Reproduction
Category : UPSC
REPRODUCTION
REPRODUCTION
Reproduction is the process by which all living organism give rise to new organisms similar to themselves. It is essential for the survival of the species since all the living beings have a similar life span. Organism reproduces by two modes asexual and sexual reproduction.
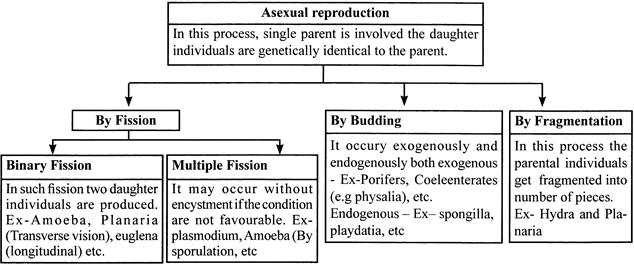
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent because the offspring are all clones. The main process of asexual reproduction is mitosis. This type of reproduction is common among same single cell organisms for example, amoeba, etc. Many plants also reproduce asexually.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a biological process that creates a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms in a process that starts with meiosis, a specialized type of cell division.
Difference between asexual and sexual reproduction
|
|
Asexual reproduction |
Sexual reproduction |
|
1. |
It occurs only in invertebrates and lower chordates. |
It occurs almost in all types of animals. |
|
2. |
It is always uniparental. |
It is usually biparental. |
|
3. |
Gametes are not formed. |
Two types of gametes are formed. |
|
4. |
It involves only mitosis. |
It involves both meiosis and mitosis. |
|
5 |
Daughter organisms are genetically identical to the parent. |
Daughter organisms genetically differ from their parents. |
|
6. |
Since there is no variation, so it does not contribute to evolution of the species. |
Because of variations, it contributes to the evolution of species. |
|
7. |
Occurs by fission, budding or fragmentation. |
Occurs by the formation of haploid gametes which fuse to form a diploid zygote. |
|
8. |
It is a quick method of multiplication. |
It is a slower method of multiplication. |
REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
In plants, asexual reproduction is of 3 types - agamospermy, spore formation and vegetative reproduction.
Vegetative Propagation
Vegetative propagation or vegetative reproduction is the process of multiplication in which a portion of fragment of the plant body functions as propagules and develop into a new individual.
Artificial Vegetative Propagation
grapes guava, apple and pear.
Underground stem
Creeper stem
Leaves - ex- Bryophyllum, Begonia, streptocarpus, saint paulia
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANT
Sexual reproduction is the process of development of new organisms through the formation and fusion of gametes. In flowering plants, stamens are male reproductive organs while carpels are female reproductive organs. Sexual reproduction can be summarised as:
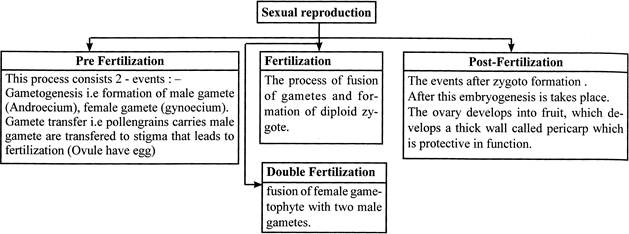
Male Reproduction Unit
It includes
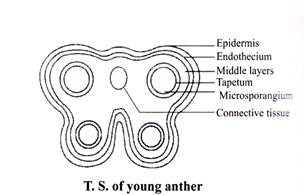
Female Reproduction Unit
It includes
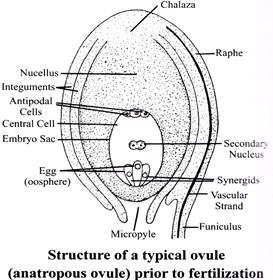
Sexual Reproduction Cycle
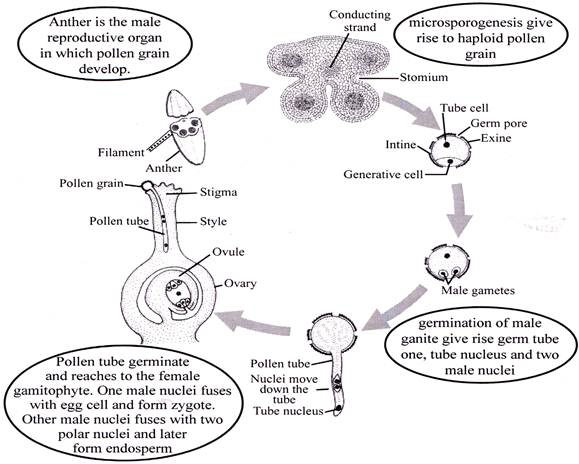
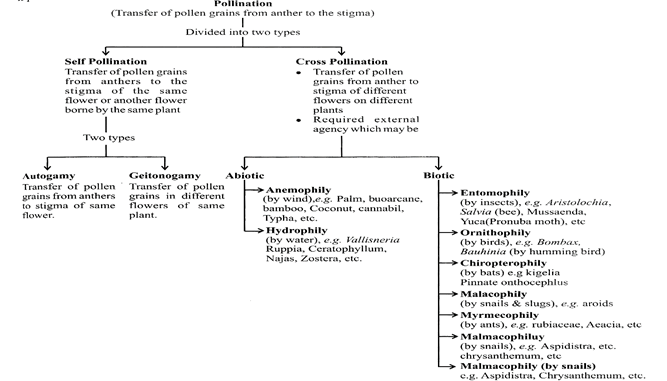
POLLINATION
The process of transfer of pollen grains form an anther to the stigma of the some flower or different flower is called pollination.
Post Fertilization Events
It involves development of endosperm, embryo, ovules and seeds
Endosperm - Endosperm is the nutritive tissue which provides nourishment to the embryo in seed plant. It also protects the embryo from mechanical injury. It may be completely consumed by developing embryo before it matures (e.g. beans and peas) or it may persist in the mature seed and used up during seed germination, e.g., coconut.
Embryo - The process of development of mature embryo from zygote or oospore is called embryogeny. Zygote starts dividing to produce embryo, together with the development of endosperm.
Seed - Seed is a fertilized ovule. It is the final product of Fertilization in angiosperm and acts as a main propagative unit in plants. Ovules mature into seed and simultaneously ovary develops into a fruit.
|
(i) Ovary wall |
Fruit wall |
|
(ii) Ovary |
Fruit |
|
(iii) Integuments |
Seed coats |
|
(iv) Outer |
Testa |
|
(v) Inner |
Tegmen |
|
(vi) Ovule |
Seed |
Handy Facts
Handy Facts
FRUIT
Some common fruits with their edible part.
Fruits can also be classified on the macro level:
REPRODUCTION IN ANIMALS
Cloning
It is the process used to create an exact copy of a cell tissue or a complete organism. It was performed by lan Wilmut and his colleagues at Roslin institute edinburg, Scotland. They cloned sheep named “Dolly”, she was born on 5th July 1996 and was the 1st mammal cloned from adult somatic cell. She died on 14th feb. 2003 due to lung disease.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Reproduction in Human
In human beings reproduction is much the same as for mammals specialized reproductive organs are located in their lower abdomen.
Puberty is the name for the time when your body beings to develop and change as your move them kid to adult. Usually, puberty starts between ages 8 and 13 in girls and ages 9 and 15 boys.
Male Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System
REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
Table: Method of Birth control
|
S. No. |
Method |
Action |
|
1. |
Withdrawal |
Penis is withdrawn before ejaculation. |
|
2. |
Tubectomy / Tubal ligation |
Woman's fallopian tubes are cut and tied, permanently blocking sperm release. |
|
3. |
Lactational amenorrhea |
As long as mother breast feeds the cild, chances of conception is nil |
|
4. |
Vasectomy |
Man?s vasa deferentia are cut and tied permanently blocking sperm passage. |
|
5 |
Tubectomy |
a small part of the fallopian tube is removed or tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through vagina. |
|
6. |
Intrauterine device (IUD) non-medicated IUDs (e.g., Lippes loop), copper releasing lUDs (CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375) and the hormone releasing lUDs (Progestasert, LNG-20). |
Small plastic or metal device placed in the uterus to -^-prevent implantation. Some contain copper, other release hormones. |
|
7 |
Oral contraceptive e.g. - saheli. MalaD. etc. |
Synthetic estrogens and progesterones prevent normal menstrural cycle; primarily prevent ovulation. |
|
8. |
Male condom |
Thin rubber sheath on erect penis collects ejaculated semen. |
|
9. |
Female condom |
Plastic pouch inserted into vagina catches semen. |
|
10. |
Diaphargm |
Soft rubber cup covers entrance to uterus, prevents sperm from reaching egg and holds spermicide. |
|
11. |
Cervical cap |
Miniature diaphragm covers cervix closely, prevents sperm from reaching egg and holds spermicide. |
·
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
Table: Some STDs and their pathogens
|
Disease |
Pathogen |
|
|
Bacterial |
||
|
1. |
Syphilis |
Treponema pallidum |
|
7 |
Gonorrhoea |
Neisseria gonormoeae |
|
3. |
Chancroid |
Haemophilus ducreyi |
|
4. |
Vaginitis |
Gardnerella vaginalis |
|
5. |
Chlamydiasis |
Chlamydia trachomatis |
|
Viral |
||
|
6. |
Herpes genitalis |
HSV-2 (DNA) virus |
|
7. |
Condyloma acuminatum |
Papova (DNA) virus |
|
8. |
Molluscum contagiosum |
Pox (DNA) virus |
|
Protozoan |
||
|
9. |
Trichomoniasis |
Trichomonas Vaginalis |
INFERTILITY
The main Art-Techniques i.e. (Assisted reproductive technology)
The main ART-techniques includes:
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
Zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICST).
Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT).
Surrogacy or surrogate motherhood.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
