Answer:
Product differentiation refers to the practice of differentiating products on lines of design, colour or packaging. In monopolistic competition, rival firms sell products which are not perfect substitutes but close substitutes of each other e.g. Pepsodent and Colgate toothpaste are close substitutes of each other due to product differentiation in their ingredients. The implications of monopolistic competition are as follows: (i) It allows firm to have a partial control over price of their product. (ii) Elasticity of demand for a product tends to be high due to presence of close substitutes. (iii) Consumer's welfare is increased due to large variety of commodity. Or Equilibrium price refers to the price at which market demand is equal to market supply (i.e. there is no excess demand or excess supply). So, the price with 'excess supply' is not the equillibrium price, This can be illustrated with the help of the following figure: 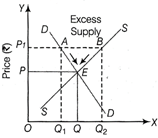 Quantity (units) Diagram Showing Excess Supply The given figure depicts, that excess supply is equal to AB =\[{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{2}}\].It implies that market supply is greater than market demand. This puts pressure on price\[(O{{P}_{1}})\]to decline. The producers reduce the quantity supplied at the lower price OP from \[O{{Q}_{2}}\]to OQ. The consumers react by increasing the quantity demanded from\[(O{{Q}_{1}})\](at\[O{{P}_{1}}\] price) to OQ (at OP price). Equilibrium is struck at point ?E?. Thus, OP and OQ are the equilibrium price and equilibrium price and quantity respectively with no excess supply.
Quantity (units) Diagram Showing Excess Supply The given figure depicts, that excess supply is equal to AB =\[{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{2}}\].It implies that market supply is greater than market demand. This puts pressure on price\[(O{{P}_{1}})\]to decline. The producers reduce the quantity supplied at the lower price OP from \[O{{Q}_{2}}\]to OQ. The consumers react by increasing the quantity demanded from\[(O{{Q}_{1}})\](at\[O{{P}_{1}}\] price) to OQ (at OP price). Equilibrium is struck at point ?E?. Thus, OP and OQ are the equilibrium price and equilibrium price and quantity respectively with no excess supply.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
