Geometry
Learning Objectives
- Understanding Polygons
- Parallelogram
- Rhombus
- Trapezium
- Kite
- Rectangle
- Square
- Practical Geometry
Understanding Polygons
- A polygon is a simple closed curve made up of only line segments.
- A line segment that connects the two non-consecutive vertices of a polygon is called a diagonal.
- A convex polygon is defined as a polygon with all its interior angles less than \[180{}^\circ \]. This means that all the vertices of the polygon will point outwards, away from the interior of the shape.
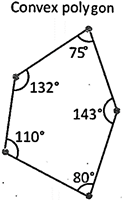
- A concave polygon is defined as a polygon with one or more interior angles greater than \[180{}^\circ \]. It looks like a vertex has been 'pushed in' towards the inside of the polygon.
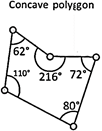
- A regular polygon is both 'equiangular' and ?equilateral?. For example, a square has sides of equal length and angles of equal measure and thus it is a regular polygon. A rectangle is equiangular but not equilateral, so it is a irregular polygon.
Properties of Polygon
- The sum of the measures of the external angles of any polygon is \[360{}^\circ \].
- For a regular polygon,
- Number of sides \[\left( n \right)=360{}^\circ \]/ (measure of an exterior angle)
Or
- Number of sides \[\left( n \right)=360{}^\circ \]/ (\[180{}^\circ \]- measure of an interior angle)
- For a regular polygon,
- Measure of interior angle \[(\theta )=180{}^\circ -\left( 360{}^\circ /n \right)\]
Or
- Measure of interior angle \[(\theta )=180{}^\circ \left( \left( n-2 \right)/n \right)\]
- A polygon having three sides is called a triangle. Similarly a polygon having four sides is called quadrilateral, a polygon having five sides is called pentagon, a polygon having six sides is called hexagon.
- A triangle can never be concave.
- The sum of all interior angles of a triangle is \[180{}^\circ \].
- The sum of all interior angles of a quadrilateral is \[360{}^\circ \].
Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral whose opposite sides are parallel.
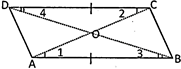
Properties of a parallelogram
- Opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
- Adjacent angles of a parallelogram are supplementary i.e. their sum is equal to \[180{}^\circ \].
- The sum of all interior angles of a parallelogram is \[360{}^\circ \].
- Opposite sides of a parallelogram are parallel (by definition) and so will never intersect.
- Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Rhombus
A rhombus is a quadrilateral whose all sides are equal and opposite sides are parallel.
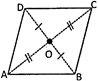
Properties of a Rhombus
- Opposite angles of a rhombus are equal.
- Adjacent angles of a rhombus are supplementary i.e. their sum is equal to \[180{}^\circ \].
- The sum of all interior angles of a rhombus is \[360{}^\circ \].
- Opposite sides of a rhombus are parallel (by definition) and so will never intersect.
- Diagonals of a rhombus perpendicularly bisect each other.
Trapezium
Trapezium is a quadrilateral with a pair of parallel sides.

Properties of a Trapezium
- The sum of adjacent angles that a non-parallel side makes with two parallel sides is equal to \[180{}^\circ \].
Kite
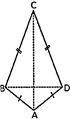
- Kite is a special type of a quadrilateral which has exactly two distinct consecutive pairs of sides of equal length. The sides with the same markings are equal i.e. AB = AD and BC = CD.
- The diagonals are perpendicular to one another and one of the diagonals bisects the other.
Rectangle
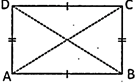
A rectangle is a quadrilateral whose all angles measure \[90{}^\circ \] and both pair of opposite sides is equal and parallel. The diagonals of a rectangle are of equal length and bisect each other. Thus, a rectangle is a parallelogram in which every angle is a right angle.
Square
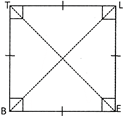
A square is a quadrilateral whose all sides are of equal measure and all of the four interior angles are equal to \[90{}^\circ \] in measure. The diagonals of a rectangle are of equal length and perpendicularly bisect each other. Thus, a square is a rhombus in which every angle is a right angle.
Practical Geometry
- To construct a quadrilateral, at least five measurements are needed. The possible combinations are as follows:
- Four sides and one diagonal are given.
- Two diagonals and three sides are given.
- Two adjacent sides and three angles are given.
- Three sides and two included angles are given.
- A square whose one side or two diagonals are given can be constructed without knowing the other parameters.
- A rhombus can be constructed if the length of its diagonals is given or a combination of one side and one angle is given.
Commonly Asked Questions
1. In the figure given below, find \[\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}+\mathbf{c}+\mathbf{d}\].
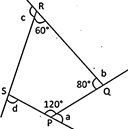
(a) \[180{}^\circ \] (b) \[360{}^\circ \]
(c) \[400{}^\circ \] (d) \[560{}^\circ \]
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)









