Notes - Important Terms and Classification of Animals
Category : NEET
Important Terms And Classification Of Animals
Outline Classification of Animal kingdom.
The animal kingdom is subdivided into two sub-kingdoms, namely Protozoa and Metazoa.
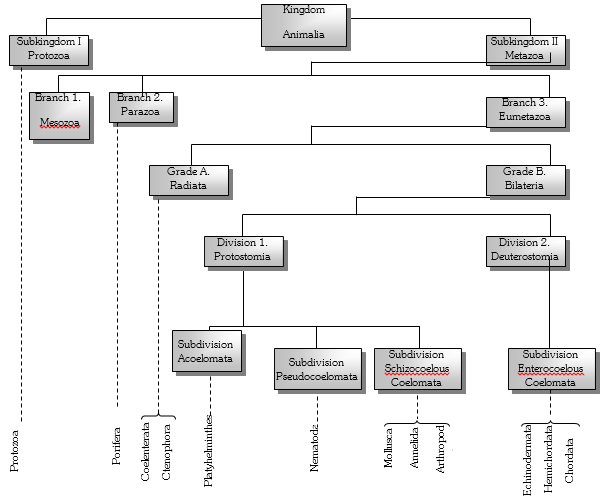
Subkingdom 1. Protozoa : It includes microscopic, unicellular animals. It contains a single Phylum called protozoa. e.g. Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium etc.
Subkingdom 2. Metazoa : This sub kingdom includes multicellular animals. e.g. Porifera to Chordata. The subkingdom Metazoa is divided into three branches, namely Mesozoa, Parazoa and Eumetazoa.
Branch 1. Mesozoa : It is intermediate between Protozoa and Metazoa. It includes endoparasitic animals. e.g. Dicyema, Rhopalura etc.
Branch 2. Parazoa : It includes sponges.
Branch 3. Eumetazoa : It includes true multicellular organisms. They have organ and organ system grade of organization. e.g. Coelenterata to Chordata. Eumetazoa is further divided into two grades, namely Radiata and Bilateria.
Grade A. Radiata : It includes radially symmetrical animals. e.g. Coelenterata.
Grade B. Bilateria : It includes bilaterally symmetrical animals. e.g. Platyhelminthes to Chordata The grade Bilateria is further divided into two divisions namely proterostomia and deuterostomia.
Division 1. Proterostomia : In this group of animals, the blastopore develops into the mouth. e.g. It is further divided into 3 sub division.
Sub division 1. Acoelomata: In this group of animals, a coelom (Cavity lying between the gut and the body wall) is absent. e.g. Platyhelminthes
Sub division 2. Pseudocoelomata: In this group of animals, a false coelom (cavity not lined with coelomic epithelium) is present. e.g. Aschelminthes or Nematoda.
Sub division 3. Schizocoelous Coelomata : In this group, a true coelom is present. e.g. Annelida to chordata.
Division 2. Deuterostomia : In this group of animals, the blastopore develops into the anus. It consist of one sub division.
Sub division 1. Enterocoelous coelomata : Coelom is enterocoel which originates as pouches of embryonic gut (archenteron)
(i) Character of Non Chordata (Invertebrates) : The animals which lack a notochord are called invertebrates. e.g. Amoeba, sponges, Hydra, worms, insects, etc., Invertebrates are characterised by the following salient features ?
(1) The vertebral column is absent.
(2) the nerve cord is solid in nature.
(3) The nerve cord is present on the ventral side and never on the dorsal side.
(4) When alimentary canal is present, it lies dorsal to the nerve cord.
(5) Invertebrates may be acoelomate or pseudocoelomate or true coelomate.
(6) They have either asymmetry or radial symmetry or bilateral symmetry.
(7) The circulatory system is open type or closed type.
(8) They exhibit all possible type of reproduction.
The invertebrates are grouped into about 30 phyla. These phyla are of two types, namely major phyla and minor phyla.
(a) Major Phyla : (1) Protozoa (2) Porifera (3) Coelenterata (4) Platyhelminthes (5) Aschelminthes (6) Annelida (7) Arthropoda (8) Mollusca, and (9) Echinodermata.
(b) Minor Phyla : (1) Mesozoa (2) Nemertinea (3) Endoprocta (4) Acanthocephala (5) Rotifera (6) Gastrotricha (7) Kinorhyncha (8) Nematomorpha (9) Ectoprocta (10) Brachiopods (11) Phoronida (12) Chaetognatha (13) Priapulida (14) Sipunculida (15) Echiuroidea (16) Pogonophora etc.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
