| Given below is the type of global biodiversity representing the proportionate number of species of major taxa of plants. Observe it carefully and answer the questions that follow. |
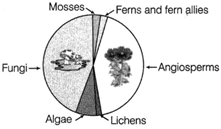 |
| Representation of global biodiversity of major taxa of plants |
| (i) Identify the most endangered group of plants among all categories. |
| (ii) What may be the reason behind such less population of mosses and ferns? |
| (iii) Name the most advanced and the most primitive group of plants in the biodiversity given above. |
| (iv) Fungi, inspite of being heterotroph are able to sustain themselves as a large population. Explain. |
| Or |
| With the help of a flowchart, explain what are the various major approaches to conserve biodiversity? |
Answer:
(i) Lichens are the most endangered plants among the given categories. (ii) Population of mosses and ferns is less may be due to following reasons (a) Habitat loss Destruction of habitat is the most important cause of extinction of mosses and ferns. It could be due to urbanisation. (b) Over - exploitation Humans are always dependent on nature for food and shelter. However, when human needs turn into greed, it leads to the over-exploitation of natural resources. Many mosses and ferns are also used for various purposes. Their over-exploitation has led to their less number. (c) Environmental pollution Many ferns and mosses cannot grow in very polluted enviornment. Thus, environmental pollution is also responsible for their less number. (d) Expansion of agriculture In the last few years, due to the expansion of agriculture, land available for natural vegetation is very less. It is also a major cause for the less number of ferns and mosses. (iii) Angiosperms are the most advanced and algae are the most primitive group of plants in the given biodiversity. (iv) Fungi are heterotrophic in nature due to lack of chlorophyll. They are able to sustain themselves as a large population because of their ability to reproduce both asexually and sexually. Or The major approaches to conserve biodiversity can be ex situ or in situ. These are given in the following flowchart. Biodiversity Conservation 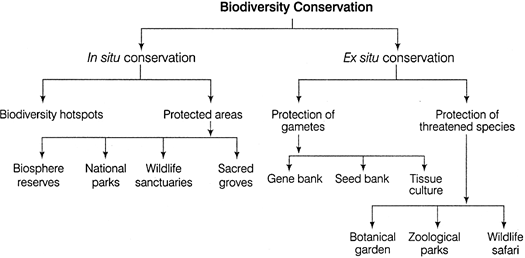
In situ Conservation It involves the protection of species in their natural habitat. (i) Biodiversity hotspots are the regions of high levels of species richness and high degree of endemism (that is species confined to that region and not found anywhere else). The total number of biodiversity hotspots is 34. Three hotspots, which cover India are Western Ghats/Sri Lanka, Indo-Burma region and Eastern Himalayas. (ii) Protected areas are ecologically and biodiversity rich regions. India has 14 Biosphere Reserves, 90 National Parks and 449 Wildlife Sanctuaries. The first National Park setup in India was Jim Corbett National Park. Ex situ Conservation It involves conservation of selected species outside their natural habitats. (i) Protection of gametes can be done by storing material in the places where stocks remain viable for a longer period of time without harming their genetic variability. (ii) Protection of threatened species comes under the category of off-site collections of various wild and domesticated species. India has around 800 parks where animals which have become extinct in wild are maintained and has around 1500 botanical gardens to collect, cultivate and display different varieties of plant species.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
