Cell in Various Positions
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) Closed circuit : Cell supplies a constant current in the circuit.
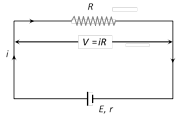
(i) Current given by the cell \[i=\frac{E}{R+r}\]
(ii) Potential difference across the resistance \[V=iR\]
(iii) Potential drop inside the cell \[=ir\]
(iv) Equation of cell \[E=V+ir\]\[(E>V)\]
(v) Internal resistance of the cell \[r=\left( \frac{E}{V}-1 \right)\,\cdot R\]
(vi) Power dissipated in external resistance (load)
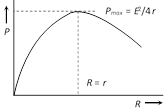
\[P=Vi={{i}^{2}}R=\frac{{{V}^{2}}}{R}={{\left( \frac{E}{R+r} \right)}^{2}}.R\]
Power delivered will be maximum when \[R=r\] so \[{{P}_{\max }}=\frac{{{E}^{2}}}{4r}\].
This statement in generalised from is called "maximum power transfer theorem".
(vii) When the cell is being charged i.e. current is given to the cell then \[E=V-ir\] and \[E<V\].
(2) Open circuit : When no current is taken from the cell it is said to be in open circuit
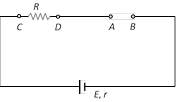
(i) Current through the circuit \[i=0\]
(ii) Potential difference between A and B, \[{{V}_{AB}}=E\]
(iii) Potential difference between C and D, \[{{V}_{CD}}=0\]
(3) Short circuit : If two terminals of cell are join together by a thick conducting wire
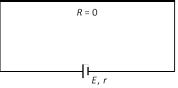
(i) Maximum current (called short circuit current) flows momentarily \[{{i}_{sc}}=\frac{E}{r}\]
(ii) Potential difference V = 0
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
