Development Banks
Category : Banking
DEVELOPMENT BANKS
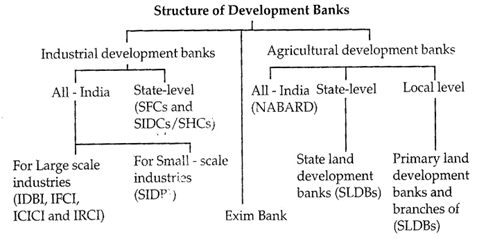

Development banks in India are classified into following four groups;
Industrial Development Banks
They include for example. Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), and Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI).
Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
The IFCI was the first specialised financial institution set up in India to provide term finance to large industries in India. It was established on 1st July, 1948 under the Industrial Finance Corporation Act of 1948.
Objectives of IFCI
The main objective of IFCI is to provide medium and long term financial assistance to large scale industrial undertakings, particularly when ordinary bank accommodation does not suit the undertaking or finance cannot be profitably raised by it from the issue of shares.
Functions of IFCI:
Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI)
Industrial development Bank of India (IDBI) came into being on 1st July, as a Development Institutions under IDBI Act 1964. It is headquartered at Mumbai.
It is regarded as a Public Financial Institution in terms of Companies Act. It continued as DPI till 2004 when it was transferred into a Bank. To transform this into Bank/ Industrial Development Bank Act 2003 was passed.
A new company under the name of Industrial Development Bank of India Ltd. was incorporated as a Govt company under the Companies Act on 27th September, 2004, and thus now it came to be known as IDBI Ltd w.e.f 1st October 2004 but it also worked as a Bank in terms of the Repeal Act.
With effect from 2nd April, 2005, IDBI Bank Ltd was finally amalgamated with IDBI Ltd and was known as IDBI Ltd. It is a Public Sector Bank as government has above 70% shareholding in this Bank.
SIDBI
Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) was set up under an Act of Parliament in 1990. Though it was a wholly owned subsidiary of Industrial Development Bank of India, presently the ownership is held by 33 Government of India owned / controlled institutions. It is headquartered in Lucknow.
Functions:
Agricultural Development Bank:
It includes, for example. National Bank for Agriculture & Rural Development (NABARD).
Role:
Export-Import Development Bank:
It includes, for example, Export-Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank).The Export-Import Bank of India (Exim Bank) is a public sector financial institution created by an Act of Parliament, the Export-import Bank of India Act, 1981. The business of Exim Bank is to finance Indian exports that lead to continuity of foreign exchange for India. The Exim Bank extends term loans for foreign trade.
Housing Development Bank:
It includes, for example. National Housing Bank (NHB). The National Housing Bank (NHB) is a state owned bank and regulation authority in India created on July 8, 1988 under section 6 of the National Housing Bank Act (1987). Its headquarter is in New Delhi. The institution owned by the Reserve Bank of India was established to promote private real estate acquisition. The NHB is regulating and re-financing social housing programs and other activities like research etc. Its vision is promoting inclusive expansion with stability in housing finance market.
MUDRA BANK
Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency Bank (MUDRA Bank) is a new institution set up on 8 April 2015 by the Government of India for development of micro units and refinance of MFIs to encourage entrepreneurship in India and provide the funding to the non-corporate small business sector.
It was announced by the Finance Minister while presenting the Union Budget for FY 2016. MUDRA has a corpus of Rs. 20,000 crore and credit guarantee corpus of Rs. 3,000 crore.
Products and Offerings:
The initial products and schemes under this umbrella have already been created and the interventions have been named 'Shishu', 'Kishor' and Tarun' to signify the stage of growth of the beneficiary micro unit / entrepreneurs.
Shishu: covering loans up to Rs. 50,000/-
Kishor: covering loans above Rs. 50 000/-and up to Rs. 5 lakh
Tarun: covering loans above Rs. 5 lakh and up to Rs. 10 lakh
Indian Postal payment Bank:
The India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) was a Public Limited Company under the Department of Posts with 100% GOI equity.
NBFC (Non-Banking Financial Company)
It is engaged in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of bonds/debentures/ securities issued by Government or local authority or other marketable securities, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance business, chit business but does not include any institution whose principal business is that of agriculture activity, industrial activity, purchase or sale of any goods or providing any services and sale or purchase of immovable property.
Difference between Banks & NBFCs
There is no Ombudsman for hearing complaints against NBFCS. In respect of credit card operations of an NBFC, which is a subsidiary of a bank if a complainant does not get satisfactory response from the NBFC within a maximum period of thirty 30 days from the date of lodging the complaint/ the customer will have the option to approach the Office of the concerned Banking Ombudsman for redressal of his grievances.
Credit Rating Agencies in India
A credit rating agency is a company which rates the debtors on the basis of their ability to pay back the debt in timely manner.
There are three big credit rating agencies inthe world which are -
There are mainly 5 credit rating agencies in
India which are
|
CARE (Credit Analysis and Research) |
CRISIL (Credit Rating Information Services of India Limited) |
ICRA (Investment information and credit rating agency) |
SMERA(SME Rating Agency of India Ltd) |
ONICRA |
|
Founded: 1993 |
Founded: 1987 |
Founded 1991 |
Founded: 2005 |
|
|
Mumbai |
Mumbai |
Gurgaon |
Mumbai |
Gurgaon, India |
|
It is the second- largest credit rating agency in India. |
* CRISIL is the largest credit rating agency in India, with a market share of greater than 60% * CRISIL's majority shareholder is Standard & Poor's. |
* It is a public limited company. *ICRA's majority shareholder is Moody's |
* SMERA is a full service credit rating agency exclusively set up for micro, small and medium enterprises (MSME) in India. |
* It is a private sec- tor agency set up by Onida Finance |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
