Answer:
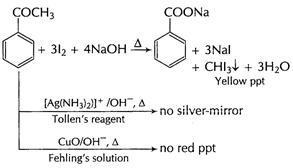
(a)![]()
(i)
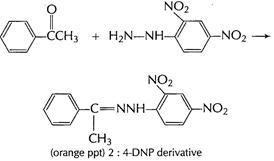
It gives orange ppt with 2,4-DNP reagent
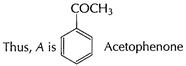
Carbonyl group present, ketonic or aldehyde
(ii)
It neither reduces Tollen's reagent or Fehling's
solution
-CHO (aldehyde group absent)
(iii)
It forms yellow precipitate with
![]() and
NaOH
and
NaOH
![]() group
present
group
present
(iv)
It does not decolourise
![]() water
or Baeyer's reagent (alkaline
water
or Baeyer's reagent (alkaline ![]() )
)
![]() or
or![]() in open
chain absent
in open
chain absent
(v)
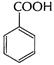
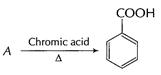
Drastic oxidation gives a carboxylic acid (B)
B has ?COOH group
![]() is
is ![]() [1]
Where R is
[1]
Where R is ![]()
![]() Thus, A B is benzoic acid
Thus, A B is benzoic acid
 [1]
Explanation
[1]
Explanation
 (b) (i) Cyclohexene to atopic acid
(b) (i) Cyclohexene to atopic acid
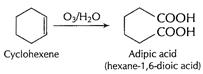 Ozonolysis by
Ozonolysis by ![]() cleaves
(C = C) bond and ? COOH is formed.
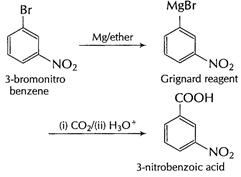
(ii) 3 bromonitrobenzene to 3-nitrobenzoic acid
cleaves
(C = C) bond and ? COOH is formed.
(ii) 3 bromonitrobenzene to 3-nitrobenzoic acid
 (a) Functional isomers (Carbonyl compounds) of the formula
(a) Functional isomers (Carbonyl compounds) of the formula
![]() are
(i)
are
(i)![]() propanone
(ii)
propanone
(ii)![]() propanal
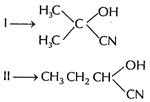
Both forms cyanohydrins with HCN.
Reaction with HCN is faster with propanal since steric
hindrance increases with (i)
propanal
Both forms cyanohydrins with HCN.
Reaction with HCN is faster with propanal since steric
hindrance increases with (i)
 Protonation increases electrophilic nature of carbonyl
compound.
In case of
Protonation increases electrophilic nature of carbonyl
compound.
In case of ![]() effect of
two methyl groups decrease positive charge on carbonyl carbon, hence its reactivity
for nucleophiric attack of CN- is decreased.
Hence,
effect of
two methyl groups decrease positive charge on carbonyl carbon, hence its reactivity
for nucleophiric attack of CN- is decreased.
Hence, ![]() reacts
completely with HCN. [1]
Final products with HCN
reacts
completely with HCN. [1]
Final products with HCN
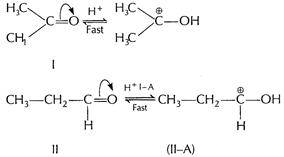
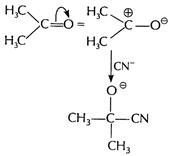
 Mechanism
Step I lonisation of weak acid in
presence of base
Mechanism
Step I lonisation of weak acid in
presence of base ![]() Step II Nucleophilic addition of
Step II Nucleophilic addition of ![]() on
carbonyl compound
on
carbonyl compound
 Step III
Step III 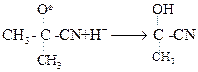 (b)
(b)![]() No stabilization by resonance
No stabilization by resonance
![]() is
stabilized by resonance
is
stabilized by resonance
![]() Thus, formation of
Thus, formation of ![]() is more
favoured than
is more
favoured than ![]() Thus, carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohol lonisation
of
Thus, carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohol lonisation
of ![]() is more
than
is more
than ![]() since
electronegativity of
since
electronegativity of ![]() F
shows more
F
shows more ![]() effect
than Cl. [1]
Thus,
effect
than Cl. [1]
Thus,
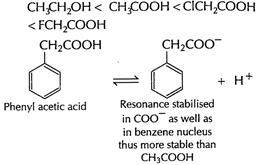 Thus, decreasing acid strength is
Thus, decreasing acid strength is
![]()
![]() [1]
[1]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
