Combination of Metallic Rods
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) Series combination : Let n slabs each of cross-sectional area A, lengths \[{{l}_{1}},\,{{l}_{2}},\,{{l}_{3}},......{{l}_{n}}\] and conductivities \[{{K}_{1}},\,{{K}_{2}},\,{{K}_{3}}......{{K}_{n}}\] respectively be connected in the series
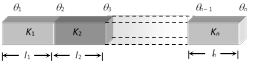
(i) Heat current : Heat current is the same in all the conductors.i.e., \[\frac{Q}{t}={{H}_{1}}={{H}_{2}}={{H}_{3}}.........={{H}_{n}}\]
\[\frac{{{K}_{1}}A({{\theta }_{1}}-{{\theta }_{2}})}{{{l}_{1}}}=\frac{{{K}_{2}}A({{\theta }_{2}}-{{\theta }_{3}})}{{{l}_{2}}}\]\[=\frac{{{K}_{n}}A({{\theta }_{n-1}}-{{\theta }_{n}})}{{{l}_{n}}}\]
(ii) Equivalent thermal resistance : \[R={{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}+.....{{R}_{n}}\]
(iii) Equivalent thermal conductivity : It can be calculated as follows
From \[{{R}_{S}}={{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}+{{R}_{3}}+...\]
\[\frac{{{l}_{1}}+{{l}_{2}}+...{{l}_{n}}}{{{K}_{s}}}=\frac{{{l}_{1}}}{{{K}_{1}}A}+\frac{{{l}_{2}}}{{{K}_{2}}A}+....+\frac{{{l}_{n}}}{{{K}_{n}}A}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[{{K}_{s}}=\frac{{{l}_{1}}+{{l}_{2}}+......\,{{l}_{n}}}{\frac{{{l}_{1}}}{{{K}_{1}}}+\frac{{{l}_{2}}}{{{K}_{2}}}+........\frac{{{l}_{n}}}{{{K}_{n}}}}\]
(a) For n slabs of equal length \[{{K}_{s}}=\frac{n}{\frac{1}{{{K}_{1}}}+\frac{1}{{{K}_{2}}}+\frac{1}{{{K}_{3}}}+.....\frac{1}{{{K}_{n}}}}\]
(b) For two slabs of equal length, \[{{K}_{s}}=\frac{2{{K}_{1}}{{K}_{2}}}{{{K}_{1}}+{{K}_{2}}}\]
(iv) Temperature of interface of composite bar : Let the two bars are arranged in series as shown in the figure.
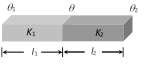
Then heat current is same in the two conductors.
i.e., \[\frac{Q}{t}=\frac{{{K}_{1}}A({{\theta }_{1}}-\theta )}{{{l}_{1}}}=\frac{{{K}_{2}}A(\theta -{{\theta }_{2}})}{{{l}_{2}}}\]
By solving we get \[\theta =\frac{\frac{{{K}_{1}}}{{{l}_{1}}}{{\theta }_{1}}+\frac{{{K}_{2}}}{{{l}_{2}}}{{\theta }_{2}}}{\frac{{{K}_{1}}}{{{l}_{1}}}+\frac{{{K}_{2}}}{{{l}_{2}}}}\]
(a) If \[{{l}_{1}}={{l}_{2}}\] then \[\theta =\frac{{{K}_{1}}{{\theta }_{1}}+{{K}_{2}}{{\theta }_{2}}}{{{K}_{1}}+{{K}_{2}}}\]
(b) If \[{{K}_{1}}={{K}_{2}}\] and \[{{l}_{1}}={{l}_{2}}\] then \[\theta =\frac{{{\theta }_{1}}+{{\theta }_{2}}}{2}\]
(2) Parallel Combination : Let n slabs each of length l, areas \[{{A}_{1}},{{A}_{2}},{{A}_{3}},.....{{A}_{n}}\] and thermal conductivities \[{{K}_{1}},{{K}_{2}},{{K}_{3}},.....{{K}_{n}}\] are connected in parallel then
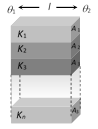
(i) Equivalent resistance : \[\frac{1}{{{R}_{s}}}=\frac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\frac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+\frac{1}{{{R}_{3}}}+.....\frac{1}{{{R}_{n}}}\]
For two slabs \[{{R}_{s}}=\frac{{{R}_{1}}{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}\]
(ii) Temperature gradient : Same across each slab. (iii) Heat current : in each slab will be different. Net heat current will be the sum of heat currents through individual slabs. i.e., \[H={{H}_{1}}+{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{3}}+....{{H}_{n}}\] \[\frac{K({{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}}+.....+{{A}_{n}})\,({{\theta }_{1}}-{{\theta }_{2}})}{l}\]
\[=\frac{{{K}_{1}}{{A}_{1}}({{\theta }_{1}}-{{\theta }_{2}})}{l}+\frac{{{K}_{2}}{{A}_{2}}({{\theta }_{1}}-{{\theta }_{2}})}{l}+...+\frac{{{K}_{n}}{{A}_{n}}\,({{\theta }_{1}}-{{\theta }_{2}})}{l}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[K=\frac{{{K}_{1}}{{A}_{1}}+{{K}_{2}}{{A}_{2}}+{{K}_{3}}{{A}_{3}}+.....{{K}_{n}}{{A}_{n}}}{{{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}}+{{A}_{3}}+.....{{A}_{n}}}\]
(a) For n slabs of equal area \[K=\frac{{{K}_{1}}+{{K}_{2}}+{{K}_{3}}+.....{{K}_{n}}}{n}\]
(b) For two slabs of equal area \[K=\frac{{{K}_{1}}+{{K}_{2}}}{2}\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
