Alternating Quantities (i or V)
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) An alternating quantity (current i or voltage V) is one whose magnitude changes continuously with time between zero and a maximum value and whose direction reverses periodically.
(2) Some graphical representation for alternating quantities
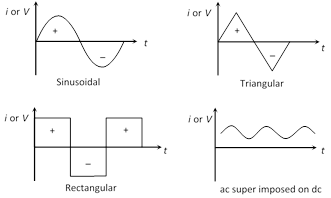
(3) Equation for i and V : Alternating current or voltage varying as sine function can be written as
\[i={{i}_{0}}\,\sin \omega t={{i}_{0}}\sin \,2\pi vt={{i}_{0}}\sin \frac{2\pi }{T}t\]
and \[V={{V}_{0}}\sin \omega t={{V}_{0}}\sin 2\pi \nu t={{V}_{0}}\sin \frac{2\pi }{T}t\]
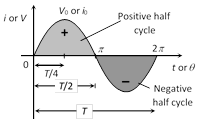
where \[i\] and \[V\] are Instantaneous values of current and voltage,
\[{{i}_{0}}\] and \[{{V}_{0}}\] are peak values of current and voltage
\[\omega =\] Angular frequency in rad/sec, \[v=\] Frequency in Hz and \[T=\]time period
(i) The time taken to complete one cycle of variations is called the periodic time or time period.
(ii) Alternating quantity is positive for half the cycle and negative for the rest half. Hence average value of alternating quantity (i or V) over a complete cycle is zero.
(iii) The value of alternating quantity is zero or maximum \[2v\] times every second. The direction also changes \[2v\] times every second.
(iv) Generally sinusoidal waveform is used as alternating current/voltage.
(v) At \[t=\frac{T}{4}\] from the beginning, i or V reaches to their maximum value.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
