Standard Forms of Equation of a Circle
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) General equation of a circle : The general equation of a circle is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\] where \[g,f,c\] are constant.
(i) Centre of the circle is\[(g,\text{ }f)\]. i.e., (\[-\frac{1}{2}\] coefficient of \[x,\,\,-\frac{1}{2}\] coefficient of \[y\]).
(ii) Radius of the circle is \[\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}\].
Nature of the circle
(i) If \[{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c>0\], then the radius of the circle will be real. Hence, in this case, it is possible to draw a circle on a plane.
(ii) If \[{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c=0\], then the radius of the circle will be zero. Such a circle is known as point circle.
(iii) If \[{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c<0\], then the radius \[\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}\] of the circle will be an imaginary number. Hence, in this case, it is not possible to draw a circle.
The condition for the second degree equation to represent a circle : The general equation \[a{{x}^{2}}+2hxy+b{{y}^{2}}\] \[+2gx+2fy+c=0\] represents a circle iff
(i) \[a=b\ne 0\]
(ii) \[h=0\]
(iii) \[\Delta =abc+2hgf-a{{f}^{2}}-b{{g}^{2}}-c{{h}^{2}}\ne 0\]
(iv) \[{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-ac\ge 0\]
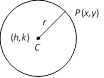
(2) Central form of equation of a circle : The equation of a circle having centre \[(h,\text{ }k)\] and radius \[r\] is
\[{{(x-h)}^{2}}+{{(y-k)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]
If the centre is origin, then the equation of the circle is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]
(3) Circle on a given diameter : The equation of the circle drawn on the straight line joining two given points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},\,{{y}_{2}})\] as diameter is
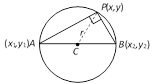
\[(x-{{x}_{1}})(x-{{x}_{2}})+(y-{{y}_{1}})(y-{{y}_{2}})=0\]
(4) Parametric co-ordinates
(i) The parametric co-ordinates of any point on the circle \[{{(x-h)}^{2}}+{{(y-k)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\] are given by\[(h+r\,\cos \,\theta ,\,k+r\,\sin \,\theta )\], \[(0\le \theta <2\pi )\].
In particular, co-ordinates of any point on the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\] are \[(r\,\cos \,\theta ,\,r\,\sin \,\theta ),\,\,(0\le \theta <2\pi )\].
(ii) The parametric co-ordinates of any point on the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\] are \[x=-g+\sqrt{({{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c})\,\,\cos \,\theta \] and \[y=-f+\sqrt{({{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c)}\,\,\sin \,\theta ,\,\] \[(0\le \theta <2\pi )\]
(5) Equation of a circle under given conditions
(i) The equation of the circle through three non-collinear points \[A\,({{x}_{1}},\,{{y}_{1}}),\,B\,({{x}_{2}},\,{{y}_{2}}),\,\,C\,({{x}_{3}},\,{{y}_{3}})\,\]is
\[\left| \,\,\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}} & x & y & 1 \\ x_{1}^{2}+y_{1}^{2} & {{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{1}} & 1 \\ x_{2}^{2}+y_{2}^{2} & {{x}_{2}} & {{y}_{2}} & 1 \\ x_{3}^{2}+y_{3}^{2} & {{x}_{3}} & {{y}_{3}} & 1 \\ \end{array}\,\, \right|\,=\,0\]
(ii) From given three points taking any two as extremities of diameter of a circle \[S=0\] and equation of straight line passing through these two points is \[L=0\]. Then required equation of circle is \[S+\lambda L=0,\] where \[\lambda \] is a parameter, which can be found out by putting third point in the equation.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
