Banking and Banking Structure - Legal Aspects
Category : Banking
DEFINITION OF BANK AND BANKING
After independence, steps were taken to regulate the banking and banking business in India. Government brought in a law in this regard, wherein banking and banking business has been defined. This law became an Act and called the Banking Regulation Act, (BR Act), 1949.
As per the Act, Section 5(c) provides that 'a banking company is a company which transacts the business of banking in India.' Further, Section 5(b) of the Act defines banking business as, 'accepting, for the purpose of lending or investment of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdrawable by cheque, draft, order or otherwise.
STRUCTURE OF BANKING IN INDIA
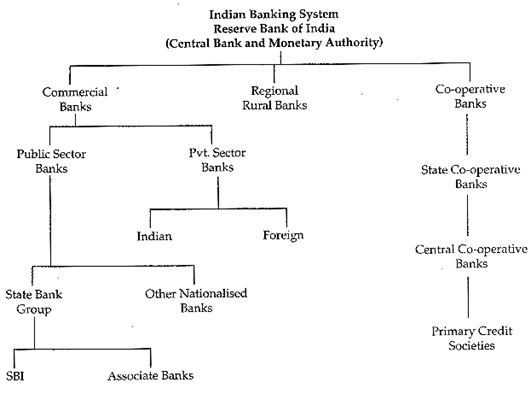
Reserve Bank of India (RBI):
The country had no central bank prior to the establishment of the RBI. The RBI is the supreme monetary and banking authority in the country and controls the banking system in India. It is called the Reserve Bank as it keeps the reserves of all commercial banks.
Development banks and other financial institutions:
A development bank is a financial institution, which provides long term funds to the industries for development purposes. These include banks like Development Credit Bank, IDBL ICICI, IFCI etc. State level institutions like SFC's SIDC's etc. They also include investment institutions like UTI, LIC, and GIC etc.
Long-term agriculture credit is provided by the Land Development Banks. The funds of the RBI meant for the agriculture sector actually pass through SCBs and CCBs. Originally based in rural sector, the cooperative credit movement has now spread to urban areas also and there are many urban cooperative banks coming under SCBs.
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS FOR SETTING UP NEW BANKS AND BRANCH AUTHORIZATION POLICY
Guidelines / Directives
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
