Chemical Effects of Electricity
Category : 8th Class
In order to generate electricity there are many methods used, one of them is chemical. Remember batteries, where electricity is generated because of chemical reactions inside cell. Also in conductors like liquids and gases electricity is carried not by electrons as it is in solid constructions(copper, aluminium, etc.), but by ions - molecules with electric charges. Even non distilled water contain enough ions to be conductive. Lets go through several chemical effects of electricity.
Electrolysis: Electrolysis is a decomposition of liquid compound by passing electric current through liquid called electrolyte(salt water, copper sulphate, sulphuric acid). Electrolysis is used very widely in industry like electroplating of metals, refining of copper and extraction of aluminum from ore. To make electrolysis happen there are two conductors used cathode (-) and anode(+).
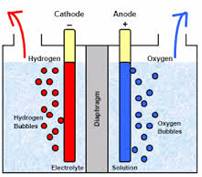
Electroplating: The process of covering a more reactive metal with a less reactive metal with the help of electricity is known as electroplating. Material to be plated should be connected as cathode while anode usually loses material.
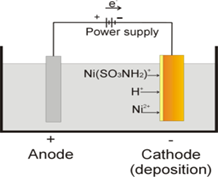
![]() Chemical Cell
Chemical Cell
According to this principal all batteries are generating electric power. Chemical cells converts chemical energy in to electrical. If there are two different conductors(eg. Copper and zinc) placed in electrolyte, electric current starts flowing between electrodes.
Each different pair of electrodes generate different potential. As long as there is an external circuit, electrons can flow through it from one electrode to another. Because zinc tends to lose electrons more readily than copper, zinc atoms in the zinc electrode lose electrons to produce zinc ions. The net result is that zinc metal reacts with copper ions to produce zinc ions and copper metal.
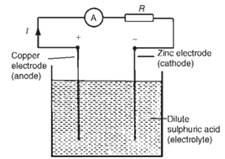
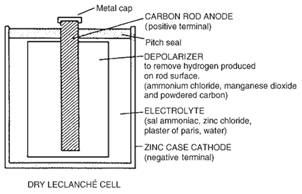
![]() Non Rechargeable Lechlanche Cells
Non Rechargeable Lechlanche Cells
These are cells that generate about 1.5V of EMS, but if falls in continuous use due to polarization of electrode. These cells are better to us for intermittent purposes like torches, bells, indicators etc. These cells are cheap and has a shelf life about 2 years.
There are more dry cell technologies that enables to remain EMF constant for longer times. Ones are Mercury cells. These cells provide 1.3V for longer time than Lechlanche cells.
![]() Rechargeable Cells
Rechargeable Cells
Rechargeable cells are most commonly used today as main factor - the price is becoming acceptable for everyone. And there is another practical approach - these cells can be recharged after use. In other words the conversion of chemical energy to electrical is reversible. There are many types of rechargeable cell technologies. Ones of common are lead-acid and the alkaline cells. These cells are usually used in cars.

![]() If an object contains more protons than electrons, the object is:
If an object contains more protons than electrons, the object is:
(a) Positively charged
(b) Negatively charged
(c) Neutral
(d) All of these
(e) None of these
Answer: (a)
![]() Which one of the following is a conductor?
Which one of the following is a conductor?
(a) Wood
(b) Rubber
(c) Iron
(d) All of these
(e) None of these
Answer: (c)
![]()
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
