Eddy Current
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
When a changing magnetic flux is applied to a bulk piece of conducting material then circulating currents called eddy currents are induced in the material. Because the resistance of the bulk conductor is usually low, eddy currents often have large magnitudes and heat up the conductor.
(1) These are circulating currents like eddies in water.
(2) Experimental concept given by Focault hence also named as 'Focault current'.
(3) The production of eddy currents in a metallic block leads to the loss of electric energy in the form of heat.
(4) By Lamination, slotting processes the resistance path for circulation of eddy current increases, resulting in to weakening them and also reducing losses causes by them
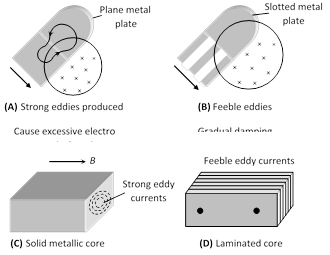
(5) Application of eddy currents : Though most of the times eddy currents are undesirable but they find some useful applications as enumerated below
(i) Dead-beat galvanometer : A dead beat galvanometer means one whose pointer comes to rest in the final equilibrium position immediately without any oscillation about the equilibrium position when a current is passed in its coil.
This is achieved by winding the coil on a metallic frame the large eddy currents induced in the frame provide electromagnetic damping.
(ii) Electric-brakes : When the train is running its wheel is moving in air and when the train is to be stopped by electric breaks the wheel is made to move in a field created by electromagnet. Eddy currents induced in the wheels due to the changing flux oppose the cause and stop the train.
(iii) Induction furnace : Joule's heat causes the melting of a metal piece placed in a rapidly changing magnetic field.
(iv) Speedometer : In the speedometer of an automobile, a magnet is geared to the main shaft of the vehicle and it rotates according to the speed of the vehicle. The magnet is mounted in an aluminium cylinder with the help of hair springs. When the magnet rotates, it produces eddy currents in the drum and drags it through an angle, which indicates the speed of the vehicle on a calibrated scale.
(v) Energy meter : In energy meters, the armature coil carries a metallic aluminium disc which rotates between the poles of a pair of permanent horse shoe magnets. As the armature rotates, the current induced in the disc tends to oppose the motion of the armature coil. Due to this braking effect, deflection is proportional to the energy consumed.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
