant. 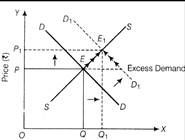 Quantity (units) Diagram Showing Effects of Fall in Price of Good X on Equilibrium Price and Quantity of Good Y (Complementary goods) Due to increase in demand of commodity Y, there will be excess demand at the original price. Therefore, supplier will be motivated to increase the price of commodity Y. The equilibrium price and quantity would tend to increase. (ii) In case of substitute goods, when the price of X falls, demand for commodity V will also fall. As a result, the demand curve of commodity Y will shift towards the left, but supply curve remains constant. Due to decrease in demand of commodity y, there will be deficient demand at the original price. Therefore, suppliers will be forced to decrease the price of the commodity Y. The equilibrium price and quantity would tend to decrease.
Quantity (units) Diagram Showing Effects of Fall in Price of Good X on Equilibrium Price and Quantity of Good Y (Complementary goods) Due to increase in demand of commodity Y, there will be excess demand at the original price. Therefore, supplier will be motivated to increase the price of commodity Y. The equilibrium price and quantity would tend to increase. (ii) In case of substitute goods, when the price of X falls, demand for commodity V will also fall. As a result, the demand curve of commodity Y will shift towards the left, but supply curve remains constant. Due to decrease in demand of commodity y, there will be deficient demand at the original price. Therefore, suppliers will be forced to decrease the price of the commodity Y. The equilibrium price and quantity would tend to decrease. 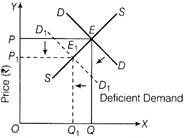 Quantity (units) Diagram Showing Effect of Fall in Price of Good X on Equilibrium Price and Quantity of Good Y (Substitute goods)
Quantity (units) Diagram Showing Effect of Fall in Price of Good X on Equilibrium Price and Quantity of Good Y (Substitute goods)
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
