Answer:
Under the acidic conditions, alcohol is initially protonated and then loses \[{{H}_{2}}O\] to form a carbocation. If \[HCl\] is used, then \[C{{l}^{-}}\] ion being a strong nucleophile will result in nucleophilic substitution to form alkyl chloride. However,\[HSO_{4}^{-}\] ion released by \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\] is a very weak nucleophile and cannot participate in the nucleophilic substitution. It will rather act as a base and eliminate a proton to form alkene as the product as follows : 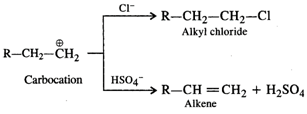 Concentrated \[HN{{O}_{3}}\] is a powerful oxidising agent. It will cause oxidation of alcohol to aldehyde and then to acid. Thus, out of the mineral acids listed, dehydration is carried by concentrated \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]. Even phosphoric acid can be used.
Concentrated \[HN{{O}_{3}}\] is a powerful oxidising agent. It will cause oxidation of alcohol to aldehyde and then to acid. Thus, out of the mineral acids listed, dehydration is carried by concentrated \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]. Even phosphoric acid can be used.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
