Mensuration
Category : 8th Class
MENSURATION
FUNDAMENTALS
Total surface Area of the cuboid \[=2\left( lb+bh+hl \right)\] sq. units.
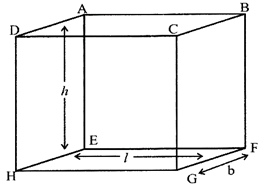
Volume of the cuboid \[={{l}^{2}}\times b\times h\]
Diagonal of the cuboid \[=\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}\]
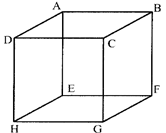
If length of each edge of a cube is a.
Then, volume of the cube \[={{a}^{3}}\]
Total surface area of the cube \[=6{{a}^{2}}\]
Diagonal of the cube\[=\sqrt{3a}.\]
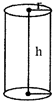
Volume of the cylinder \[=\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
Area of the base \[=\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Area of the curved surface \[=2\pi rh\]
Total surface Area
\[=27\pi rh+2{{\pi }^{2}}h=2\pi r(h+r)\]
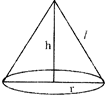
Radius = r, Height = h
Slant height = l
Volume of the cone \[\frac{1}{3}=\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
Area of the Base \[=\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Area of the curved surface \[=\pi r\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}}=\pi rl\]
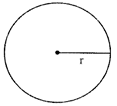
Radius = r
Volume of a sphere\[~=\frac{4}{3}\pi {{r}^{3}}\]
Surface Area of a sphere \[=4\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
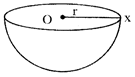
Radius \[=Ox=r\]
Volume of a Hemisphere\[\frac{2}{3}\pi r3\]
Curved surface area of a Hemisphere \[=27\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Total surface area of a Hemisphere \[=37\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
\[=Area\text{ }of\text{ }Base\times Height.\]
Lateral surface of prism
\[=Perimeter\text{ }of\text{ }base\times Height\]
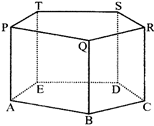
\[=\frac{1}{2}\left( perimeter\text{ }of\text{ }base \right)\times Slant\text{ }Height\]
\[=\frac{1}{3}\left( Area\text{ }of\text{ }base \right)\times height.\]

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
