Manganese Containing Compound
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
Potassium Permanganate, \[(KMn{{O}_{4}})\]
Potassium permanganate is a salt of an unstable acid \[HMn{{O}_{4}}\] (permanganic acid). The Mn is an +7 state in this compound.
Preparation : Potassium permanganate is obtained from pyrolusite as follows.
Conversion of pyrolusite to potassium manganate : When manganese dioxide is fused with potassium hydroxide in the presence of air or an oxidising agent such as potassium nitrate or chlorate, potassium manganate is formed, possibly via potassium manganite.
\[Mn{{O}_{2}}+2KOH\xrightarrow{fused}\underset{potassium\,manganite}{\mathop{{{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{3}}}}\,+4{{H}_{2}}O]\times 2\]
\[2{{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{3}}+{{O}_{2}}\to 2{{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{4}}+\,2\,{{H}_{2}}O\]
\[\underset{pyrolusite}{\mathop{2Mn{{O}_{2}}}}\,+4KOH+{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{fused}\underset{\underset{\left[ dark-green\,\,mass \right]}{\mathop{potassium\,manganate}}\,}{\mathop{2{{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{4}}}}\,+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
Oxidation of potassium manganate to potassium permanganate : The potassium manganate so obtained is oxidised to potassium permanganate by either of the following methods.
By chemical method : The fused dark-green mass is extracted with a small quantity of water. The filtrate is warmed and treated with a current of ozone, chlorine or carbon dioxide. Potassium manganate gets oxidised to potassium permanganate and the hydrated manganese dioxide precipitates out. The reactions taking place are,
When \[C{{O}_{2}}\] is passed
\[\underset{potassium\,manganate}{\mathop{3{{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{4}}+}}\,2{{H}_{2}}O\to \underset{potassium\,permanganate}{\mathop{2KMn{{O}_{4}}}}\,+Mn{{O}_{2}}\downarrow +4KOH\]
\[2C{{O}_{2}}+4KOH\to 2{{K}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
When chlorine or ozone is passed
\[2{{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{4}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to 2KMn{{O}_{4}}+2KCl\]
\[2{{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{4}}+{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to 2KMn{{O}_{4}}+2KOH+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
The purple solution so obtained is concentrated and dark purple, needle-like crystals having metallic lustre are obtained.
Electrolytic method : Presently, potassium manganite \[({{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{4}})\] is oxidised electrolytically. The electrode reactions are,
At anode: \[\underset{green}{\mathop{2MnO_{4}^{2-}}}\,\to \underset{purple}{\mathop{2MnO_{4}^{-}}}\,+2{{e}^{-}}\]
At cathode: \[2{{H}^{+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
The purple solution containing KMnO4 is evaporated under controlled condition to get crystalline sample of potassium permanganate.
Physical properties
\[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] crystallizes as dark purple crystals with greenish luster (m.p. 523 K).
It is soluble in water to an extent of 6.5g per 100g at room temperature. The aqueous solution of \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] has a purple colour.
Chemical properties : Some important chemical reactions of \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] are given below,
Action of heat : \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] is stable at room temperature, but decomposes to give oxygen at higher temperatures.
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}\left( s \right)\xrightarrow{heat}{{K}_{2}}Mn{{O}_{4}}\left( s \right)+Mn{{O}_{2}}+{{O}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
Oxidising actions : KMnO4 is a powerful agent in neutral, acidic and alkaline media. The nature of reaction is different in each medium. The oxidising character of \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] (to be more specific, of \[MnO_{4}^{-}\]) is indicated by high positive reduction potentials for the following reactions.
Acidic medium
\[MnO_{4}^{-}+8{{H}^{+}}+5{{e}^{-}}\rightleftharpoons M{{n}^{2+}}+4{{H}_{2}}O\,\,\,\,\,\,{{E}^{o}}=1.51\,V\]
Alkaline medium
\[MnO_{4}^{-}+2{{H}_{2}}O+3{{e}^{-}}\rightleftharpoons Mn{{O}_{2}}+4O{{H}^{-}}\,\,\,{{E}^{o}}=1.23\,V\,\]
In strongly alkaline solutions and with excess of \[MnO_{4}^{-}\], the reaction is \[MnO_{4}^{-}+{{e}^{-}}\rightleftharpoons MnO_{4}^{2-}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{{E}^{o}}=0.56\,V\]
There are a large number of oxidation-reduction reactions involved in the chemistry of manganese compounds. Some typical reactions are,
In the presence of excess of reducing agent in acidic solutions permanganate ion gets reduced to manganous ion, e.g., \[5F{{e}^{2+}}+MnO_{4}^{-}+8{{H}^{+}}\to 5F{{e}^{3+}}+M{{n}^{2+}}+4{{H}_{2}}O\]
An excess of reducing agent in alkaline solution reduces permanganate ion only to manganese dioxide e.g.,
\[3NO_{2}^{-}+MnO_{4}^{-}+2O{{H}^{-}}\to 3NO_{3}^{-}+Mn{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
In faintly acidic and neutral solutions, manganous ion is oxidised to manganese oxidised to manganese dioxide by permanganate.
\[2MnO_{4}^{-}+3M{{n}^{+2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O\to 5Mn{{O}_{2}}+4{{H}^{+}}\]
In strongly basic solutions, permangante oxidises manganese dioxide to manganate ion.
\[Mn{{O}_{2}}+2MnO_{4}^{-}+4O{{H}^{-}}\to 3MnO_{4}^{2-}+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
In acidic medium, \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] oxidises,
Ferrous salts to ferric salts
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}O+5\left[ O \right]\]
\[\underset{\underline{2KMn{{O}_{4}}+8{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+10FeS{{O}_{4}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+5F{{e}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}+8{{H}_{2}}O}}{\mathop{\underline{2FeS{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+\left[ O \right]\to F{{e}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O]\times 5}}}\,\]
Ionic equation
\[2MnO_{4}^{-}+16{{H}^{+}}+10F{{e}^{2+}}\to 2M{{n}^{2+}}+10F{{e}^{3+}}+8{{H}_{2}}O\]
The reaction forms the basis of volumetric estimation of Fe2+ in any solution by KMnO4.
Oxalic acid to carbon dioxide
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}O+5\left[ O \right]\]
\[{{\left( COOH \right)}_{2}}+\left[ O \right]\to 2C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O]\times 5\]
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+5{{\left( COOH \right)}_{2}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+10C{{O}_{2}}+8{{H}_{2}}O\] Ionic equation
\[2MnO_{4}^{-}+6{{H}^{+}}+5{{\left( COOH \right)}_{2}}\to 2M{{n}^{2+}}+10C{{O}_{2}}+8{{H}_{2}}O\]
Sulphites to sulphates
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}O+5\left[ O \right]\]
\[N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}+\left[ O \right]\to N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}]\times 5\]
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+5N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+5N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}O\]
Ionic equation
\[2MnO_{4}^{-}+6{{H}^{+}}+5SO_{3}^{2-}\to 2M{{n}^{2+}}+5SO_{4}^{2-}+3{{H}_{2}}O\]
Iodides to iodine in acidic medium
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}O+5\left[ O \right]\]
\[2KI+{{H}_{2}}O+\left[ O \right]\to {{I}_{2}}+2KOH\times 5\]
\[2KOH+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2{{H}_{2}}O\,\,]\times 5\]
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+8{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+10KI\to 6{{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+5{{I}_{2}}+8{{H}_{2}}O\]
Ionic equation
\[2MnO_{4}^{-}+16{{H}^{+}}+10{{I}^{-}}\to 2M{{n}^{2+}}+5{{I}_{2}}+8{{H}_{2}}O\]
Hydrogen peroxide to oxygen
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}O+5\left[ O \right]\]
\[{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}+\left[ O \right]\to {{H}_{2}}O+{{O}_{2}}\uparrow \times 5\]
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+5{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2MnS{{O}_{4}}+8{{H}_{2}}O+5{{O}_{2}}\]
Manganous sulphate (MnSO4) to manganese dioxide (MnO2)
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to 2KOH+2Mn{{O}_{2}}+3\left[ O \right]\]
\[MnS{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}O+\left[ O \right]\to Mn{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\times 3\]
\[2KOH+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\to {{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+3MnS{{O}_{4}}+2{{H}_{2}}O\to 5Mn{{O}_{2}}+{{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+2{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]
Ionic equation
\[2MnO_{4}^{-}+3M{{n}^{2+}}+2{{H}_{2}}O\to 5Mn{{O}_{2}}+4{{H}^{+}}\]
Ammonia to nitrogen
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to 2Mn{{O}_{2}}+2KOH+3\left[ O \right]\]
\[2N{{H}_{3}}+3\left[ O \right]\to {{N}_{2}}\left( g \right)+3{{H}_{2}}O\]
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+2N{{H}_{3}}\to 2Mn{{O}_{2}}+2KOH+2{{H}_{2}}O+{{N}_{2}}\left( g \right)\]
Uses : \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] is used,
(i) As an oxidising agent. (ii) As a disinfectant against disease-causing germs. (iii) For sterilizing wells of drinking water. (iv) In volumetric estimation of ferrous salts, oxalic acid etc. (v) Dilute alkaline \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] solution known as Baeyer’s reagent.
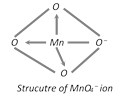
Structure of Permanganate Ion \[(\mathbf{Mn}{{\mathbf{O}}_{\mathbf{4}}}^{})\] : Mn in \[Mn{{O}_{4}}^{}\] is in +7 oxidation state. \[M{{n}^{7+}}\] exhibits \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridisation in this ion. The structure of \[Mn{{O}_{4}}^{}\] is, shown in fig.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
