Boyle's Law
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) In 1662, Robert Boyle discovered the first of several relationships among gas variables (P, T, V).
(2) It states that, "For a fixed amount of a gas at constant temperature, the gas volume is inversely proportional to the gas pressure."
Thus, \[P\propto 1/V\] at constant temperature and mass
or \[P=K/V\] (where K is constant)
or\[PV=K\] or \[{{P}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}=K\] (For two or more gases)
(3) Graphical representation of Boyle's law : Graph between P and V at constant temperature is called isotherm and is an equilateral (or rectangular) hyperbola. By plotting P versus \[1/V\], this hyperbola can be converted to a straight line. Other types of isotherms are also shown below,
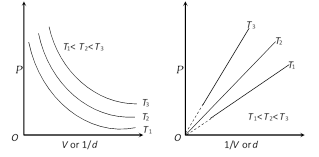
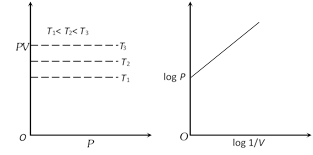
(4) At constant mass and temperature density of a gas is directly proportional to its pressure and inversely proportional to its volume.
Thus, \[d\propto P\propto \frac{1}{V}\]
\[\left[ \because V=\frac{\text{mass}}{d} \right]\]
or \[\frac{{{d}_{1}}}{{{d}_{2}}}=\frac{{{P}_{1}}}{{{P}_{2}}}=\frac{{{V}_{2}}}{{{V}_{1}}}=.......=K\]
(5) At altitudes, as P is low d of air is less. That is why mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
