Era of Rapid Changes
Category : Teaching
Era of Rapid Changes
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
MUGHAL EMPIRE
Mughal empire was the greatest empire of its time but it started declining in the first half of 18th century. There are many reasons behind this declination. Few reasons are rise of new powers, European entry in Indian subcontinent, policies of Aurangzeb, and attacks of Middle eastern powers. We can understand the reasons of declination of Mughal empire in few points:
1. Aurangzeb's religious policy, and imposition of Jajiya on the basis of religion.
2. The south policy of Aurangzeb also enriched his power in the South and almost forgot the northern part of his empire.
3. Corruption in military administration.
4. Selfishness of Mansabdars of Mughal empire.
5. Jats' and Rajputs' revolts during the period of Aurangzeb.
6. Over ambitiousness of Aurangzeb.
7. Rise of Maratha power.
8. Exploitative Jagirdah system.
9. Inner conflict of Mughal nobles: Turanians, Iranians, Afghans, and Indians.
10. Entry of European powers.
After the death of Aurangzeb, the Mughal empire became very unstable. Due to the instability of central power, a chain of changes started. These changes were rapid in nature. As we know power has direct relationship with political structures and economic system, and if there is a slight change in the power, some changes will surely be observed in politics and economics. When the Mughal empire was falling towards its declination, the Indian sub-continent was also going through some rapid changes. The main reason for these changes was the new raising of local and economic powers. Bengal, Awadh, Hyderabad, Mysore, and Maratha kingdom became the new centres of powers.
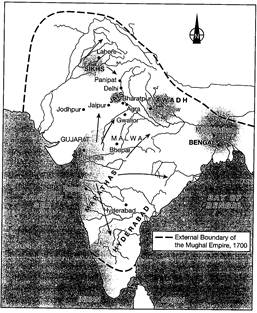
Figure 7.1 External boundary of the Mughal Empire 1700 and raising of new powers
Bengal
Due to delineation of central powers, Murshid Quli Khan and Alivardi khan made Bengal free from central Mughal empire. Murshid Quii khan was appointed as Nawab (deputy governor) of Bengal. Although it was not that powerful post but Murshid Quail khan did thing very fast in effective manner to control the total power of Bengal. He was on the footsteps of Awadh ruler. He decreased the Jagirdars appointed by Mughal emperor. In order to reduce Mughal intervention in Bengal administration, he transferred all Mughal Jagirdars to Orissa. He made major raise in revenues of Bengal in order to reduce power of zamindars. Due to high revenue rates, small
zamindars came into debt and only bigger zamindars remained powerful. The formation of a regional state in 18th century of Bengal led to considerable change amongst the zamindars. The close connection between the state and bankers - noticeable in Hyderabad and Awadh as well was evident in Bengal under the rule of Alivardi Khan (r. 1740-1756). During his reign, the banking house of Jagat Seth became extremely prosperous (NCERT textbook. Our Pasts II, Chapter 10, pp. 145)
Hyderabad
Nizam-ul-Mulk (Asal Jah) was the founder of Hyderabad state. He was also a powerful member of the court of Mughal emperor. Due to his powerful status in the emperor court, he got some very important responsibilities. First, he got governorship of Awadh, then later he was given Governorship of Deccan. This governorship made Asal Jah more powerful. Within very little time, he got full control over the political and financial administration and became the actual ruler of Deccan provinces. He made many changes in the administration of Deccan with permission of Mughal emperor. He was very impressed by the skilled soldiers and administrators of north India;
therefore, he brought some of them to Deccan. The appointment of Mansabdars and grant them Jagirs are one of the independent decision of Asal Jah.
Awadh
Burhan-ul-Mulk Sa'adat Khan was the founder of Awadh state. He was appointed as a Subahdar of Awadh in 1724 but in very little time, he controlled the administration of Awadh. Awadh was a very important region because it was situated in the middle of north India and Bengal trade route. Apart from the responsibility as Subahdar, he also had responsibilities of financial and military affairs of the Awadh province. As he was getting total control over Awadh, he has started reducing Mughals appointed officers from the province. There was a managed way to control financial administration in Awadh state. "The state depended on local bankers and Mahajans for loans. It sold the right to collect tax to the highest bidders. These 'revenue farmers' (ijaradars) agreed to pay the state a fixed sum of money. Local bankers guaranteed the payment of this contracted amount to the state. In turn, the revenue-farmers were given considerable freedom in the assessment and collection of taxes. These developments allowed new social groups, such as moneylenders and bankers, to influence the management of the state's revenue system, something that had not occurred in the past"(NCERT, class textbook - our pasts II, page 144, chapter -10)
Mysore
During the delineation of Mughal empire, the region of Mysore raised as a powerful state of south. Hyder All was the person in which Mysore got that powerful emergence. Hyder Ali was born in an obscure family. In his early life, he started his career with a job in army. He was a petty officer there. However, because of his intelligence, political strategies, determination and ability to catch the opportunities, he become very powerful administrator of Mysore in 1771 to over through Nanjaraja. To get full control over Mysore, he started reducing the power of rebellious zamindars. He started to overtake the power of Bindur, Sunda, Sera, Canara, and Malabar. During his entire political career, he was fully engaged in different wars. He fought with Maratha Sardars, Nizams, and the British army. After his death in second Anglo-Mysore war (1782), his son Tipu Sultan became the administrator of Mysore. He was a different type of ruler. He made some major changes in Mysore during his time. He introduced a new calendar, new coinage system, and new scales of weights and measures.
EMERGENCE OF NEW POWERS
Rajput
When the Mughal empire was on its peak, many Rajput kings were under the Mughal empire with a little autonomy of their Watan Jagirs. They were allowed to enjoy their kingdoms but under Mughal emperor. With the declination of Mughal empire, these Rajput kings attempted to take full control over their regions. In these processes, the role of Ajit Singh (king of Jodhpur) was very vital. He had the powerful effect in Mughal court and he tried to get profit from it. At that time, the province of Gujarat and Malwa was very rich. Due to their richness, all the powerful Rajput kings started claiming the Subahdar of that province. After the very hard work and strong political strategies. Raja Ajit Singh of Jodhpur got the governorship of Gujarat and Sawai Raja Jai Singh of Amber got the governorship of Malwa.
Maratha Kingdom
When Mughal empire was falling down, a new power, the Maratha kingdom, was rising. It was very powerful kingdom in comparison to others. It was the only powerful kingdom of that time that could fulfil the emptiness created by the declination of Mughal empire. It is important to know that Mughal declination was a result of fearlessness and determination of few Maratha administrators and Shivaji was one of them. Shivaji (1674-1680) established the powerful and stable kingdom with the help of powerful warrior families such as Deshmukhs and Kunbis. Shivaji challenged Mughals many times. The main strength of Shivaji administration was the policy of Ashta pradhan, and it means eight ministers with different responsibilities.
Shivaji's Ashta pradhan
1. Peshwa (Mukhya pradhan) - responsibilities of finance and general administration.
2. Majumdar (Amatya) - responsibility of revenue and finance.
3. Waqianavis (Mantri) - responsibility of home affairs.
4. Dabir (Sumant) - responsibility of foreign affairs.
5. Surnavis (Sachiv) - head of royal correspondence
6. Pandit Rao (Sadar) - responsibilities of religious affairs
7. Masahisa (Chief Justice) - responsibility of justice.
8. Sar-i-naubat (Senapati) - responsibilities of military
After the death of Shivaji, the family of Chitpavan Brahmanas (also called Peshwas) came into power and Pune became the capital of Maratha kingdom. Peshwas gave Maratha empire new heights. They developed a powerful army in very short period and they became strong opponent of Mughals. During the that period (1720-1761), Maratha empire expanded greatly Chauth and Sardeshmukhi were the famous taxes possessed by Maratha empire from 1735 to 1740 Marhatha domination expanded into the provinces of Rajasthan, Punjab, Bengal, Orissa, Karnataka, Tamilnadu, and Andhra Pradesh. In 1761, Marathas fought a war with the king of Afghanistan. This is called third war of Panipat. Marathas were great fighters but they were skilled administrators in their rule and new trade routes also emerged. Their financial administration was also effectively managed.
Maratha Rulers
Shivaji (1674-1680)
Sambhaji (1680-1689)
Rajaram (1689-1700)
Tarabai (1700-1707)
Shahu (1707-1749)
Balaji vishwanath (1713-1720) first Peshwa
Maratha Confederacy
Bajirao I (1720-1740)
Balaji Bajirao (1740-1761)
Jats
Jats were basically agriculturists. They lived in the region of Delhi, Agra, and Mathura. The main reason behind their entry in mainstream politics of that time was oppression by Mughal officials. They revolted in 1669 and 1688 under the powerful Jat zamindars. These revolts were not that well managed and strategically sound in nature. Therefore, they were crushed by Mughals; however, after the death of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb, Mughal empire fell down and they made a powerful comeback. That was the time when Jat state of Bhamtpur was set up. It was set up by Churaman and Badan Singh. Jats became very powerful in very short period of time and they started participating in court intrigues at Delhi but they achieved their highest glory under the administration of Raja Sura] Mal (1759-1763). Suraj Mal expanded his kingdom over a large area from Ganga in the East and Chambal in the South. After the death of Suraj Mal in 1763, Jats did not get any powerful leader and this is the reason they were split up among many zamindars.
Sikhs
Sikhs were the member of Sikhs religion found by Guru Nanak in the end of 15th century. It spread very fast in the region of Punjab. It made roots among the Jat peasantry and lower castes of the Punjab. The credit of Sikhs transformation in fighting community goes to Guru Hargobind (1606-1645). Sikhs became a strong power under the leadership of Guru Gobind Singh (1664-1708). Guru Gobind Singh was the last guru of the Sikhs. In the time period of Guru Gobind Singh, Sikhs formed a strong military force. Sikhs fought many times against Mughals, especially Aurangzeb. The tradition of Guruship in Sikh came to an end with the death of Guru Gobind Singh. After the death of Guru Gobind Singh, Banda Singh (Banda Bahadur) came in power as a leader and not as a guru. He struggled against Mughal army for more than 8 years. He died in 1715. After the death of Banda Bahadur, Sikhs got divided and declined. However, attacks of Nadir Shah and Ahmad Shah Abdali gave Sikhs a new opportunity for powerful come- back. From 1765 to 1800, Sikhs successfully controlled Jammu. Their military administration was divided into 12 Mists (confederacies) and these 12 divided Misls became the main strength of Sikhs. These Misls had equal rights, voices, and responsibilities. Very soon, this democratic nature of Misls got demolished just because of some powerful chiefs. With the declination of Misls, Sikhs power divided. The raise of Ranjit Singh brought good days for Sikhs. He was the chief of a, Sukerchakia Misls. He was a strong, skilled, and determined soldier. He was a good administrator too. In the end of 18th century under the leadership of Ranjit Singh, Sikhs captured Lahore and Amritsar. Very soon, he controlled Kashmir, Peshawar, and Multan.
European Powers
India has very old trade relationship with Europe. This relationship had many trade routes in middle ages.
(i) India - Persian Gulf - Iraq - Turkey - Venice and Genoa.
(ii) India-Red sea-Alexandria (Egypt)-Venice and Genoa
(iii) India - Central Asia - Russia - Baltic
On these trade routes, there was monopoly of two groups of merchants and sailors. Arab merchants and sailors had monopoly on Asian part of trade and Italian merchants and sailors had monopoly on Mediterranean and European part. There was a well-managed trade system between Asia and Europe. Tolls, duties, securities, and shelters all things used to work in a manner. Things started changing after the raise of Ottoman empire, they captured Asia Minor and Constantinople in 1453. Due to this change in power politics, Turkey got a total control on old trading routes between Europe and Asia. On the other side, Venice and Genoa took a full control on the trade between Europe and Asia. Both the region never gave enough space to western Europe to make a trade to Asia. That was the time when new nation states were emerging in western Europe. Those states were Spain and Portugal. Monopoly of Venice and Genoa and Turkish empire made trade and spices very expensive for western Europe. This time western Europe was also facing shortage of gold. These were the few reasons for the west European states to find new and safer sea routes to Asia, especially India and Indonesia. First, Vasco da Gama of Portugal discovered a new sea route between western Europe and India. It was just like to open a gateway for western Europe to India.
Portugal Entry to India
Portuguese was the first who find the new sea trade route between Western Europe and India so they got high profit for their achievement. They got monopoly on the new discovered route. They established their trade offices on the coastal areas of Cochin, Goa, Diu, and Daman. In order to establish their coastal settlements, they used force with trade but very soon they realised that they cannot go far with this strategy. Although they had armed ships with them, they are very few in numbers. Therefore, they started taking advantage of rivalries of Indian kings. In order to start working on their new strategy, they intervened in the conflict of Calicut and Cochin. This became the very successful step for Portugal. Very soon, they got full control on the western coast of India. They captured Goo in 1510.
British East India Company
When Portuguese traders were getting rich by their Indian tours, British merchants were looking greedily on their success. However, due to their weak naval position, they were not thinking to challenge the monopoly of Portugal and Spain. In the end of 16th century, they started searching new trade routes to India but did not get success. In these 50 years, they gathered more sea power in order to get entry in Asia. Finally, in 1588, the defeat of Spanish armada gave the golden opportunity to Britain. The famous British trade company East India Company was formed in 1599. This was formed by the merchants and trades of Britain. Because of profitable trade route of Western Europe and Asia, this company got exclusive privilege by Queen Elizabeth on 31 December 1600. This company also got royal charter. Expected bright future of this company linked it with monarch, as queen Elizabeth became the shareholder of the company. The company cached Asia in 1601, and they sailed their ships to the coast of Indonesia. They reached India in 1608, .they made their entry from the coast of Surat and Gujrat. In the leadership of Captain Hawkins, East India Company made a way to Jahangir's court. The company got Mansab of 400 and a Jagir. However, Mughal court was very influenced by Portuguese; due to this influence, East India Company suffered in their initial years. To get total monopoly on the trade of India, portuguese and East India Company fought many times against each other at different places. East India Company defeated Portuguese in 1612 and 1614. These victories made things easy or East India Company. Mughals get impressed by the naval power of East India Company and started thinking to use it in their favour as they were very weak in naval powers. This quality of East India Company led them to get royal Farman to open factories on different places on west coast. However, it was just a start; very soon. East India Company became more demanding to mughals. They send Sir Thomas Roe to Mughal court to get some more rights in order to establish Heir trade in India. East India Company took the advantage of weak Mughal naval powers, and they gave threats to Mughals for harassing Indian sea merchants in red sea. These pressure did a tremendous work in the favour of East India Company. They got an imperial Farman to trade and establish factories in all parts of the Mughal empire. After this, Portuguese became angry, and in 1620, naval battles started between both. Finally, East India Company won and their hostilities Game to end in 1630. In next 30-35 years, Portuguese lost all their settlements in India except Goa, Daman, and Diu. On the other side. East India Company and Dutch Company fighting over the trade of Indonesia. The war between East India Company and Dutch Company had begun in 1654, which ended in 1667. In the end of this battle. East India Company gave all their claims of Indonesia and Dutch Company gave up their claims of India but it took almost 30 years to expel the Dutch from India completely. By the end of 1765, Dutch lost their last possession in India. In the next few decades. East India Company took over a very large portion of India. They applied the same strategy that was applied by Portuguese in their initial stage in India. They took advantage of internal disputes of Indian kings. They started work to take over powerful Indian regions such as Bombay, Madras, and Calcutta. They were developing these coastal cities as the centre of trade for their profits. As per some sources in 1612, the East India Company made a big profit of 10,00,000 Euro and this process of making high profits never stopped till the entry of crown rule in India. Very soon, East India Company realised that the future of company is not that bright and sustainable without getting political power in India and company began their political career with the battle of Plassey in 1757. In this battel. East India Company and Nawab of Bengal, Siraj ud-daulah was standing in the front of each other. In the end, Siraj ud-daulah got defeated from the company; In 1764, Mir Qasim, Shuja-ud-daulah, and Shah Alam II allied to fight with company, and they clashed with company's army in the famous battle of Buxar in 1764. Company made a powerful victory. Further, this victory had established the supremacy of company. This victory gave company the total control over Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, and Awadh. East Indian Company used their dual system of administration policy in Bengal after the battle of Buxar. According to this policy, company started using the powers of Diwan and Deputy Subahdar. Due to the treaty of nizam-ud-daulah and company, company got the right to nominate Diwan and Deputy Subahdar. The work of Diwan was to collect revenues from state and the work of Deputy Subahdar to control the Nizamat (police and judicial powers). By this dual system of administration, company got supreme power in Bengal without any responsibility.
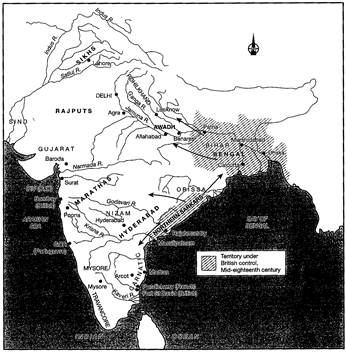
Figure 7.2 Territory under British control in mid-eighteenth century
French East India Company
French East India Company was formed by the group of French traders and merchants in 1664. It did not make an impact on European-Indian trade till 1720. In 1720, French East India Company reorganised itself. After their reorganisation, French East India Company came in the competition with East India Company of Britain. French Company established their factory on east coast of India near Calcutta and Pondicherry. In the later period, French Company started some more factories in east and west coasts. In between, French East India Company took control over Mauritius. French East India Company had some limitation as it was mainly dependent on French government. The share holder of this company wanted fast profit and they did not support commercial strategies of company. Government meddling in company matters made things very difficult for the company. In 1742, there was a war that broke out between France and England. This war was happening in Europe but the flame of this war easily reached India and the Anglo French conflict begun. It took 20 years to resolve this conflict. French Company made high profit from their possessions in India. Especially, in Hyderabad, French Companies were very successful. French Company also made profit from another east coast factory.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
