NCERT Extracts - Natural Vegetation and Wild Life
Category : UPSC
Forests
Tropical Evergreen Forests
- These forests are also called tropical rainforests. These thick forests occur in the regions near the equator and close to the tropics. These regions are hot and receive heavy rainfall throughout the year.
- As there is no particular dry season, the trees do not shed their leaves altogether. This is the reason they are called evergreen.
- The thick canopies of the closely spaced trees do not allow the sunlight to penetrate inside the forest even in the day time. Hardwood trees like rosewood, ebony, mahogany are common here.
Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Tropical deciduous are the monsoon forests found in the large part of India, northern Australia and in central America.
- These regions experience seasonal changes. Trees shed their leaves in the dry season to conserve water. The hardwood trees found in these forests are sal, teak, neem and shisham.
- Hardwood trees are extremely useful for making furniture, transport and constructional materials.
- Tigers, lions, elephants, langoors and monkeys are the common animals of these regions.
Temperate Evergreen Forests
- The temperate evergreen forests are located in the mid-latitudinal coastal region.
- They are commonly found along the eastern margin of the continents, e.g., In south east USA, South China and in South East Brazil. They comprise both hard and soft wood trees like oak, pine, eucalyptus, etc.
Temperate Deciduous Forests
- As we go towards higher latitudes, there are more temperate deciduous forests. These are found in the north eastern part of USA, China, New Zealand, Chile and also found in the coastal regions of Western Europe.
- They shed their leaves in the dry season. The common trees are oak, ash, beech, etc. Deer, foxes, wolves are the animals commonly found. Birds like pheasants, monals are also found here.
Mediterranean Vegetation
- Most of the east and north east margins of the continents are covered by temperate evergreen and deciduous trees. The west and south west margins of the continent are different.
- They have Mediterranean vegetation. It is mostly found in the areas around the Mediterranean sea in Europe, Africa and Asia, hence the name.
- This kind of vegetation is also found outside the actual Mediterranean region in California in the USA, south west Africa, south western South America and South west Australia.
- These regions are marked for hot dry summers and mild rainy winters.
- Citrus fruits such as oranges, figs, olives and grapes are commonly cultivated here because people have removed the natural vegetation in order to cultivate what they want to. There isn't much wildlife here.
- Mediterranean trees adapt themselves to dry summers with the help of their thick barks and wax coated leaves which help them reduce transpiration.
- Mediterranean regions are known as 'Orchards of the world' for their fruit cultivation.
Coniferous Forests
- In the higher latitudes (50°-700) of Northern hemisphere the spectacular Coniferous forests are found. These are also called as Taiga.
- These forests are also seen in the higher altitudes. They are tall, softwood evergreen trees. The woods of these trees are very useful for making pulp, which is used for manufacturing paper and newsprint.
- Match boxes .and packing boxes are also made from softwood. Chir, pine, cedar are the important variety of trees in these forests. Silver fox, mink, polar bear are the common animals found here.
Grasslands
Tropical grasslands
- These occur on either side of the equator and extend till the tropics. This vegetation grows in the areas of moderate to low amount of rainfall.
- The grass can grow very tall, about 3 to 4 metres in height. Savannah grasslands of Africa are of this type. Elephants, zebras, giraffes, deer, leopards are common in tropical grasslands.
Temperate grasslands
- These are found in the midlatitudinal zones and in the interior part of the continents, Usually, grass here is short and nutritious. Wild buffaloes, bisons, antilopes are common in the temperate region.
Thorny bushes
- These are found in the diy desert like regions. Tropical deserts are located on the western margins of the continents. The vegetation cover is scarce here because of scanty rain and scorching heat.
- If you reach the polar region you will find the place extremely cold. The growth of natural vegetation is very limited here. Only mosses, lichens and very small shrubs are found here.
- It grows during the very short summer. This is called Tundra type of vegetation. This vegetation is found in the polar areas of Europe, Asia and North America. The animals have thick fur and thick skin to protect themselves from the cold climatic conditions.
- Seal, walruses, musk-oxen, Arctic owl. Polar bear and snow foxes are some of the animals found here.
- Grasslands are known by different names in different regions.
- Tropical Grasslands : East Africa - Savanna, Brazil - Campos, Venezuela - Llanos.
- Temperate Grasslands : Argentina - Pampas, N. America - Prairie, S. Africa - Veld, Central Asia - Steppe, Australia - Down.
- The Prairies
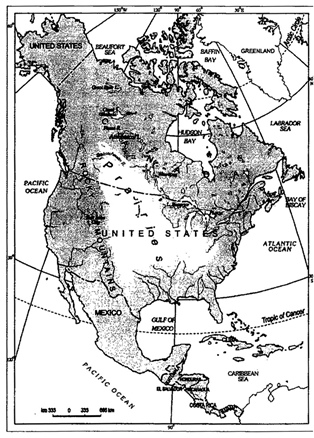
The prairies in North America
- The temperate grasslands of North America are known as the Prairies. It is a region of flat, gently sloping or hilly land. For the most part, prairies are treeless but, near the low lying plains, flanking river valleys, woodlands can be found.
- Tall grass, upto two metres high, dominates, the landscape. It is actually a "sea of grass."
- The prairies are bound by the Rocky Mountains in the West and the Great Lakes in the East. The prairies cover parts of United States of America and parts of Canada.
- In the USA, the area is drained by the tributaries of Mississippi and the Canadian prairies are drained by the tributaries of Saskatchewan Rivers.
- The grasslands of Prairies were the home of native Americans often called "Red Indians".
- They were the actual habitant of the continent. The Prairies were home of other tribes also like the Apache, the Crow, the Cree and the Pawnee.
- Chinook is a hot wind that blows in winter and therefore raises the temperature within a short time. This increase in temperature results in the melting of snow, making pasture land available for grazing of animals.
Climate
- The annual rainfall is moderate and is ideal for the growth of grass. Due to the absence of the north-south barrier, a local wind "Chinook" blows here.
Flora and Fauna
- Prairies are practically tree-less. Where water is available, trees such as willows, alders and poplars grow. Places that receive rainfall of over 50 cm, are suitable for farming as the soil is fertile..
- Though the major crop of this area is maize, other crops including potatoes, soybean, cotton and alfa-alfa is also grown.
- Areas where rainfall is very little or unreliable, grasses are short and sparse. These areas are suitable for cattle rearing. Large cattle farms called ranches are looked after by sturdy men called cowboys.
- Bison or the American buffalo is the most important animal of this region.
- It nearly got extinct due to its indiscriminate hunting and is now a protected species.
- The other animals found in this region are rabbits, coyotes, gophers and Prairie dog.
- Important cities in the American prairies are Chicago, Minneapolis, Indianapolis, Kansas and Denver.
- In the Canadian prairies the important cities are Edmonton, Saskatoon, Calgary and Winnipeg.
The Velds
- The temperate grasslands of South Africa are called the velds.
- Velds are rolling plateaus with varying heights ranging from 600 m to 1,100 m.
- It is bound by'the Drakensburg Mountains on the east.
- To its west lies the Kalahari desert. On the northeastern part, "high velds" are located that attain a height of more than 1,600 m, in some places.
- The Veld name was given by the Dutch settlers before South Africa was colonized by the British.
Climate
- The velds have a mild climate due to the influence of the Indian Ocean. Winters are cold and dry.
- Temperatures vary between 5°C and 10°C and July is the coldest month.
- Summers are short and warm. Johannesburg records about 20°C temperature in the summer.
- The velds receive rainfall mainly in the summer months from November to February.
- This is mainly because of the warm ocean currents that wash the shores of the velds. If the rainfall is scanty in the winter months from June till August, drought may occur.
Flora and Fauna
- The vegetation cover is sparse. Grasses dominate the landscape. Red grass grows in bush velds.
- In the high velds acacia and maroola are seen to be growing. The animals of the velds are primarily lions, leopards, cheetah and kudu.
People
- Velds are known for cattle rearing and mining. The soils are not very fertile in the velds due to the presence of discontinuous grasses exposing barren surface.
- However where the land is fertile crops are grown. The main crops are maize, wheat, barley, oats and potato. Cash crops like tobacco, sugarcane and cotton are also grown.
- Sheep rearing is the most important occupation of the people. Sheep is bred mainly for wool and has given rise to the wool industry in the velds.
- Merino sheep is a popular species and their wool is very warm. Dairy farming is the next important occupation.
- Cattle are reared in the warmer and wetter regions and the dairy products like butter, cheese are produced for both domestic supply and also for export.
- The velds have rich reserve of minerals. Iron and steel industry has developed where coal and iron are present. Gold and diamond mining are major occupations of people of this region.
- Johannesburg is known for being the gold capital of the world. Kimberley is famous for its diamond mines.
Life in the Amazon Basin
- The tropical region lies very close to the equator; between 10°N and 10°S. So, it is referred to as the equatorial region. The river Amazon flows through this region.
- The place where a river flows into another body of water is called the river's mouth.
- Numerous tributaries join the Amazon River to form the Amazon basin. The river basin drains portions of Brazil, parts of Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, Columbia and a small part of Venezuela.
- When Spanish explorers discovered the Amazon river, they were attacked by a group of local tribes wearing headgears and grass skirts. These people reminded them of the fierce tribes of women warriors known in ancient Roman Empire as the Amazons. Hence the name Amazon.
Climate
- The Amazon Basin stretches directly on the equator and is characterized by hot and wet climate throughout the year. Both day and nights are almost equally hot and humid.
- The skin feels sticky. It rains almost everyday, that too without much warning. The day temperatures are high with very high humidity. At night the temperature goes down but the humidity remains high.
Rainforests
- As it rains heavily in this region, thick forests grow. The forests are in fact so thick that the dense "roof created by leaves and branches does not allow the sunlight to reach the ground.
- The ground remains dark and damp. Only shade tolerant vegetation may grow here. Orchids, bromeliads grow as plant parasites.
- The rainforest is rich in fauna. Birds such as toucans, humming birds, bird of paradise with their brilliantly coloured plumage, oversized bills for eating make them different from birds we commonly see in India.
- These birds also make loud sounds in the forests. Animals like monkeys, sloth and ant-eating, tapirs are found here.
- Variousspecies of reptiles and snakes also thrive in these jungles. Crocodiles, snakes, pythons abound. Anaconda and boa constrictor are some of the species.
- Besides, the basin is home to thousands of species of insects. Several species of fishes including the flesheatmg Piranha fish is also found in the river.
- Tins basin is thus extraordinarily rich in the variety of life found there.
The Hot Desert: Sahara
- Desert: It is an-arid region characteriesed by extremely high or low temperatures and has scarce vegetation.
- The Sahara desert covers a large part of North Africa. It is the world's largest desert. It has an area of around 8.54 million sq.km. The Sahara desert touches eleven countries.
- These are Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia and Western Sahara.
- Besides the vast stretches of sands, that Sahara desert is covered with, there are also gravel plains and elevated plateaus with bare rocky surface. These rocky surfaces may be more than 2,500 m high at some places.
- You will be surprised to know that present day Sahara once used to be a lush green plain.
- Cave paintings in Sahara desert show that there used to be rivers with crocodiles. Elephants, lions, giraffes, ostriches, sheep, cattle and goats were common animals,. But the change m climate has changed it to a very hot and dry region.
- Al Azizia in the Sahara desert, south of Tripoli, Libya recorded the highest temperature of \[57.7{{\,}^{o}}C\]in 1992.
Climate
- The climate of the Sahara desert is scorching hot and parch dry. It has a short rainy season. The sky is cloudless and clear.
- Here, the moisture evaporates faster than it accumulates. Days are unbelievably hot.
- The temperatures during the day may soar as high as 50°C, heating up the sand and the bare rocks, which in turn radiates heat making everything around hot. The nights may be freezing cold with temperatures nearing zero degrees.
Flora and Fauna
- Vegetation in the Sahara desert includes cactus, date palms and acacia. In some places there are oasis - green islands with date palms surrounding them.
- Camels, hyenas, jackals, foxes, scorpions, many varieties of snakes and lizards are the prominent animal species living there.
People
- The Sahara desert despite its harsh climate has been inhabited by various groups of people, who pursue different activities. Among them are the Bedouins and Tuaregs.
- These groups are nomadic tribes rearing livestock such as goats, sheep, camels and horses.
- These animals provide them with milk, hides from which they make leather for belts, slippers, water bottles; hair is used for mats, carpets, clothes and blankets. They wear heavy robes as protection against dust storms and hot winds.
- The oasis in the Sahara and the Nile Valley in Egypt supports settled population. Since water is available, the people grow date palms. Crops such as rice, wheat, barley and beans are also grown. Egyptian cotton, famous worldwide is grown in Egypt.
- The discovery of oil - a product in great demand throughout the world, in Algeria, Libya and Egypt is constantly transforming the Sahara desert.
- Other minerals of importance that are found in the area include iron, phosphorus, manganese and uranium.
- The cultural landscape of the Sahara is undergoing change. More and more nomadic herdsmen are taking to city life finding jobs in oil and gas operations.
The Cold Desert: Ladakh
- Ladakh is made up of two words - "La" meaning 'mountain pass' and "Dak" meaning 'country'.
- Ladakh is a cold desert lying in the Great Himalayas, on the eastern side of Jammu and Kashmir. The Karakoram Range in the north and the Zanskar mountains in the south enclose it. Several rivers flow through Ladakh, Indus being the most important among them.
- The rivers form deep valleys and gorges. Several glaciers are found in Ladakh, for example the Gangri glacier.
- Drass, one of the coldest inhabited places on earth is located in Ladakh.
- The altitude in Ladakh varies from about 3000 m in Kargil to more than 8,000 m in the Karakoram. Due to its high altitude, the climate is extremely cold and dry.
- The air at this altitude is so thin that the heat of the sun can be felt intensely. The day temperatures in summer are just above zero degree and the night temperatures well below -30°C.
- It is freezing cold in the winters when the temperatures may remain below -40°C for most of the time.
- As it lies in the rain shadow of the Himalayas, there is little rainfall, as low as 10 cm every year.
- The area experiences freezing winds and burning hot sunlight. You will be surprised to know that if you sit in the sun with your feet in the shade, you may suffer from both) sunstroke and frost bite at the same time.
Flora and Fauna
- Due to high aridity, the vegetation is sparse. There are scanty patches of grasses and shrubs for animals to graze. Groves of willows and poplars are seen in the valleys.
- During the summers, fruit trees such as apples, apricots and walnuts bloom. Several species of birds are sighted in Ladakh. Robins, redstarts, Tibetan snowcock, raven and hoopoe arc common.
- Some of these are migratory birds. The animals of Ladakh are wild goats, wild sheep, yak and special kinds of dogs. The animals are reared to provide for the milk, meat and hides.
- Yak's milk is used to make cheese and butter. The hair of the sheep and goat is used to make woollens.
People
- Do you find any resemblance between the people of Ladakh and the inhabitants of Tibet and Central Asia? The people here are either Muslims or Buddhists.
- In fact several Buddhists monasteries dot the Ladakhi landscape with their traditional 'gompas'. Some famous monasteries are Hemis, Thiksey, Shey and Lamayuru.
- In the summer season the people are busy cultivating barley, potatoes, peas, beans and turnip. The climate in winter months is so harsh that people keep themselves engaged in festivities and ceremonies.
- The women are very hard working. They work not only in the house and fields, but also manage small business and shops.
- Leh, the capital of Ladakh is well connected both by road and air. The National Highway 1A connects Leh to Kashmir Valley through the Zoji la Pass.
- Tourism is a major activity with several tourists streaming in from within India and abroad. Visits to the gompas, treks to see the meadows and glaciers, witnessing ceremonies and festivities are important activities.
Some Important Facts
- Ladakh is also known as Khapa-chan which means snow land.
- The Chiru or the Tibetan antelope is an endangered species. It is hunted for its wool known as shahtoosh, which is light in weight and extremely warm.
- The fines cricket bats arc made from the wood of the willow trees.
- Manali-Leh highway crosses fourpasses, Rohtang la, Baralacha la, Lungalacha la and Tanglang la. The highway opens only between July and September when snow is cleared from the road.
- Tributaries: These are small rivers that join the main river. The main river along with all its tributaries that drain an area forms a river basin or the catchment area. The Amazon Basin is the largest river basin in the world.
- Bromeliads are special plants that store water in their leaves. Animals like frogs use these pockets of water for laying their eggs.
- Terraces are built on steep slopes to create flat surfaces on which crops are grown. The slope is removed so that water does not run off rapidly.
- In the fresh waters of River Ganga and River Brahmaputra, a variety of dolphin locally called Susu (also called blind dolphin) is found.
- The presence of Susu is an indication of the health of the river. The untreated industrial and urban wastes with high amount of chemicals are killing this species.
- The tropical evergreen forest in Brazil is so enormous that it is like the lungs of the earth.
- Anaconda, one of the world's largest snakes is found in the tropical rainforest. It can kill and eat a large animal such as a crocodile.

