Business Modules & Concept in India
Category : UPSC
Business Modules & Concept in India
Introduction
Business is a concept to perform some work is an organized way for profit. It starts with a process of thinking and acting like an entrepreneur and acquiring both the theoretical and practical expertise to setup and run a company. In this chapter, different business anti ties and functioning are discusses.
Business Entities
Sole Proprietorship
Ii is an unincorporated business with one owner who pays personal income tax on profits from the business.
Partnership
A type of business organisation in which two or more individual?s pool money, skills, & other resources, & share profit & loss in accordance with terms of the partnership agreement.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
Ii is a partnership in which some or all partners have limited liabilities.
Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
Ii is an extended family arrangement prevalent throughout the Indian subcontinent consisting of many generations living in the same household, all bound by the common relationship. A HUP is a legal term related to the Hindu Marriage Act. The female members are also given the right of share to the property in HUF.
Cooperative
It is a firm owned, controlled, & operated by a group of users for their own benefit. Each member contributes equity capital & shares in the control of the firm on the basis of one-member, one-vote principle.
Dormant Company
The Companies Act 2013 (section 455) introduces a concept of d dormant company within its ambit. The Dormant Company a company formed & registered under this act for a future project or to hold an asset or intellectual property & has no significant accounting transaction, such a company or an inactive company may make an application to the registrar in such manner as may be prescribed for obtaining the status of a Dormant company.
Family Owned Business
It is a kind of business in which two or more family members are involved & the majority of ownership or control lies within the family.
Private Limited Company
A type of company that offers limited liability, or legal protection for its shareholders but places certain restrictions on its ownership.
Small Company
It is a company that satisfies either of the following conditions:
(i) Paid-up share capital which does not exceed 50 lakh rupees or such higher amount as may be prescribed which shall not be more than 5 crore rupees.
OR
(ii) Turnover of which as per its last profit & loss account does not exceed 2 crore rupees or such higher amount as may be prescribed which shall not be more than 20 crore rupees.
Public Limited Company
A company whose securities are traded on a stock exchange & can be bought & sold by anyone. Its formation, working & its winding up, in fact, all its activities are strictly governed by laws, rules & regulations.
Public Sector Unit (PSU)
The government owned corporations are termed as public sector undertakings (PSUs) in India. In a PSU, majority (51 % or more) of the paid up share capital is held by Central Government or by any state government & partly by one or more state governments.
One Person Company
It is a registered company who has only one shareholder. It is a private company.
Unlimited Company
It is a company in which all members or shareholders have total & joint responsibility to cover all debts & other liabilities the company generates, regardless of how much capital each contributes.
Incorporated Company
A company that has been granted a charter legally recognizing it as a separate entity having its own privileges, rights, & liabilities distinct from other business & persons.
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The framework of rules & practices by which a Board of Directors ensures accountability, fairness, & transparency in a company?s relationship with its all stakeholders (financiers, customers, management, employees, government, & the community).
The corporate governance framework consists of:
1. explicit & implicit contracts between the company & the stakeholders for distribution of responsibilities, rights & rewards.
2. procedures for reconciling the sometimes conflicting interests of stakeholders in accordance with their duties, privileges & roles.
3. procedures for proper supervision, control & information- flows to serve as a system of checks & balances.
COMPANIES ACT AMENDMENT BILL 2016
The Companies Act (Amendment) Bill 2016 seeks to amend the Companies Act 2013 which regulates the incorporation, regulation and winding up of companies. The Bill in the wake of facilitating ease of doing business aims to bring some radical changes in the previous Act. In March 2016, the Bill was introduced in Lok Sabha. This Bill is mainly based on the recommendations of the companies Law Committee. The Bill was then referred to the standing Committee on finance for examination.
Brief description of the key changes proposed is 2016 Bill compared with provisions of the 2013 Act:
|
Key Features |
Companies Act, 2013 |
Companies (Amendment) Bill, 2016 |
|
Private Placement |
Separate offer letter to be given to private individuals. A record of such offers must be filed with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) in 30 days. |
Removes the requirement of issuing a separate offer letter, and recording such offers with the ROC. |
|
Forward dealing & Insider trading |
Prohibits forward dealing in securities by the Director or Key managerial personnel. Prohibits insides trading by all persons in a company. |
Removes the provisions related to prohibition of forward dealing and insider trading. |
|
Memorandum of a Company |
Requires to state the objects for which the company is being incorporated, and other related matters. |
Memorandum may contain general objects which state that the company may engage in any lawful activities or businesses. . |
|
Managerial remuneration |
Approval of the Central Government and shareholders must be obtained for payment of managerial remuneration if exceeds prescribed limits. |
Omits the requirement of obtaining approval from the Central Government. |
|
Cap on investments |
Investments in a company cannot be made through more than two layers of investment companies. |
Removes the restrictions on number of layers of investment companies. |
|
Subsidiary company and Associate Company |
Subsidiary Company is one in which a parent company holds more than 50% of its 'Shares?. Associate Company is one where another company holds at lest 20% of its 'Shares?. (Includes equity & Preferential shareholders). |
Replaces the term 'shares' with voting power. Preferential shareholders, who do not have voting power are excluded. |
|
Ratification of Auditors |
Appointment or continuance of auditor of a company should be ratified annually by the members of the company. |
Omit this requirement |
|
Loans to Directors |
A company is not allowed to advance any loan to its Directors or to any person in whom the director is interested. |
Allows company to advance a loan in relation to any person a Director is interested in if the company passes a special resolution. |
|
Register as a Private Company |
Any company formed, consisting of seven or more members, may at any time register under this Act as an unlimited company, or as a company limited by shares, or as a company limited by guarantee. |
For the words 'seven or more members', the words 'two or more member' shall be substituted. A company with less than seven members shall register as a private company. |
PENSION SYSTEM
Pension Plans provide financial security & stability during old age when people don't have a regular source of income.
To provide social security to more citizens the Government of India has started the National Pension System. Government of India established Pension Fund Regulatory & Development Authority (PFRDA) on 10th October 2013 to develop & regulate pension sector in the country. The National Pension System (NPS) was launched in 1st January, 2004 with the objective of providing retirement income to all the citizens. With effect from 1st May 2009, NPS has been provided for all citizens of the country including the unorganised sector workers on voluntary basis. Additionally, Central Government launched a co-contributory pension scheme, 'Swavalamban Scheme' in the Union Budget of 2010-11, under which the Government will contribute a sum of Rs.1,000 to each eligible NPS subscriber who contributes a minimum of Rs.1,000 & maximum Rs.12,000 per annum.
The NPS is structured in 2 tiers. A Tier-1 account is a basic retirement pension account available to all citizens from 1 May 2009. It does not permit withdrawal of funds before retirement. A Tier-2 account is a prospective payment system account that permits some withdrawal of pension prior to retirement under exceptional circumstances, usually related to the provision of health care.
MINISTRY OF CORPORATE AFFAIRS
MCA regulates corporate affairs in India through the
Companies ACT, 1956. 2013 and other allied Acts, Bills and Rules. MCA also protects investors and offers many important services to stakeholders.
The Ministry is also responsible for administering the Competition Act, 2002 to prevent practices having adverse effect on competition, to promote and sustain competition in markets, to protect the interests of consumers through the commission set up under the Act.
Besides, it exercises supervision over the three professional bodies, namely, Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) which are constituted under three separate Acts of the Parliament for proper and orderly growth of the professions concerned
Registrar of Companies
Registrars of Companies (ROC) appointed under Section 609 of the Companies Act covering the variuous States and Union Territories are vested with the primary duty of registering companies and LLPs floated in the respective states and the Union Territories and ensuring that such companies and LLPs comply with statutory requirements under the Act. These offices function as registry of records relating to the companies registered with them, which are available for inspection by members of public on payment of the prescribed fee. The Central Government exercises administrative control over these offices through the respective Regional Directors.
Income Tax Department
The Income Tax Department, also referred to as IT Department, is a government agency in charge of monitoring the income tax collection by the
Government of India. It functions under the Department of Revenue of the Ministry of Finance. It is responsible for administering following direct taxation acts passed by Parliament of India.
· Income Tax Act
· Wealth Tax Act
· Gift Tax Act
· Expenditure Tax Act
· Interest Tax Act
· Various Finance Acts [Passed Every Year in Budget Session)
The IT Department is also responsible for enforcing the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements and deals with various aspects of international taxation such as Transfer Pricing.
BALANCE SHEET
A financial statement that summarizes a company's assets, liabilities and shareholders' equity at a specific point in time.
These three balance sheet segments give investors an idea as to what the company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by shareholders.
The balance sheet adheres to the following formula:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity

SOURCES OF FUNDS
Debt
A duty or obligation to pay money delivery goods or render service under an express or implied agreement'
Debentures
It is a medium- to long-term debt instrument used by large companies to borrow money, at a fixed rate of interest.
Shareholder's Equity
It represents the amount by which a company is financed through common and preferred shares.
Seed Funding
It is a type of securities contribution in which an investor invests capital in exchange for an equity stake in the company.
This sort of funding is done in the initial stages of a business.
Venture Funding
It is the capital invested, or available for investment, in an enterprise that offers the probability of profit along with the possibility of loss.
This sort of funding is done, generally, after a company has a proof of concept and has crossed early stages of business.
IPO
Initial public offering or IPO is the first sale of a company?s shares to the public, leading to a stock market listing. A lot of venture funds adopts this route to exit a company in which they have invested.
Shares
A unit of ownership that represents an equal proportion of a company's capital. It entitles its holder (the shareholder) to a nequal claim on the company's profits & an equal obligation for the company's debts & losses.
There are 2 major types of shares-
· Ordinary shares: Entitles the shareholder to share in the earnings of the company & to vote at the company?s annual general meetings & other official meetings.
· Preference shares: Entitles the shareholder to a fixed periodic income but generally do not give him/her voting rights.
Loans: A loan is a debt provided by an entity (organisation of individual) to another entity at an interest rate.
Performance of a company
Debt/Equity Ratio
It is a debt ratio used to calculate company's financial leverage.
It is calculated by dividing a company's total liabilities by its stockholder's equity. It shows how much debt a corporations using to fund its assets relative to the amount of value represented in shareholder's equity.
P/E Ratio
The price-to earnings ratio is an equity valuation multiple. It is defined as market price per share divided by annual earnings per share, (EPS = total income of company divided by number of shares issued)
Turnover Ratio
The turnover ratio measures how well a company is utilizing its capital to support a given Level of Sales. A high turnover ratio indicates that management is being extremely efficient is using a firm's short term assets & liabilities to support sales.
Conversely, a low ratio indicates that a business is investing in too many accounts receivable & inventory assets to support its sales, which could eventually lead to an excessive amount of bad debts & obsolete inventory.
Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs); sometimes also small and medium enterprises) or small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are businesses whose personnel numbers fall below certain limits. Indian Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) sector has emerged as a highly vibrant and dynamic sector of the Indian economy over the last five decades. SMEs not only play crucial role in providing large employment opportunities at comparatively lower capital cost than large industries but also help in industrialization of rural areas.
SMEs are complementary to large industries as ancillary units and this sector contributes enormously to the socio-economic development of the country. The sector consisting of 36 million units, as of today, provides employment to over 80 million persons. The Sector through more than 6,000 products contributes about 8% to GDP besides 45% to the total manufacturing output and 40% to the exports from the country. The SME sector has the potential to spread industrial growth across the country and can be a major partner in the process of inclusive growth. SMEs also play a significant role in Nation development through high contribution to Domestic Production, Significant Export Earning, Low Investment Requirements, Operational Flexibility, Location Wise Mobility, Low Intensive Imports, Capacities to Develop Appropriate Indigenous Technology, Import Substitution, Contribution towards Defence Production, Technology ? Oriented Industries, Competitiveness in Domestic and Export Markets thereby generating new entrepreneurs by providing knowledge and training.
E-Commerce in India
E-commerce or electronic commerce deals with the buying & selling of goods & services, or the transmitting of funds or data, over an electronic platform, mainly the internet. These business transactions are categorised into-
· Business to Business (B2B)
· Business to Consumers (B2C)
· Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
· Consumer to Business(C2B) Business to Business to Consumer
E-commerce processes are conducted using applications, such as Email, fax, online catalogues & shopping carts, electronic data interchange, file transfer protocol & web services & e-newsletters to subscribers. E-Travel is the most popular form of E-commerce, followed by e-Tail which essentially means selling of retail goods on the internet conducted by the B2C category.
Mobile Commerce (M - Commerce)
M-Commerce is the buying & selling of goods & services through wireless handheld services such as cellular telephone & personal digital assistants. The phrase mobile commerce was originally coined in 1997 by Kevin Duffey at the launch of the Global Mobile Commerce Forum. Mobile Commerce transaction continues to grow, & the term includes online banking, bill payment & so on.
MNC
A corporation that has its facilities and other assets in at least one country other than its home country. Such companies have offices and/or factories in different countries and usually have a centralized head office where they co-ordinate global management. It can also be referred as an international corporation, a 'transnational corporation', or a stateless corporation.
NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an organization that is neither a part of a government nor a conventional for-profit business.
The term 'non-governmental organization' was first coined in 1945, when the United Nations (UN) was created. The UN, itself an inter-governmental organization, made it possible for certain approved specialized international non-state agencies, i.e. non-governmental organizations to be awarded observer status at its assemblies and some of its meetings. Later the term became used more widely. Today, according to the UN, any kind of private organization that is independent from government control can be termed an 'NGO', provided it is not-for-profit, Non-prevention, and not simply an opposition political party.
Examples include improving the state of the natural environment, encouraging the observance of human rights, improving the welfare of the disadvantaged, or representing a corporate agenda.
However, there are a huge number of such organizations and their goals cover a broad range of political and philosophical positions. This can also easily be applied to private schools and athletic organizations.
FICCI (Federation of Indian Chamber of
Commerce & Industry)
Established in 1927, FICCI is the largest and oldest apex business organisation in India. A non-government, not-for-profit organisation, FICCI is the voice of India's business and industry. From influencing policy to encouraging debate, engaging with policy makers and civil society, FICCI articulates the views and concerns of industry.
Agmark
It is a certification mark employed on agricultural products in India, assuring that they confirm to a set of standards approved by the Directorate of Marketing & Inspection, an agency of the Government of India.
ISI Mark
ISI (Indian Standards Institute) mark is a certification mark for industrial products in India. The mark certifies that a product confirms to the Indian Standard, mentioned as IS: xxxx on top of the mark, developed by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). The ISI mark is mandatory for certifying products to be sold in India, like many of the electrical appliances, kitchen appliances, other products like LPG valves, LPG cylinders, automotive tyres, etc.
Important Business Terms
|
Term |
Meaning |
|
Ahead of the Curve |
To be more advanced than the competition |
|
Backroom Deal |
An agreement or decision that is made without the public knowing about it. |
|
Go broke |
To go bankrupt or to lose all the money a person or business had. |
|
In the black |
If a company is ?in the black?, it means that they are making a profit |
|
In the red |
If a company is ?in the red? it means that they are not profitable & are operating at a loss. |
|
Lose - Lose situation |
When someone has to choose between various options & all the options are bad.
|
|
Pink Slip |
If someone gets the ?pink slip?, it means they have fired. |
|
Snail Mail |
Letter or messages that are not sent by email, but by regular post. |
|
Blue Collar Worker |
Someone who works with his/her hands (manufacturing construction, maintenance, etc.) |
|
White Collar Worker |
Someone who works in an office (customer service, management, sales, etc.) J |
|
Win - Win situation |
A situation where everyone involved gains something. |
|
Corner a market |
To dominate a particular market. |
|
Downsizing |
A planned reduction in the number of employees needed in a firm in order to reduce costs & make the business more efficient. |
|
Venture Capital |
Money that is invested in new or emerging companies that are perceived as having great profit potential. |
|
Opportunity Cost |
Cost in terms of foregone alternatives. |
|
Logistics |
Process of strategically managing the efficient flow & storage of raw materials, in-process inventory, & finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. |
|
Equity |
Difference between market value of a property & claims held against it. |
|
Merger |
Combination of two or more companies into a single firm. |
|
Acquisition |
Taking over the control of one company by another. |
|
Hedging |
A Risk management strategy used in limiting or offsetting probability of loss from fluctuations in the prices of commodities, currencies, or securities. |
|
Intellectual Property |
Knowledge creative ideas or expressions of human mind that have commercial value & are protectable under copyright, patent, service mark, trademark, or trade secret laws from imitation infringement, & dilution. |
|
Swap |
Exchange of one type of asset, cash flow, investment, liability, or payment for another. |
|
Bankrupt |
When individual/company cannot pay their debts & are not able to reach an agreement with their creditors. |
|
Liquidity |
How quickly assets can be converted into cash. |
Business CONCEPTS
Agent
A business entity that negotiates, purchases, and/or sells, but does not take title to the goods.
Doing Business as (DBA)
DBA stands for 'Doing Business As.' which is a company name, also commonly called a 'Fictitious business name.' When a sole proprietor operates a company using any name except his or her own given name, then the DBA or fictitious business name registration establishes the legal ownership to satisfy banks, local authorities, and customers.
Ideas vs. Opportunities
Ideas are the basis of potential business opportunities. Good ideas do not necessarily represent good opportunities.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
A corporation?s initial efforts of raising capital through the sale of securities on the public stock market.
Inventory Goods in stock, either finished goods or materials to be used to manufacture goods.
Outsourcing
Purchasing an item or a service from an outside vendor to replace performance of the task with an organization?s internal operations.
SWOT Analysis
A formal framework of identifying and framing organizational growth opportunities. SWOT is an acronym for an organization?s internal Strengths and Weaknesses and external Opportunities and Threats.
CRM
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. At its simplest, a CRM system allows businesses to manage business relationships and the data and information associated with them.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
It is the oversight of materials, information, and finances as they move in a process from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer. Supply chain management involves coordinating and integrating these flows both within and among companies.
Memorandum of Association (MoA)
MoA is a legal document prepared in the formation & registration process of a limited liability company to define its relationship with shareholders.
Articles of Association
It is a document of a company which defines the responsibilities of die directors, the kind of business to be undertaken, & the means by which the shareholders exert control over me board of directors.
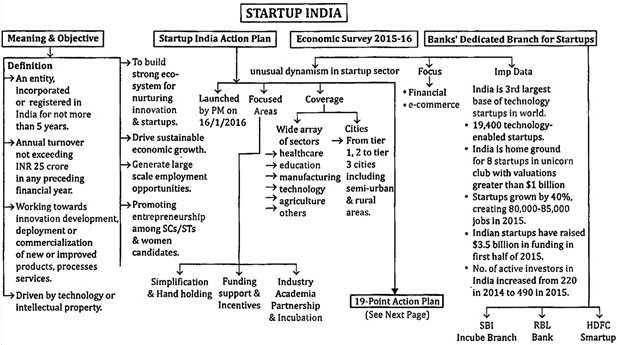
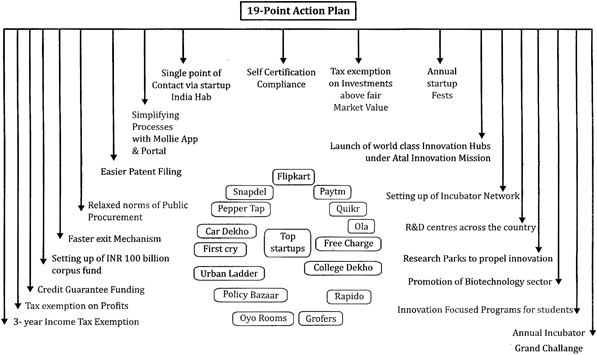
Start-ups
A start-up company is an entrepreneurial venture or a new business in the form of a company, a partnership or temporary organization designed to search for a repeatable and scalable business model. These companies, generally newly created, are innovative in a process of development, validation and research for target markets.
Boot Strap
A situation in which an entrepreneur starts a company with little capital. An individual is said to be boot strapping when he or she attempts to lay foundation and build a company from personal finances or from the operating revenues of the new company.
Employees' State Insurance (ESI)
ESI is a self-financing social security & health insurance scheme for Indian workers. The ESI is managed by the ESI Corporation (ESIC) according to rules and regulations stipulated there in the ESI Act 1948, which oversees the provision of medical and cash benefits to the employees and their family through its large network of branch offices, dispensaries and hospitals throughout India.
Provident Fund (PF)'
It is a fund which is composed of contributions & made by the employee during the time he/she worked along with an equal contribution by his employer. Its purpose is to help employees save a fraction of their salary every month, to be used in an event that the employee is temporarily or no longer fit to work or at retirement.
TDS
Tax deducted at source (TDS), as the very name implies aims at collection of revenue at me very source of income. It is essentially an indirect method of collecting tax which combines the concepts of "pay as you earn" and "collect as it is being earned." Its significance to the government lies in the fact that it prepones me collection of tax, ensures a regular source of revenue, provides for a greater reach and wider base for tax. At the same time, to the tax payer, it distributes the incidence of tax and provides for a simple and convenient mode of payment.
Lease
A legal document outlining the terms under which one party agrees to rent property from another party. A lease guarantees the lessee (the renter) use of an asset and guarantees the lessor (the property owner) regular payments from the lessee for a specified number of months or years. Both the lessee and the lessor must uphold the terms of the contract for the lease to remain valid.
Financial Leasing
As one of the most popular financing tools in modern business world, Financial Leasing Services uses finance leases to leverage assets. A Finance Lease (or Capital Lease) is a lease that is primarily a method of raising finance to pay for assets, rather than a genuine rental.
It is a commercial arrangement where:
· the lessee (customer or borrower) will select an asset (equipment, vehicle, software);
· the lessor (finance company) will purchase that asset;
· the lessee will have use of that asset during the lease;
· the lessees will pay a series of rental or installments for the use of that asset;
· the lessor will recover a large part or all of the cost of the asset plus earn interest from the rentals paid by the lessee;
· the lessee has the option to acquire ownership of the asset (e.g. paying the last rental, or bargain option purchase price).
The finance company is the legal owner of the asset during duration of the lease.
E-FILING
Electronic tax filing, or e-filing, is a system for submitting tax documents to a revenue service electronically, often without the need to submit any paper documents. E-filing has manifold benefits; the taxpayer can file a tax return from the comfort of home, at any convenient time, once the tax agency begins accepting returns. E-filing saves the tax agency time and money, because the tax data is transmitted directly into its computers, significantly reducing the possibility of keying and input errors.
Corporate Tax
Corporate taxes are taxes against profits earned by businesses during a given taxable period. Corporation tax is a tax imposed on the net income of the company. The present corporate tax is 30% on the Net Income of the company.
It was announced in Union Budget 2015 that corporate tax rate will be gradually reduced from 30% to 25% over the period of 4 years, starting in April 2016. 2% surcharge was introduced on earnings above 10 crores.
Surcharge is applied in the following cases:
· If the company has a total income less than Rs.1 crore, then it does not have to pay any income tax.
· If me net income of the company for that year is in the range of Rs.10 crore then 5% surcharge is applied on its net income.
· If the net income of the company for that year exceeds Rs.10 crore then 10% surcharge is applied on its net income education cess
Profitability of Company
Profitability is the ability of a business to earn a profit. A profit is what is left of the revenue a business generates after it pays all expenses directly related to the generation of the revenue, such as producing a product, and other expenses related to the conduct of the business activities.
Dividend a share of the after-tax profit of a company, distributed to its shareholders according to the number and class of shares held by them.
Start-ups and other high-growth companies such as those in the technology or biotechnology sectors rarely offer dividends because all of their profits are reinvested to help sustain higher-than-average growth and expansion. Larger, established companies tend to issue regular dividends as they seek to maximize shareholder wealth in ways aside from supernormal growth.
Issued Capital
The share capital that has been issued to the shareholders. This is part of a company's authorised capital.
Paid up Capital
The amount of a company's capital that has been funded by shareholders. Paid-up capital can be less than a company's total capital because a company may not issue all of the shares that it has been authorized to sell. Paid-up capital can also reflect how a company depends on equity financing.
|
MAJOR ACQUISITIONS IN 2016 |
||
|
Company |
Company that is Acquired |
|
|
1. |
Mindtree |
Magnet 360. |
|
2. |
Tech Mahindra Ltd. |
BIO Agency Ltd. |
|
3. |
Dabur |
Discaria. |
|
4. |
Myntra |
Jabong |
|
5. |
Quikr |
Common Floor. |
|
6. |
Titan Industries |
Carat Lane. |
|
7. |
Yatra |
Mgaadi. |
|
8. |
Road Runnr |
Tiny Qwl |
|
9. |
Shop clues |
Momoe. |
|
10. |
Russia's Rosneft Oil Company |
India's Essar Oil |
|
11. |
Sony Pictures Networks |
Sports Channels of Zee Entertainment. |
|
12. |
IDFC Bank |
Grama Vidiyal Micro Finance Ltd. |
|
13. |
|
Moodstocks. |
|
14. |
Aditya Biria Fashion and Retail |
Forever 21. |
|
15. |
Future Group |
Fab Furnish. |
|
16. |
Flipkart |
Phone Pe International Pvt. Ltd. |
|
17. |
Bharti Airtel Ltd. |
Videocon Telecommunication Ltd?s Spectrum. |
|
Reliance Communications and Marxis Communications Berhad, promoters of Aircel, merged their wireless businesses to form the 4th largest telecom operator in the country. |
||
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
