Methods Of Preparation Of Monocarboxylic Acid
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) By oxidation of alcohols, aldehydes and ketones
\[\underset{\text{alcohol}}{\mathop{RC{{H}_{2}}OH}}\,\underset{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{[O\}}}}\,RCHO\underset{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{[O]}}}\,\underset{\text{Carboxylic acid}}{\mathop{RCOOH}}\,\]
\[\underset{\text{Aldehyde}}{\mathop{RCHO}}\,\xrightarrow{[O]}\underset{\text{monocarboxylic acid}}{\mathop{RCOOH}}\,\]
\[R\underset{O}{\mathop{\underset{|\,|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-C{{H}_{3}}+3{{I}_{2}}+3NaOH\underset{{{H}_{2}}O}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{\Delta }}}\,\]
\[R-\underset{O}{\mathop{\underset{|\,|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-OH+CH{{I}_{3}}+3NaI+3{{H}_{2}}O\]
(2) By Hydrolysis of nitriles, ester, anhydrides and acid chloride
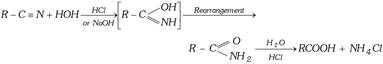
(ii) Hydrolysis of Esters
\[\underset{\text{Ester}}{\mathop{RCOOR'}}\,+HOH\underset{O{{H}^{-}}}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{HCl}}}\,\underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{RCOOH}}\,+\underset{\text{Alcohol}}{\mathop{R'OH}}\,\]
(iii) Hydrolysis of Anhydrides
\[\underset{\text{Ethanoic anhydride}}{\mathop{\begin{matrix} C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{|\,|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\, \\ C{{H}_{3}}-\underset{O}{\mathop{\underset{|\,|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\, \\ \end{matrix}\ \ \ \ \ O+HOH}}\,\xrightarrow{{{H}^{+}}/O{{H}^{-}}}\underset{\text{Ethanoic acid}}{\mathop{2C{{H}_{3}}COOH}}\,\]
(iv) Hydrolysis of acid chloride and nitro alkane
\[R-\underset{O}{\mathop{\underset{|\,|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-Cl+HOH\xrightarrow{{{H}^{+}}/O{{H}^{-}}}RCOOH+HCl\]
\[R-C{{H}_{2}}-N{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{85%{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}RCOOH\]
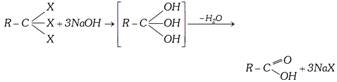
(v) Hydrolysis of Trihalogen :
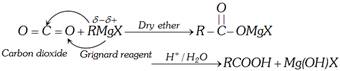
(3) From Grignard Reagent
(4) From Alkene or Hydro-carboxy-addition (koch reaction)
\[C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+CO+{{H}_{2}}O\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}500-1000atm \\ \And 350{}^\circ C \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}}}}\,C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH\]
(5) Special methods
(i) Carboxylation of sodium alkoxide
\[\underset{\text{Sod}\text{. alkoxide}}{\mathop{RONa+CO}}\,\to \underset{\text{Sod}\text{. salt}}{\mathop{RCOONa}}\,\xrightarrow{HCl}\underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{RCOOH}}\,\]
(ii) Action of heat on dicarboxylic acid
![]()
(iii) From acetoacetic ester
![]()
(iv) Oxidation of alkene and alkyne
\[\underset{\text{Alkene}}{\mathop{RCH=CH{R}'}}\,\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} \text{Hot alkaline } \\ \,\,KMn{{O}_{4}} \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{[O]}}}\,RCOOH+{R}'COOH\]
\[\underset{\text{Alkyne}}{\mathop{R-C\equiv C-{R}'}}\,\underset{(ii){{H}_{2}}O}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{(i){{O}_{3}}}}}\,R-COOH+{R}'COOH\]
(v) The Arndt-Eistert synthesis
\[R-\underset{O}{\mathop{\underset{|\,|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-Cl\,\,\,\,+C{{H}_{2}}{{N}_{2}}\to R-\underset{O}{\mathop{\underset{|\,|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-CH{{N}_{2}}\underset{A{{g}_{2}}O}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}O}}}\,\]
\[R-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\]
(vi) From acid amides
\[\underset{\text{Amide}}{\mathop{RCON{{H}_{2}}}}\,+{{H}_{2}}O\underset{\text{or }Alkali}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{\text{Acid}}}}\,\underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{RCOOH}}\,+N{{H}_{3}}\]
\[\underset{\text{Amide}}{\mathop{RCON{{H}_{2}}}}\,+\underset{\text{Nitrous acid}}{\mathop{HN{{O}_{2}}}}\,\to RCOOH+{{N}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
