Origin and Development of Banking in India
Category : Banking
Origin and Development of Banking in India
A bank is a financial institution that provides banking and other financial services to their customers. A bank is generally understood as an institution which provides Fundamental Banking Services such as accepting deposits and providing loans.
History of Banking in India
Banking system has been existing in India since ancient times. Though it was not in organised form before the arrival of Britishers, various banking activities were performed. After the arrival of Britishers in 17th century foreign banking system started declining. Mayser's Alexander and company established the first European bank The Bank of Hindustan in 1770.
The development of Banking system in India can be understood with the help of following choronology. We can summarise the origin of banking in India in the following way,
Early Phase of Indian Banks before 1935
The pre-independence period was largely characterised by the existence of private banks organized as joint stock companies. Most banks were small and had private shareholding of the closely held variety. They were largely localized and many of them failed.
Organization of RBI
Banking crisis during 1913-1917 and failure of 588 banks in various parts of the country underlined the need for regulating and controlling the commercial banks. RBI was established as regulator of banking system of India. It was established in 1935. The Head Office of the RBI was established in Calcutta (now Kolkata, but was moved to Bombay (now Mumbai) in 1937.
The general functions of the banks are as follows
Banking Sector Reforms till 1991
In 1955, government nationalised the Imperial Bank of India and gave the name 'State Bank of India' to act as the principal agent of the RBI and to handle banking transactions of the Union Government and State Governments all over the country.
7 banks owned by the Princely states were nationalised in 1959 and they became subsidiaries of the State Bank of India. In 1969, 14 commercial banks in the country were nationalised.
In the phase of banking sector reforms, 7 more banks were nationalised in 1980. With this, 80% of the banking sector in India came under the government ownership.
New Phase of Indian Banking System, Reforms after 1991
Nationalisation of Banks
The nationalisation of commercial banks took place with an aim to achieve Social Welfare, Controlling Private Monopolies, Expansion of Banking, Reducing Regional Imbalance, Priority Sector Lending and Developing Banking Habits. In order to have more control over banks, on 19th July, 1969 Mrs Indira Gandhi, the then Prime Minister nationalised 14 large commercial banks whose reserves were more than ` 50 crore. Following is the list of banks, -which got nationalized at that time
On 15th April, 1980 the banks with more than ` 200 crore of reserves got nationalised.
Those six banks which got nationalised are the following
Later on, in the year 1993, the government merged New Bank of India with Punjab National Bank. It was the only merger between nationalised banks. Now, total nationalised banks were 19.
Indian Banking Structure
An outline of the Indian banking structure may be presented as follows
Reserve bank of India
(Central Bank and Supreme Monltary Authority)
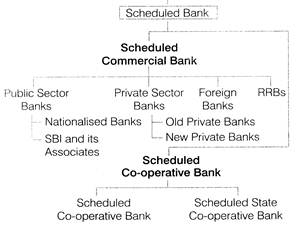
Scheduled Banks
Scheduled banks are those banks whose minimum paid up capital and reserve amounts to ` 25 lakh. These bank have to submit details of their activities to the Reserve Bank of India every week. All Indian and foreign commercial banks, RRBs and co-operative banks are scheduled banks.
Non-Scheduled Banks
Non-scheduled banks are depository or lending institutions that do not meet the Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India Act.
These banks may be legal entities, but they do not have procedural endorsement of the government. The bank has to pay compulsorily a reserve capital of ` 5 lakh to the RBI and this capital must be maintained throughout their operational period. It is an important condition for Non-scheduled bank.
Tit – Bits
Commercial Banks
This is a financial institution providing services for businesses, organisations and individuals. Services include offering current, deposit and saving accounts as well as giving out loans to businesses. A commercial bank is defined as a bank whose main business is deposit-taking and making loans. Commercial bank may be Scheduled Commercial and Non-Scheduled Commercial Bank.
Functions of Commercial Banks
The main functions of commercial banks are as follows
(i) Receive Deposits The most important activity of a Commercial Bank is to mobilise deposits from the public. Depending upon the nature of deposits, funds deposited with bank also earn interest. Thus, deposits with the bank grow along with the interest earned. Some of the important deposit accounts are as given below.
(ii) Current Account Current account is a type of deposit account that caters to the need of professionals and businessmen alike. These deposits are the most liquid deposits and there are no limits for numbers of transaction or amount of transactions in a day.
(iii) Saving Account It is generally opened in bank by salaried persons or by the persons who have a fixed regular income. This facility is also given to students, senior citizens, pensioners and so on. The saving account holder is allowed to withdraw money from the account as and when required. The interest which is given on saving accounts is sometime attractive, but often nominal.
(iv) Fixed Account A deposit of money that pays higher interest than a savings account, but imposes conditions on the amount, frequency, and/or period of withdrawals is called fixed account.
Difference between Saving Account and Current Account
|
Basis of Difference |
Savings Account |
Current Account |
|
Purpose |
To encourage saving |
Many transaction |
|
Ideal for |
Salaried person |
Business person |
|
Minimum Amount |
Less amount |
Higher amount(depending on the bank) |
|
Interest Rates |
4% - 6% |
Normally, no interest is paid |
|
Overdraft |
Not Allowed |
Allowed |
(v) Cash Credit Account It can be opened as per terms and conditions of sanction of given credit limits. The rules prescribed for the current accounts is applicable to Cash Credit accounts, in addition to the sanctioned terms and conditions.
(vi) Recurring Deposit Account In banking terminology, the term recurring deposit refers to the periodic placement of a fixed sum of funds with a bank or financial institution into a special term account, with a specified tenure, generally between 1 and 5 years.
At the end of the tenure, the funds with accrued interest are typically withdrawn by the depositor.
(vii) To Lend Money Another important function of a Commercial Bank is to grant loans and advances. Such loans and advances are given to the public and business community at a higher rate of interest than allowed by banks on various deposit accounts.
Types of loans of commercial bank are given below
(viii) Agency Functions Agency functions include the following
(ix) Miscellaneous Functions Issuing letters of credit, travellers cheques, circular notes, etc.
Non-Performing Asset (NPA)
It is a classification used by financial institutions that refers to loans that are in jeopardy of default. Once The borrower has failed to make interest or principal payments for 90 days the loan is considered to be a Non-performing asset. (Also known as 'non-performing loan’,) Nonperforming assets are problematic for financial institutions since the depend on interest payments for income.
Private Banks
Private Banks are banks owned by either an individual or a general partner(s) with limited partner(s). But licence is provided by Reserve bank of India.
Private Sector Banks
|
Bank |
Place |
|
Kotak Mahindra Bank, (1985) |
Mumbai |
|
ICICI Bank, (1994) |
Vadodara |
|
AXIS Bank, (1994) (UTI renamed in 30th July, 2007) |
Ahmedabad |
|
Indusland Bank, (1994) |
Pune |
|
Global Trust Bank, (1994) |
Secunderabad |
|
HDFC Bank, (1995) |
Mumbai |
|
Times Bank, (1995) |
Faridabad |
|
Centurion Bank, (1995) |
Panji |
|
Bank of Punjab, (1995) |
Chandigarh |
|
Development Credit Bank Ltd. (1995) |
Mumbai |
|
Yes Bank, (2004) |
Mumbai |
|
Bandhan Bank, (2015) |
Kolkata |
|
IDFC Bank, (2015) |
Mumbai |
Types of Banks on the Basis of Function
Following are the types of banks classified on the basis of their functions.
Agricultural Banks
An agricultural bank may, in particular undertake the following types of business
(i) granting short term credit to buy seeds, fertilizers and other inputs, and
(ii) granting long term credit to purchase land, to make permanent improvements on land, to purchase agricultural machinery and equipment, etc,
Post Office Saving Banks
It is a bank which accepts deposit of small amount only and provide the withdrawal facilities to their customers. ATM facility is also available in this bank.
Foreign Exchange Banks
Foreign Exchange Bank is the bank which is involved in sale and purchase of the foreign exchange bill and exchange of one currency for another or the conversion at one currency into another currency.
The foreign exchange banks work through financial institutions and it operates on several levels. Behind the scenes banks turn to a smaller number of financial firms known as 'dealers/ who are actively involved in large quantities of foreign exchange trading. Payment of International Loans, Export-Import of securities and forward exchange trade are also done by these banks.
Foreign Banks
These banks are registered and have their headquarters in a foreign country but operate their branches in our country.
Important Foreign Bank in India
|
Name of Bank |
Country of Incorporation |
|
AB Bank Ltd. |
Bangladesh |
|
KBC Bank NV |
Belgium |
|
Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Ltd. |
China |
|
Deutsche Bank |
Germany |
|
HSBC Ltd |
Hong Kong |
|
The Royal Bank of Scotland NV |
Netherlands |
|
Doha Bank |
Qatar |
|
DBS Bank Ltd. |
Singapore |
|
Shinhan Bank |
South Korea |
|
Korea Exchange Bank |
South Korea |
|
Bank of Ceylon |
Sri Lanka |
|
UBS AG |
Switzerland |
|
Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank Ltd. |
UAE |
|
Barclays Bank Pie. |
United Kingdom |
|
Standard Chartered Bank |
United Kingdom |
|
American Express Banking Corporation |
USA |
|
Bank of America |
USA |
Co-operative Banks
Co-operative banks operate in both urban and rural areas. All banks registered under the Co-operative Societies Act, 1912 are considered co-operative banks.
Commercial banks, are driven by profit while co-operative banks work on a "no profit, no loss" basis. These are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 and Banking Laws (Application to Co-operative Societies) Act, 1965.
There are two types of co-operative banks.
(i) State Co-operative Banks SCBs mean the principal co-operative society in a state, the primary object of which is the financing of other co-operative societies in the state.
(ii) District/Central Urban Co-operative Banks UCBs are registered under the Co-operative Societies Act of the respective State Governments. UCBs having a multi-state presence are registered under the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act and are regulated by the Central Government.
Development Banks
Development banks are specialized financial institutions. To promote economic development, development banks provide medium term and long term loans to the entrepreneurs at relatively low rate of interest rates.
Some examples of development banks in India are Industrial Development Banks of India (IDBI), Industrial Financial Corporation of India (IFCI), etc.
Retail Banks
A retail bank is a bank that works with customers offering basic banking services. Examples include savings banks, savings and loan associations, and recurring and fixed deposits. Products and service include safe deposit boxes, checking and savings accounting, certificates of deposit (CDs), mortgages, personal, consumer and car loans.
Central Banks
Central banks are bankers' banks. They guarantee stable monetary and financial policy from country to country and play an important role in the economy of the country.
Typical functions include implementing monetary policy, managing foreign exchange and gold reserves, making decisions regarding official interest rates, acting as banker to the government and other banks, and regulating and supervising the banking industry.
These banks buy government debt, have a monopoly on the issuance of paper money, and often act as a lender of last resort to commercial banks.
It controls and coordinates currency and credit policies of any country. The Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of India.
Investment Banks
An investment bank is a financial institution that assists individuals, corporations and governments in raising capital by underwriting and/or acting as the client's agent in the issuance of securities. An investment bank may also assist companies involved in mergers and acquisitions, and provide ancillary services such as market making, trading of derivatives, fixed income instruments, foreign exchange, commodities, and equity securities.
Investment banks aid companies in acquiring funds and they provide advice for a wide range of transactions.
Online Banks
Online banking gives you the ability to manage your money online - over the internet - so you do not have to visit a bank branch. Operate entirely online - there are no physical branch locations to talk with a teller or personal banker. Many brick-and-mortar banks also offer online services, such as the ability to view accounts and pay bills online, but internet only banks are different: they often offer competitive rates on saving accounts and they're likely to offer free checking.
Types of Banking in India on the Basis of the Organisation
Branch Banking
Branch banking is the most common type of banking and still an integral part of Indian banking system as most Indians still believe in cash transactions and prefer to visit banks in person for routine banking operations. Banks branches are the face of the banks where customers can visit and talk to the officials for pelting better insights into new policies, investment schemes, other banking services, etc.
Unit Banking
Unit banking, which originated in US, is a limited way of banking where banks operate only from a single branch (or a few branches in the same area) taking care of local community.
Mixed Banking
When the banks undertake activities of commercial and investment banking together; it is called mixed banking. Mixed banking promotes rapid industrialisation.
Chain Banking
Chain banking system is involved when a group of persons came together to own and control three or more independently chartered banks. Individuals secure enough stocks to get the controlling interest in the banking corporations involved. The management can also be established via a board of directors.
Wholesale Banking
Wholesale banking involves banking services for high net-worth clients like corporate, commercial banks, mid-size companies, etc,
The services which come under the net of wholesale banking involves wholesaling, underwriting, market making, consultancy, mergers and acquisitions, joint ventures, fund management, etc.
Relationship Banking
Relationship banking involves going beyond the normal banking services and understanding customer's needs before offering him any special product,
The knowledge about existing and potential clients is essential for all banks.
Correspondent Banking
Correspondent banks are financial institutions that provide banking or financial services on. behalf of other equal or unequal financial institution.
These are used to conduct banking operations in foreign countries as the domestic banks have limited access to foreign markets and cannot directly reach clients.
The services which come under the blanket of correspondent banking are cash/fund management; international fund transfers, clearance of cheques, drawing of demand drafts, etc.
Rural Banking
Rural banking has become integral to the Indian financial markets with a majority of Indian population still living in rural or semi-urban areas.
Universal Banking
Universal banking is a system of banking under which big banks undertake a variety of banking services like commercial banking, investment banking, mutual funds, merchant banking, insurance, etc.
In simple words, Universal Banking means that Financial Institutions (FIs) and Banks are allowed to undertake all kinds of activity of banking, financing and related businesses.
Narrow Banking
The Narrow Banking is very much an antonym to the Universal Banking. Narrow Banking means Narrow in the sense of engagement of funds and not in activity. The Tarapore Committee had recommended that to bring down the Non-Performing Assets (NPAs), the incremental sources of the banks (called narrow banks) should be restricted only to investments in Government Securities. Thus, Tarapore Committee is best known for giving Concept of Narrow Banking as a solution to the problem of Non-Performing Assets.
Social Banking
The concept of social banking was to provide banking for the poor population, working for their developmental needs, providing them with easy formal credit, minimal requirements to open accounts, ease of access and friendly staff etc.
Virtual Banking
Virtual or internet banking is a system where all the transactions of the bank are done online and there are no physical branches of the banks.
India's Key Banks State Bank of India
On the recommendation of All India Rural Credit Survey Committee, Imperial Bank was nationalised to become State Bank of India on 1st July, 1955.

Shareholding
Government of India held around 62% equity shares in SBI. Over 800000 individual shareholders hold approx. 5.7% of its shares. Life Insurance Corporation of India is the largest non-promoter shareholder in the company with 10.9% shareholding.
|
Shareholders |
Shareholding |
|
Promoters Government of India |
62.31 % |
|
Insurance Companies |
11.90% |
|
Foreign Institutional Investors |
09.79% |
Functions of State Bank of India
The functions of SBI can be grouped under two categories, viz., the Central banking functions and Ordinary banking functions. The SBI acts as an agent of the RBI at the places where the RBI has no branch.
Accordingly, it renders the following functions
General/Ordinary Banking Functions
Besides the above specialized functions, the SBI renders the following functions
SBI Agriculture Loan
SBI provides SBI Agriculture loan (term loan) for asset (bullocks, farm machinery, sheep, etc.) purchase as well as asset creation (poultry, orchard development, dairy development, etc.) which are connected with activities in rural areas.
The rate of interest varies from 8.5% to 12.75% depending on the loan amount and in the extreme cases of very high loan amounts, credit risk assessment is required. Repayment period varies from 5-15 years and is based on the income generation of activity for which loan was taken
Merging of SBI and Mahila Bank
The Union Cabinet, on 15th June, 2016, approved the merger of five associate banks as well as Bharatiya Mahila Bank with State Bank of India. It is the first move to consolidate the country's struggling Public Sector Banks. The country's largest lender, State Bank of India (SBI), has decided to merge its five associate Public Sector Banks (PSBs) and the Bharatiya Mahila Bank (BMB) with itself.
In this regard, the SBI has informed the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) that it is seeking in-principle approval for acquistior from the Union government.
5 subsidiary banks are
Associate Banks of SBI and their Merger
In 1959, the government passed the State Bank of India (Subsidiary Banks) Act. Under this Act, 8 SBI subsidiaries were made. Three of them had already merged with SBI. State Bank of Saurashtra, State Bank of lndore (founded in 1920). In 1963, SBI merged State Bank of Jaipur (founded in 1943) and State Bank of Bikaner (founded in 1944) to form State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur. State Bank of Saurshtra merged with SBI in 2008. Then in 2010, the State Bank of lndore (founded in 1920) also merged with SBI leaving the associate banks of SBI to 5 in number.
At present, the SBI has 14 regional hubs and 57 Zonal Offices that are located at important cities throughout India. It has more than 17000 branches in India presently, of which 9851 (66%) are in Rural and Semi-urban areas. It has 190 overseas branches spread over 36 countries.
Other Important Banks in India
United Bank of India

Headquarters Kolkata, West Bengal, India
Founded 1950, India
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line The Bank that begins with 'U'
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by UBI are
UCO Bank
Headquarters Kolkata
Founded 6 jauanry, 1943
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Honors Your Trust
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by UCO Bank are
Union Bank of India

Headquarters Mumbai
Founded 11 November, 1919
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Good People to Bank With
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Union Bank are
Central Bank of India

Headquarters Mumbai
Founded 21 Decembar, 1911
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Build A Better Life Around Us
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by CBI are
Allahabad Bank

(A Govt. of India Undertaking)
Headquarters Kolkata
Founded 1865
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Tradition of Trust
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Allahabad Bank are
Andhra Bank
![]()
Headquarters Hyderabad
Founded 20 November, 1923
Nationalisation 1980
Punch Line Much More to do with You in Focus
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Andhra Bank are
Bank of Baroda

Headquarters Baroda
Founded 20 July, 1908
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line India's International Bank
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Bank of Baroda are
Bank of India

Headquarters Mumbai
Founded 7 September, 1906
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Relationships Beyond Banking
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Bank of India are
Bank of Maharashtra

Headquarters Pune
Founded 16 September, 1935
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line One Family One Bank
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Bank of Maharashtra is
Canara Bank

Headquarters Bengaluru
Founded 1906
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line It's easy to Change for those who you love; Together we can
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Canara Bank are
Indian Bank
Headquarters Chennai
Founded 5 March, 1907
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Taking Banking Technology to Common man, your tech-friendly bank
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Indian Bank are
Corporation Bank

Headquarters Mangalor
Founded 12 March, 1906
Nationalisation 1980
Punch Line Prosperity for All
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Corporation Bank is
Dena Bank

Headquarters Mumbai
Founded 26 May, 1938
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Trusted Family Bank
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Dena Bank are
Punjab National Bank

Headquarters New Delhi
Founded 1895
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line The Name you can Bank Upon
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by PNB are
Indian Overseas Bank

Headquarters Chennai
Founded 1937
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Good People to Grow with
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Overseas Bank are
Oriental Bank of Commerce
![]()
Headquarters New Delhi
Founded 1943
Nationalisation 1980
Punch Line Where Every Individual is Committed
Punjab and Sindh Bank

Headquarters New Delhi
Founded 24 June, 1908
Nationalisation 1980
Punch Line Where Service is a Way of Life
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by PSB is
Vijaya Bank

Headquarters Bengaluru
Founded 1931
Nationalisation 1980
Punch Line A Friend you can Bank Upon
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Vijaya Bank is
Syndicate Bank

Headquarters Manipal
Founded 1925
Nationalisation 1969
Punch Line Yaur Faithful and Friendly Financial Partner
Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Syndicate Bank are
IDBI Bank
![]()
Headquarters Mumbai
Founded July, 1964
Punch Line Banking for all, not just for big boys, Aao Sochein Bada.
In September 2004, the Reserve Bank of India incorporated IDBI as a 'scheduled bank' under the RBI Act, 1934.
Bharatiya Mahila Bank

Headquarters New Delhi, India
Founded 19 November, 1913
Punch Line Empowering Women, Empowering India
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
