Visualising Solid Shapes
Category : 8th Class
Visualising Solid Shapes
Plane shapes have two measurements - length and breadth and therefore they are called two-dimensional shapes.
e.g.,
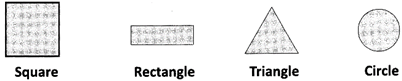
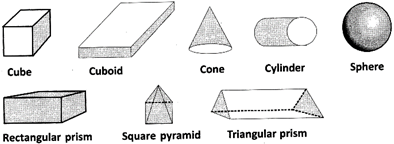
Solid objects have three measurements – length, breadth and height or depth. So, they are called three – dimensional shapes. Also, Solids Occupy some Space.
e.g.,
·
|
S.NO. |
Solid Shape |
Number of Vertices |
Number of edges |
Number of faces |
|
1. |
Cube |
8 |
12 |
6 |
|
2. |
Cuboid |
8 |
12 |
6 |
|
3. |
Cone |
1 |
1 Curved edge |
1 Curved face, 1 flat face |
|
4. |
Cylinder |
Nil |
2 Curved edges |
2 flat face 1 Curved face |
|
5. |
Sphere |
Nil |
Nil |
1 Curved face |
(i) A solid figure bounded by plane polygonal faces is called a polyhedron.
(ii) The point at which three or more faces of a polyhedron intersect is called a vertex.
(iii) A line along which two faces of a polyhedron intersect is called an edge.
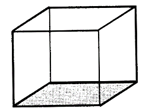
This polyhedron is regular. Its faces are congruent, regular polygons. Vertices are formed by the same number of faces.
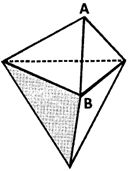
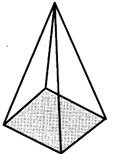
F + V = E + 2
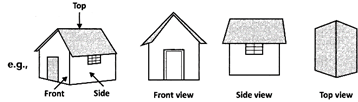
(i) We use symbols to depict different objects/places.
(ii) In a map, there is no reference or perspective.
(iii) Maps involve a scale that is fixed for a particular map.
e.g.,
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
