Microsoft Windows
Category : Banking
Microsoft Windows
When referring to an operating system. Windows is an operating environment created by Microsoft that provides an interface known a s Graphical User Interface (GUI) for computers/laptops/notebooks etc. Windows eliminates the need for a user to type each command at a command line, like MS-DOS, by using a mouse to navigate through drop-down menus, dialog boxes, buttons, tabs, and icons.
BASIC OF MICROSOFT WINDOWS
Developer(s) Microsoft
Initial release November 19, 1990; almost 24 years ago
Stable release 2010 (14.0.6023.1000 SP1) / June 28, 2011
Development status Active
Written in C++
Operating system Microsoft Windows
Available in Over 35 languages
Type Office suite
GENERATIONS OF M ICROSOFT WlNDOWS
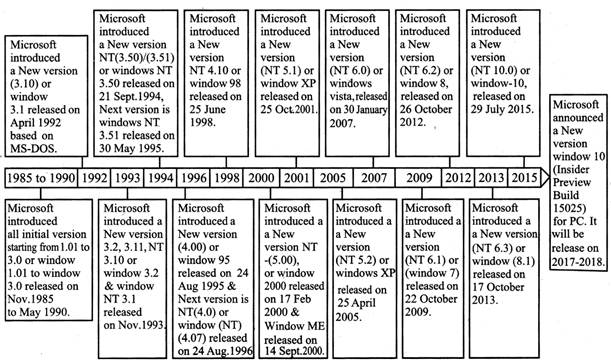
MICROSOFT WINDOWS VERSIONS
Microsoft Windows Versions for Personal Computers
The following details the history of Microsoft Windows Versions designed for personal computers (PCs).
Windows XP comes in two versions, Home and Professional. Microsoft focused on mobility for both editions, including plug and play features for connecting to wireless networks. The operating system also utilizes the 802.1 Ix wireless security standard.
Microsoft described Windows 10 as an "operating system as a service" that would receive ongoing updates to its features and functionality, augmented with the ability for enterprise environments to receive non-critical updates at a slower pace, or use long-term support milestones that will only receive critical updates, such as security patches, over their five-year lifespan of mainstream support.
Microsoft Windows Versions for Servers and Mobile Devices
Apart from Windows Versions designed for use on personal computers (PCs) and laptops, Microsoft has also developed operating systems for services, handheld devices, and mobile phones.
POPULAR MOBILE OPRATING SYSTEMS
It is a Google's open and free software stack that includes an operating system, middleware and also key applications for use on mobile devices, including smart phones. Updates for the open source Android mobile operating system have been developed under "dessert-inspired" code names (Cupcake, Donut, eclair. Gingerbread, Honeycomb, and Ice Cream Sandwich) with each new version arriving in alphabetical order with new enhancements and improvements.
It was originally developed for use on its iPhone devices. Now, the mobile operating system is referred to as iOS and is supported on a number of Apple devices including the iPhone, iPad, iPad 2 and iPod Touch. The iOS mobile operating system is available only on Apple's own manufactured devices as the company does not license the OS for third-party hardware. Apple iOS is derived from Apple's Mac OS X operating system.
It is a proprietary mobile operating system developed by Research in Motion for use on the company's popular BlackBerry handheld devices. The BlackBerry platform is popular with corporate users as it offers synchronization with Microsoft Exchange, Lotus Domino, Novell GroupWise email and other business software, when used with the BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
It is a proprietary Samsung mobile OS that was first launched in 2010. The Samsung Wave was the first smart phone to use this mobile OS. Bada provides mobile features such as multipoint-touch, 3D graphics and of course, application downloads and installation
A joint open source mobile operating system which is the result of merging two products based on open source technologies: Maemo (Nokia) and Moblin (Intel). Mee Go is a mobile OS designed to work on a number of devices including smart phones, net books, tablets, in-vehicle information systems and various devices using Intel Atom and ARMv7 architectures.
It is a mobile operating system (OS) targeted at mobile phones that offers a high-level of integration with communication and personal information management (PIM) functionality. Symbian OS combines middleware with wireless communications through an integrated mailbox and the integration of Java and PIM functionality (agenda and contacts). Nokia has made the Symbian platform available under an alternative, open and direct model, to work with some OEMs and the small community of platform development collaborators. Nokia does not maintain Symbian as an open source development project.
It is a proprietary mobile operating system (PDA operating system) that was originally released in 1996 on the Pilot 1000 handheld. Newer versions of the Palm OS have added support for expansion ports, new processors, external memory cards, improved security and support for ARM processors and smart phones. Palm OS 5 was extended to provide support for a broad range of screen resolutions, wireless connections and enhanced multimedia capabilities and is called Garnet OS.
It is a mobile operating system that runs on the Linux kernel. Web OS was initially developed by Palm as the successor to its Palm OS mobile operating system. It is a proprietary Mobile OS which was eventually acquired by HP and now referred to as web OS (lower-case) in HP literature. HP uses web OS in a number of devices including several smart phones and HP Touch Pads.
WINDOWS STRUCTURE
Desktop Applications
The first version of MS-Word, released in the autumn of 1983, was for the MS-DOS operating system and had the distinction of introducing the mouse to a large population of computer users. Word 1.0 could be purchased with a bundled mouse, though none was required. Following the precedents of Lisa Write and MacWrite, Word for Macintosh attempted to add closer WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) features into its package. Word for Mac was released in 1985. Word for Mac was the first graphical version of Microsoft Word. Despite its bugs, it became one of the most popular Mac applications.
Other desktop applications (Windows versions only)
WINDOWS DESKTOP
The following terms used to describe the Windows desktop:
Note: Microsoft has changed "My Documents" to "Documents" in the most recent versions of Windows.
It can open in three ways:
An icon for Network Neighborhood, My Network Places, or Network may be on the Windows Desktop and is also accessible through the Windows Explorer.
(a)Start Button: This button resides on the extreme left side of the taskbar. When we click on the start button then the start menu will appear.
(b) Quick Launch Icons: On the right side of the Start Button, there are some little icons. Windows and Internet Explorer, when installed, automatically puts the icons of some of the very helpful things there. For example, with just one click on its icon. Internet Explorer browser can be launch from here. "Show Desktop" icon is a quick way of minimizing all open windows on the desktop at once (with just one click) and revealing the desktop,
(c) Open Applications: The middle and longest portion of the taskbar remains empty until you launch a program. As soon as you open a program in your computer its name appears in this middle part of the taskbar.
(d) Tray Icons: Next on the taskbar are the tray icons. These icons represent programs that are running silently in the background and will jump into action the moment it becomes necessary.
(e) Clock: On the extreme right side of the taskbar resides the computer clock. The clock is actually a part of the tray icons. But the clock will be there even if you run Windows in safe mode.
(a) Left Pane: The left pane shows recently ran programs or any pinned program shortcuts,
(ii) All Programs: At the bottom of the left pane is the "All Programs" option, which displays all programs that have been installed on the computer.
(ii) Search: The "Search" bar is useful feature allows to type in the name of the program or file looking for and have the results displayed above.
(b) Right Pane: The right pane shows each of the more commonly accessed sections of the computer such as your computer, Control Panel, documents, music, and pictures.
(i) Personal folder: Opens your personal folder, which is named for whoever is currently logged on to Windows.
(ii) Documents: Opens the Documents library, where a user can access and open text files, spreadsheets, presentations, and other kinds of documents.
(iii) Pictures: Opens the Pictures library, where a user access and view digital pictures and graphics files.
(iv) Music: Opens the Music library, where a user can access and play music and other audio files.
(v) Games: Opens the Games folder, where a user can access all of the games on computer.
(vi) Computer: Opens a window where you a user can access disk drives, cameras, printers, scanners, and other hardware connected to computer.
(vii)Control Panel: Opens Control Panel, where you a user customize the appearance and functionality of your computer, install or uninstall programs, set up network connections, and manage user accounts.
(viii) Devices and Printers: Opens a window where you a user can view information about the printer, mouse, and other devices installed on computer.
(ix) Default Programs: Opens a window where you user can choose which program in indows to use for activities such as web browsing.
(x) Help and Support: Opens Windows Help and Support, where a user can browse and search Help topics about using Windows and computer.
(c) Shut down (Turn Off): The Shutdown button allows to Shut down the computer or click the arrow next to the Shutdown button to switch user, log off, restart, and sleep the computer.
Folders: A folder is a location that stores multiple files and other folders found on Apple computers, computers running Microsoft Windows, and other GUI operating systems, when in a command line, folders are referred to as directories.
Title bar: Title Bar at the top of open window that will tell what the folder/window is (the title) and contains the minimize, maximize and close buttons. It can also use the title bar to move a window around.
Cursor: Cursor is the symbol which is used to for action performing. The cursor changes its shape from the default arrow to various shapes according to the purpose it is serving at the time. For instance, it may from an I-beam shape when user selects a text in a documents or a double-arrow when use resized a window.
Scroll bar: scroll bar appears when there is some information in the window than can be displayed and the information is more than that. This is usually a vertical scroll bar, but a horizontal scroll bar may display if the width of the window is too narrow.
Address Bar: Address Bar allows you to navigate up and down a series of windows by double-clicking on a folder. The folder with the Back/Fwd Buttons in Windows 7 would allow you to return to the previous folder.
Dialog box: In a graphical user interface operating system, a dialog box or dialogue box is a new window that appears above the rest that lists additional information errors, or options.
MOUSE CLICKS ON WINDOWS
A mouse has two buttons and most current mouse have a middle button as well. The type of click means the button you push when you click.
When a user right-click to obtain a menu, it will select the menu with the left button (generally just referred to as selecting or clicking — the left mouse button click is assumed).
Context Sensitive
This refers to the fact that the menu varies when you place it on different items:
FILES & FILE EXTENSIONS
A file is an object on a computer that stores data, information, settings, or commands that are used with a computer program. In a graphical user interface (GUI) such as Microsoft Windows, files are shown as unique icons that relate to the program that opens the file.
File extensions are the part of the filename that is after the dot in Window®. For example, a text file like readme. txt has txt as its extension. -
Extensions Tell What Type of File
The extension tells Windows how to deal with a certain file by identifying the type of file it is. By associating a certain extension with a default program to deal with that sort of file, you can open the program by double- clicking on the filename. The type of file is usually indicated by its icon as well.
Common Extensions
There are hundreds of extensions, many of which are proprietary (e.g. specific to a particular program) and quite a few that are legacy (no longer in active use). Some of the more common ones are:
Dangerous Extensions
Some Windows extensions can indicate programs that can do harm to your computer. You should always be careful with files that have the following extensions, particularly if attached to an email message, because they can be used to install malicious or unwanted programs:
Most users should not see any of these sorts of files attached to emails. While any of these could be legitimate files it is more likely that its purpose is to infect your computer with a virus or other malicious program.
Hidden By Default
Windows hides "known" extensions by default (Windows "knows" what the extension is — you may not). This was probably done to make it look less intimidating, but you should re-enable the display of these extensions (see Folder Options). Many file extensions are not safe to open unless provided by a trusted source.
For example, if you see a file attached to an email, you may not know that the attachment is unsafe to open:
ACCESSORIES IN WINDOWS
How to open Windows Notepad
Click Start—>Click Programs and then Accessories—>Click the "Notepad" icon.
How to open Windows Notepad
Click Start—>Click Programs and then Accessories—>Click the "WordPad" icon.
How to open Windows Paint
Click Start—>Click Programs and then Accessories-*Click the "Paint" icon.
Keyboard Shortcuts for Windows
|
To |
Press |
|
Displays the properties of the selected object. |
ALT +Enter |
|
"Close the active item, or quit the active program. |
ALT +F4 |
|
Switch between open items. |
ALT +TAB |
|
Carry out the corresponding command or select the corresponding option in a dialog box. |
ALT +Underlined letter
|
|
Display the corresponding menu. |
ALT +Underlined letter in a menu name |
|
Select a button if the active option is a group of option buttons in a dialog box. |
Arrow keys |
|
View the folder one level up in My Computer or Windows Explorer. |
BACKSPACE |
|
Open a folder one level up if a folder is selected in the Save As or Open dialog box in a dialog box. |
BACKSPACE |
|
Copy selected item. |
CTRL while dragging an item |
|
Select all. |
CTRL+A |
|
Copy |
CTRL+C |
|
Move the insertion point to the beginning of the next paragraph. |
CTRL+DOWN ARROW |
|
Display the Start menu. |
CTRL+ESC |
|
Close the active document in programs that allow you to have multiple documents open simultaneously. |
CTRL+F4
|
|
Move the insertion point to the beginning of the previous word. |
CTRL+LEFT ARROW |
|
Move the insertion point to the beginning of the next word. |
CTRL+RIGHT ARROW |
|
Highlight a block of text. |
CTRL+SHIFT with any of the arrow keys |
|
Move backward through tabs in a dialog box. |
CTRL+SHIFT+TAB |
|
Move forward through tabs in a dialog box. |
CTRL+TAB |
|
Paste. |
CTRL+V |
|
Cut. |
CTRL+X |
|
Undo. |
CTRL+Z |
|
Delete. |
DELETE |
|
Display the bottom of the active window. |
END |
|
Cany out the command for the active option or button in a dialog box. |
ENTER |
|
Cancel the current task. |
ESC |
|
Display Help in a dialog box. |
F1 |
|
Activate the menu bar in the active program. |
F10 |
|
Rename selected item. |
F2 |
|
Search for a file or folder. |
F3 |
|
Display the Address bar list in My Computer or Windows Explorer. |
F4 |
|
Display the items in the active list in a dialog box. |
F4 |
|
Refresh the active window |
F5 |
|
Cycle through screen elements in a window or on the desktop. |
F6
|
|
Display the top of the active window. |
HOME |
|
Open the next menu to the left, or close a submenu. |
LEFT ARROW |
|
Collapse current selection if it's expanded, or select parent folder. |
LEFT ARROW |
|
Display the items in the active list in a dialog box. |
F4 |
|
Refresh the active window. |
F5 |
|
Cycle through screen elements in a window or on the desktop. |
F6 |
|
Display the top of the active window. |
HOME |
|
Open the next menu to the left, or close a submenu. |
LEFT ARROW |
|
Collapse current selection if it's expanded, or select parent folder. |
LEFT ARROW |
|
Display the items in the active list in a dialog box. |
F4 |
|
Refresh the active window. |
F5 |
|
Cycle through screen elements in a window or on the desktop. |
F6 |
|
Display the top of the active window. |
HOME |
|
Open the next menu to the left, or close a submenu. |
LEFT ARROW |
|
Collapse current selection if it's expanded, or select parent folder. |
LEFT ARROW |
|
Display the shortcut menu for the selected item. |
Menu key |
|
Display all subfolders under the selected folder. |
NUM LOCK+ASTERISK on numeric keypad (*) |
|
Collapse the selected folder. |
NUM LOCK+MINUS SIGN on numeric keypad (-) |
|
Display the contents of the selected folder. |
NUM LOCK+PLUS SIGN on numeric keypad (+) |
|
Open the next menu to the right, or open a submenu. |
RIGHT ARROW |
|
Display current selection if it's collapsed, or select first subfolder. |
RIGHT ARROW |
|
display the items in the active list in a dialog box. |
F4 |
|
refresh the active window. |
F5 |
|
Cycle through screen elements in a window or on the desktop. |
F6 |
|
Display the shortcut menu for the selected item. |
Menu key |
|
Collapse the selected folder. |
NUM LOCK+MINUS SIGN on numeric keypad (-) |
|
Display the contents of the selected folder. |
NUM LOCK+PLUS SIGN on numeric keypad (+) |
|
Open the next menu to the right, or open a submenu. |
RIGHT ARROW |
|
Display current selection if it's collapsed, or select first subfolder. |
RIGHT ARROW |
|
Delete selected item permanently without placing the item in the Recycle Bin. |
SHIFT+DELETE |
|
Display the shortcut menu for the selected item. |
SHIFT+F10 |
|
Move backward through options in a dialog box. |
SHIFT+TAB |
|
Select or clear the check box if the active option is a check box in a dialog box. |
SPACEBAR |
|
Move forward through options in a dialog box. |
TAB |
|
Display or hide the Start menu. |
Windows Key |
|
Lock your computer if you are connected to a network domain, or switch users if you are not connected to a network domain. |
Windows Key+ L |
|
Show the desktop. |
Windows Key +D |
|
Open My Computer. |
Windows Key +E |
|
Search for a file or folder. |
Windows Key +F_ |
|
Display Windows Help. |
Windows Key +F 1 |
|
Minimize all windows. |
Windows Key +M |
|
Open the Run dialog box. |
Windows Key +R |
|
Restores minimized windows. |
Windows Key + Shift + M |
|
Opens Utility Manager. |
Windows Key + U |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
