Mensuration
Category : 8th Class
Mensuration
(i) Perimeter of the rectangle \[=2\left( l+b \right)\] units
(ii) Diagonal of the rectangle,\[~d=\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}\] units
(iii) Area of the rectangle \[=\text{ }\left( \text{l}\times b \right)\]sq. units
(iv)\[\operatorname{Length}=\left( \frac{area}{breadth} \right)units\]
(v) \[\operatorname{Breadth}=\left( \frac{area}{length} \right)units\]
Then (i) Area of four walls \[=2\left( l+2 \right)\times h\]sq. units
(i) Perimeter of the square = (4a) units
(ii) Diagonal of the square
\[=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}=\sqrt{2a}=a\sqrt{2}\] Units.
(iii) Area of the square \[={{a}^{2}}\]sq. units
(iv) Area of the square \[=\frac{1}{2}\times {{\left( diagonal \right)}^{2}}\] sq. units
(v) Side of the square \[=\sqrt{Area}\]units.
(i) Let 'a', 'b' and 'c' be the lengths of sides of a triangle. Then, perimeter of the triangle is given by (a + b + c) units.
\[s=\frac{1}{2}\left( a+b+c \right)\]is called semi-perimeter of the triangle.
(ii) Area of the triangle \[=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\] sq. units
(iii) Let the base of a triangle be 'b' units and its corresponding height (or altitude) be 'h' units.
Note: We may consider any side of the triangle as its base.
The the corresponding height would be the length perpendicular to this side from the opposite vertex.
(v) Height of an equilateral triangle of side 'a' units \[\left( \frac{\sqrt{3}a}{2} \right)\]Units.
Note: The sides containing the right angle are known as legs of a right triangle.
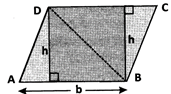
Then area of parallelogram = (base x height) sq. units
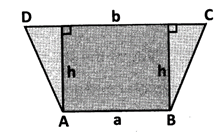
Then area of trapezium ABCD
\[=\frac{1}{2}\times \left( a+b \right)\times h\]sq. units
The fixed point 0 is called the centre of the circle and the constant distance V is called the length of radius of the circle.
Note: Distance between the parallel sides = height
Here, \[\pi \left( Pi \right)\]is a constant.
Note: The approximate value as \[\frac{\mathbf{22}}{\mathbf{7}}\] or 3.14
However is not a rational number. It is an irrational number and is defined as the ratio of circumference of a circle to its diameter
Area of a ring: The region enclosed between two concentric circles of different radii is called a ring.
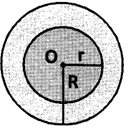
Area of the ring \[=\text{ }\left( \pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi {{r}^{2}} \right)\]sq. units \[=\pi \left( {{R}^{2}}-{{r}^{2}} \right)\] sq. units
\[=\pi \left( R+r \right)\left( R-r \right)\]sq. units
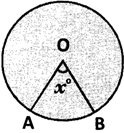
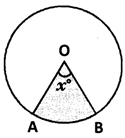
\[\frac{l\left( \overset\frown{AB} \right)}{Circumference}=\frac{{{x}^{o}}}{{{360}^{o}}}\]or \[l\left( \overline{AB} \right)=\frac{2\pi r{{x}^{o}}}{{{360}^{o}}}\]
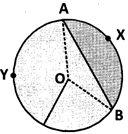
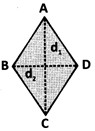
Area of minor segment AXB = area of sector OAXB - area of \[\Delta \]OAB
Area of major segment AYB = area of circle - area of minor segment AXB
The units of volume are cubic centimeters \[\left( c{{m}^{3}} \right)\]or cubic metres \[\left( {{m}^{3}} \right)\]etc.
For a cuboid of length \['l'\] units, breadth 'b' units and height 'h' units,
(i) Volume of the cuboid \[=\left( l\times b\times h \right)\]cubic sq. units
(ii) Diagonal of the cuboid \[\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}\]units
(iii) Total surface area of the cuboid \[=2\left( lb+bh+lh \right)\] sq. units
(iv) Lateral surface area of the cuboid
\[=\left[ 2\left( l+b \right) \right]\text{ }\times h\]sq. units
(vi) Area of 4 walls of a room \[=\left[ 2\left( l+b \right)\times h \right]\]units
For a cube of edge 'a' units,
(i) Volume of the cube \[={{a}^{3}}\]cubic units
(ii) Diagonal of the cube \[=a\sqrt{3}\]units
(iii) Total surface area of the cube \[=\left( 6{{a}^{2}} \right)\]sq. units
(iv) Lateral surface area of the cube = (4a2) sq. units
|
Relation between units |
|
|
Units of length |
Units of Volume
|
|
1cm =10 mm |
1\[C{{m}^{3}}\]=1000\[m{{m}^{3}}\] |
|
100 cm = 1 m |
1\[{{m}^{3}}\]=1000000\[C{{m}^{3}}\] |
|
|
1 liter =10\[C{{m}^{3}}\] |
|
|
kiloliter = 1000 liters = 1\[{{m}^{3}}\] |
Note: If the axis of the Cylinder is perpendicular to each Cross – Section, the Cylinder is called a right cylinder.
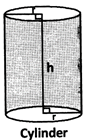
(i) Volume of cylinder \[\left( \pi {{r}^{2}}h \right)\]cubic units
= (base area) \[\times \] height
(ii) Area of curved surface \[==\left( 2\pi rh \right)\]sq. units
Total surface area\[=\left( 2\pi rh+2\pi {{r}^{2}} \right)\] sq. units
\[=\text{ }2\pi r\text{ }\left( h+r \right)\]sq. units
Volume and Capacity are similar words
(i) Volume is the amount of space occupied by an object
(ii) Capacity is the quantity that a container holds.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
