Diversity in Living Organisms
Category : UPSC
Diversity in Living Organisms
Differentiation in Plants
(i) Thallophyta
- Plants that do not have well differentiated body design fall in this group.
- The plants in this group are commonly called algae. These plants are predominantly aquatic.
E.g.: Spirogyra, cladophora and chara.
(ii) Bryophyte
- These are called the amphibians of the plant kingdom. There is no specialized tissue for the conduction of water and other substances from one past of the plant body to another.
E.g.: moss (fumaria) and marchantia
(iii) Pteridopheysta
- In this group plant body is differentiated into roots, stem and leaves and has specialized tissue for the conduction of water and other substances from one plant of the plant body to another.
E.g- marsilea, ferns, and horse tails.
(iv) Gymnosperms
- The plant of this group bear naked seeds and one usually perennial and evergreen and woody.
E.g.: pines such as deodar.
(v) Angiosperms
- The seeds develop inside an organ which is modified to become a fruit. These are also called flowering plants.
- Plant embryos in seeds have structures called cotyledons. Cotyledons are called seed leaves because in many instances they emerge and become green the seed germinates.
- The angiosperms are divided into two groups on the basis of the number of cotyledons present in the seed.
- Plants with seeds having a single cotyledon are called monocotyledons or monocots. Eg- paphiopedilum.
- Plants with seeds having two cotyledons are called dicots. Eg- ipomoce.
Differentiation of Animals
(i) Porifera
These are non-mobile animals attached to some solid support. There are holes or pores all over the body. These lead to a canal system that helps in circulating water throughout the body to bring in food and They are commonly called sponges mainly found in marine habitats.
(ii) Coelenterate
- These are animals living in water. The body is made up of two layers of cells. One makes up cells on the outside of the body and the other makes the inner living of the body.
- Some of these species live in colonies while others have a solitary life e.g. span (Hydra) jellyfish are common example.
(iii) Platyhelminthes
- There are three layers of cells from which different tissues can be made. This allow outside and inside body linings as well as some organs to be made.
- Thus there is some degree of tissues formation.
- They are either free living or parasitic. e.g. Planarians, liver flukes.
(iv) Nematode
- These are very familiar as parasitic worms causing diseases such as the worms causing elephantiasis (filarial worms) or the worms in the intestine (round or pin worms)
(v) Annelida
- They have true body cavity. This allows true organs to be packaged in the body structure. There is thus an extensive organ different ion. This differentiation occurs in a segmentation fashion with the segment lined up one after the other from head to tail. Eg- Earthworms, leeches.
(vi) Arthropods
- There is an open circulatory system and so the blood does not flow in well-defined blood vessels. They have joint legs.
Eg- prawns, butterflies, houseflies, spiders, scorpions and crabs.
(vii) Mollusca
- They have an open circulatory system and kidney like organs for excretion. There is a little segmentation. There is a foot that is used for moving around.
Eg-snails, and mussels, octopus.
(viii) Echinodermata
- There are spiny skinned organisms. These are exclusively free living marine animals. They have peculiar water driven tube system that they use for moving around. They have hard calcium carbonate structure that they use as skeleton.
Eg- starfish, sea cucumber.
(ix) Protochordats
Eg- balanoglossus, hard mania and amphioxus.
(x) Vertebrata
- These animals have a true vertebral column & internal skeleton. These are grouped into five classes.
Pisces
- These are fish. They are cold blooded and their hearts have only two chambers unlike the four that human have.
- Some with skeletons made entirely of cartilage, such as shark.
- Some with skeleton made of both bones and cartilages such as tuna or rohu.
(xi) Amphibian
- They have mucus glands in the skin and a three chambered heart. Respiration is through either gills or lungs.
Eg- frogs, toads, and salamanders.
(xii) Reptilian
- These animals are cold blooded have scales and breathe through lungs. While most of them have a three chamber heart while crocodile have four heart chambers.
Eg- snakes, turtles, lizards and crocodiles.
(xiii) Aves
- These are warm blooded animals and have a four chambered heart. They Say eggs. They breathe through lungs. All birds fall in this category.
(xiv) Mammalia
- They are warm blooded animals with four chambered hearts.
- They have mammary glands for the production of milk to nourish their young. They produce live young ones.
- However a few of them like platypus and the echidna lay eggs.
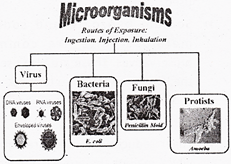
Micro Organisms: Friend and Foe
Facts from NCERT
Micro organisms are classified into four major groups. These groups are bacteria, fungi, protozoa and algae.
- Viruses : They reproduce only inside the cells of the host organisms which may be bacterium, plants or animal.
- Common cold, influenza and most coughs are caused by viruses.
- Serious diseases like polio and chicken pox are also caused by viruses.
- Micro organisms may be single celled like bacteria. Some algae and protozoa. Multicellular such as algae and fungi.
- Micro organisms like amoeba can live alone, while fungi and bacteria may live in colonies.
Friendly Micro Organisms
- Making of curd and breed:-milk is turned into curd by bacteria. The bacterium lacto bacillus promotes the formation of curd.
- Yeast reproduces rapidly and produces during respiration. Bubbles of the gas fill the dough and inert-volume; this is the basis of the use of yeast in the booking industry for making breads, pastries and cakes.
- Yeast is used for commercial production of alcohol and wine. For this purpose yeast is grown as natural sugars present in grains like barley, wheat, rice, crushed fruit juice etc.
- This process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is known as fermentation Lewis Pasteur discovered fermentation.
Medicinal Use of Micro Organisms
- The medicine which kills or stops the growth of diseases causing microorganism is called antibiotics.
- Streptomycin, tetracycline and erythromycin are some of the commonly known antibiotics- Which are made from fungi and bacteria.
- Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin.
- Antibiotics are not effective against cold and flu as these are caused by virus.
Vaccine
- When a disease carrying microbe enters our body, the body produces antibodies to fight the invader.
- The antibodies remain in the body and we are protected from the disease causing microbes. This is how a vaccine work.
- Several diseases including cholera, TB, small pox and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination.
- Edward Jenner discovered the vaccine for small pox.
Increasing Soil Fertility
- Some bacteria and blue green algae are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich the soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility.
- These microbes are commonly called biological nitrogen fixer.
Harmful Microorganisms
- Microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through air water, food, or physical contact are called communicable diseases, i.e. cholera, common cold, chicken pox and TB.
- There are some insects and animals which act as carrier of disease causing microbes like house fly. Another is female anopheles mosquito which carries the parasite of malaria.
- Female aides mosquito acts as carrier of dengu virus.
- Robert Koch discovered the bacteria (bacillus anthraces) which causes anthrax disease.
- It is a dangerous human & cattle disease.
Common Methods of Preserving Food in our Homes
- Chemical method: salt and edible oils are the common chemical generally used.
- Sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are common preservatives. These are also used in the James and squashes to check their spoilage.
Preservation by sugar:
- Sugar reduces the moisture context which inhibits the growth of bacteria which spoil food.
- Use of oil and vinegar prevents spoilage of pickles become bacteria cannot live in such an environment.
- Pasteurized milk : the milk is heated to about for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored.
- This process was discovered by lowise Pasteur. It is called pasteurization.
Some Common Plant Disease Caused by Microorganisms
|
Plant disease
|
Microorganism
|
Mode of transmission
|
|
Citrus canker
|
Bacteria
|
Air
|
|
Rust of wheat
|
Fungi
|
Air, seeds
|
|
Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi
|
Virus
|
insect
|
Facts from Human Machine
- Camels have long legs which help to keep their bodies away from the heat of the Sand. They excrete small amount of urine, their dung is dry and they do not sweat. Since Camels lose very little water from their bodies, they can live for many days without water.
- Fish have slippery scales on their bodies. These scales protect the fish and also help in easy movements through water. The presence of specific features of certain habits, which enable a plant or an animal to live in its Surroundings, is called adaptation.
- There are some sea animals like squids and octopus, which do not have this streamlined shape. These animals have gills to help them use oxygen dissolved in water.
- There are some sea animals like dolphins and whales that do not have gills. They breathe in air through nostrils or blowholes that are located on the upper parts of their heads. This allows them to breathe in air when they swim near the surface of water. They can stay inside the water for a long time without breathing. They come out to the surface from time to time, to breathe in air.
- When we breathe out, the air moves from inside out body to outside. Breathing is part of a process called respiration. In respiration, some of the oxygen of the air we breathe, in used by the living body. We breathe out the Carbon dioxide produced in this process.

