Different Measuring Instruments
Category : JEE Main & Advanced

(1) Galvanometer : It is an instrument used to detect small current passing through it by showing deflection. Galvanometers are of different types e.g. moving coil galvanometer, moving magnet galvanometer, hot wire galvanometer. In dc circuit usually moving coil galvanometer are used.
(i) It's symbol : ![]() where G is the total internal resistance of the galvanometer.
where G is the total internal resistance of the galvanometer.
(ii) Full scale deflection current : The current required for full scale deflection in a galvanometer is called full scale deflection current and is represented by \[{{i}_{g}}\].
(iii) Shunt : The small resistance connected in parallel to galvanometer coil, in order to control current flowing through the galvanometer is known as shunt.
Merits and demerits of shunt
| Merits of shunt | Demerits of shunt |
| To protect the galvanometer coil from burning | Shunt resistance decreases the sensitivity of galvanometer. |
| It can be used to convert any galvanometer into ammeter of desired range. |
(2) Ammeter : It is a device used to measure current and is always connected in series with the 'element' through which current is to be measured.
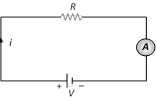
(i) The reading of an ammeter is always lesser than actual current in the circuit.
(ii) Smaller the resistance of an ammeter more accurate will be its reading. An ammeter is said to be ideal if its resistance r is zero.
(iii) Conversion of galvanometer into ammeter : A galvanometer may be converted into an ammeter by connecting a low resistance (called shunt S) in parallel to the galvanometer G as shown in figure.
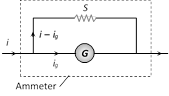
(a) Equivalent resistance of the combination \[=\frac{GS}{G+S}\]
(b) G and S are parallel to each other hence both will have equal potential difference i.e. \[{{i}_{g}}G=(i-{{i}_{g}})S\]; which gives
Required shunt \[S=\frac{{{i}_{g}}}{\mathbf{(}i-{{i}_{g}}\mathbf{)}}G\]
(c) To pass nth part of main current (i.e. \[{{i}_{g}}=\frac{i}{n}\]) through the galvanometer, required shunt \[S=\frac{G}{\mathbf{(}n-\mathbf{1)}}\].
(3) Voltmeter : It is a device used to measure potential difference and is always put in parallel with the 'circuit element' across which potential difference is to be measured.
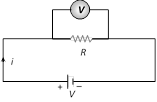
(i) The reading of a voltmeter is always lesser than true value.
(ii) Greater the resistance of voltmeter, more accurate will be its reading. A voltmeter is said to be ideal if its resistance is infinite, i.e., it draws no current from the circuit element for its operation.
(iii) Conversion of galvanometer into voltmeter : A galvanometer may be converted into a voltmeter by connecting a large resistance R in series with the galvanometer as shown in the figure.
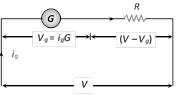
(a) Equivalent resistance of the combination \[=G+R\]
(b) According to ohm's law \[V={{i}_{g}}(G+R);\] which gives Required series resistance \[R=\frac{V}{{{i}_{g}}}-G=\left( \frac{V}{{{V}_{g}}}-\mathbf{1} \right)\,G\]
(c) If \[{{n}^{th}}\] part of applied voltage appeared across galvanometer (i.e. \[{{V}_{g}}=\frac{V}{n}\]) then required series resistance \[R=\mathbf{(}n-\mathbf{1)}\,G\].
(4) Wheatstone bridge : Wheatstone bridge is an arrangement of four resistance which can be used to measure one of them in terms of rest. Here arms AB and BC are called ratio arm and arms AC and BD are called conjugate arms
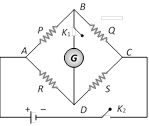
(i) Balanced bridge : The bridge is said to be balanced when deflection in galvanometer is zero i.e. no current flows through the galvanometer or in other words \[{{V}_{B}}={{V}_{D}}\]. In the balanced condition \[\frac{P}{Q}=\frac{R}{S}\], on mutually changing the position of cell and galvanometer this condition will not change.
(ii) Unbalanced bridge : If the bridge is not balanced current will flow from D to B if \[{{V}_{D}}>{{V}_{B}}\] i.e. \[({{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{D}})<({{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}})\] which gives \[PS>RQ\].
(iii) Applications of wheatstone bridge : Meter bridge, post office box and Carey Foster bridge are instruments based on the principle of wheatstone bridge and are used to measure unknown resistance.
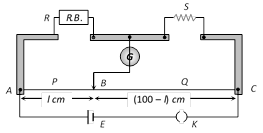
(5) Meter bridge : In case of meter bridge, the resistance wire AC is 100 cm long. Varying the position of tapping point B, bridge is balanced. If in balanced position of bridge \[AB=l,\,BC(100-l)\] so that \[\frac{Q}{P}=\frac{(100-l)}{l}\]. Also \[\frac{P}{Q}=\frac{R}{S}\]\[\Rightarrow \]\[S=\frac{(100-l)}{l}R\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
