Notes - Life In The Tropical And Sub-Tropical Regions
Category : 7th Class
Life In The Tropical And Sub-Tropical Regions
You have studied about the realms of our earth i.e., the lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere which together provide a platform for the origin, development and growth of the biosphere. Have you ever noticed how we adjust, adapt and modify our physical surroundings within the limits of nature? Our economic, social and cultural practices are by and large governed by our physical environment. Through the interactions, of man with the three realms, a distinct kind of human environment develops in each region. These regions are termed as Natural Regions as they follow the boundaries of the natural features.
Natural regions are broadly classified on the basis of temperature belts and rainfall distribution pattern of the world. These are classified into six major categories: i) Tropical equatorial region, ii) Sub tropical region, iii) West tropical desert region, iv) Warm temperate region, v) Cool temperate region and vi) Polar region.
In this chapter, we will learn about the life in two regions?one, the Amazon Basin of South America under the tropical region; and the other is the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin of the Indian subcontinent under sub the tropical region.
The tropical regions near the equator are covered by tropical rainforests that are characterised by dense vegetation, seasonally warm temperature and abundant rainfall. These locations include Africa-Zaire basin and Madagascar, Central
America and Amazon River basin. Sub-tropical climate refers to the zones between 10° and 30° latitudes in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The sub-tropical climate can be found in the south-eastern United States, south- eastern South America, coastal southeast South Africa, eastern Australia, and eastern Asia from northern India through south China to Japan.
EQUATORIAL TROPICAL REGION
THE AMAZON BASIN
Location
The Amazon Basin in South America is the largest river basin in the world and is a typical tropical or equatorial region as it lies between 10°N and 10°S. A network of nearly 500 tributaries form the river basin.
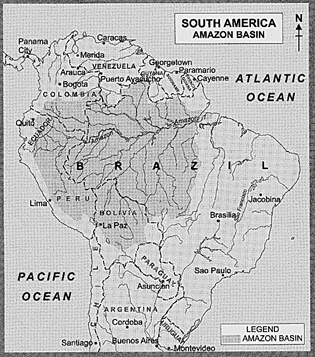
Mop. No. 9.1 Amazon Basin in South America
Geography Reveals
The Amazon Rainforest is thought to be the oldest tropical forest in the world, perhaps as old as 10,00,00,000 years.
· It covers five million sq. kms.-the largest in the world and nine countries.
· It is home to two and a half million different species of insects, more than forty thousands varieties of plants and one and a half thousand bird species and over two thousand fish species.
· Foods like bananas, chocolate, coffee, pineapple, rice and tomatoes come originally from here.
· The Toucan, the loudest creature in the Amazon rainforest can be heard half a mile away!
· Only 1% of modern medicines from plants found here have been tested so far?with over forty thousand plant varieties-new vaccines, etc. pose an immense possibility!
The Amazon Basin includes extensive portions of Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador and Columbia. The Amazon Basin has about 22,500 kilometres of navigable waterways. The Amazon River rises in the snow-covered Andes Mountain in Peru and flows eastward, to empty into the Atlantic Ocean. Its water discharge is 60 times greater (about 12.8 million cubic metres per minute) than that of River Nile. The Amazon River adds most of the moisture content to the earth's water cycle.

Tropical Evergreen forest
Climate
The Sun's rays fall directly on this region/ hence it receives maximum heat from the Sun also the temperature ranges from 25 C + 30 C, which is very small temperature range throughout the year. The annual precipitation averages 2,160 millimetres. It rains almost every day in the afternoon. This afternoon rain is also called the '4 O'clock rain'. The level of humidity in the Amazon Basin remains high throughout the year. At the same time/ the temperature in this region ranges from 25°C to 30°C, which is a very small temperature range.
Vegetation
Vegetation in the tropical region of Amazon Basin is characterised by the equatorial rainforests. The Amazonian equatorial rainforests are biomes with the most diverse vegetation and wildlife. These forests are very dense and are characterised by tall, broad-leaved evergreen trees. The forest has different layers. In the emergent layer, the tallest trees stick out from the canopy. The canopy layer is found beneath the emergent layer. Underneath the canopy layer is an understorey layer formed by shrubs and small trees. The forest floor is the ground layer. On an average, one can find more than 300 species of trees per square kilometre. They are mostly hardwood trees, e.g. ebony, teak, mahogany, Rosewood, cinchona and rubber. Deciduous trees found in the Amazonian rainforests grow to a height of 50 metres, with shallow roots; but they develop buttress roots above the ground to support their height. Trees grow so densely that they form a thick canopy which restricts the sunlight from penetrating to the surface/ hence a limited growth occurs. There is no grass. Woody vines called 'lianas' coil around the trees.
Wildlife
The Amazon rainforests have the most diverse biosphere in the world. They are home to Animals found in the Tropical Evergreen forest thousands of species of mammals, amphibians, reptiles, birds and insects. Different types of animals occupy different layers of the forests.
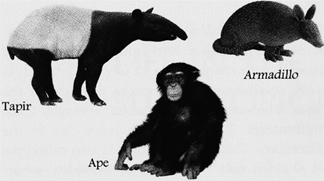
Animals found in of Tropical Evergreen forest
Birds in the Amazonian rainforests have colourful feathers and long beaks, e.g. macaw, hoatzin, toucan, bird of paradise, humming birds, etc. Monkeys, apes, sloths, bears and squirrels abound in the Amazonian rainforests.
Large size mammals such as tapir, deer, capybara, manatee, giant ant-eater, armadillo, jaguars, etc. are also found on the floor of the rainforests. Some snakes like the giant anaconda, emerald tree boa and pythons are found here in large numbers. Lizards and tree frogs are commonly found in the Amazonian rainforests. Reptiles like alligators and crocodiles are found in the swamps and rivers of the Amazonian rainforests.
Human Activity
The Kayapo tribe is considered the original inhabitants of the Amazon Basin. Their main occupations are hunting, fishing, gathering fruits from the forests and shifting agriculture. This system of agriculture is also called 'slash and burn agriculture'. The ash formed from the burnt trees act as fertiliser. Crops like yams, rhizomes, cassava, coffee and cocoa are grown. The rubber tree and grasses for cattle are also grown. Forest timber is used to fulfil the local needs as well as for export.

Kayapo Chief RAONI speaking, against the construction of the international barrage 'de Belo Monte' at an international forum
In recent years there has been massive deforestation in the Amazon Basin. The shifting cultivation has also posed a threat to the forests along with Oil and Gas exploration. Illegal logging and the spread of ranching and farming is also creating problem for local people. This has disturbed the balance of the ecosystem. Some environmental groups such as World Wide Fund (WWF) and Friends of the Earth are campaigning for forest conservation. The Rio Conference in 1992 and the UNO has suggested some steps to control the rate of deforestation.
Roads are being built to develop this region commercially. Over 12,000 kilometres of new roads have been built, the longest being the 5300 kilometre Trans-Amazonian highway
Geography Reveals
A Swedish millionaire 'Johan Eliasch' purchased 400,000 acres of the Amazon Rainforest from a logging company for $14,000,000 for the sole purpose of its preservation. He is the founder of Cool Earth, (www.coolearth.org.)

That links Manaus to Roraima in Brazil. Manaus is an important rubber-collecting centre. A 900-kilometre railway line links Carajas (a mining area in the Amazon basin) to the sea coast. Belem is the most developed part of the
Amazon. Numerous airstrips have been made for the air transportation of raw and finished goods. These rainforests are storehouse of a number of minerals such as iron ore, bauxite, manganese, diamond, gold and silver.
A large number of dams have been built in this region to harness the water resources and to produce hydroelectricity. Although these changes are planned for the betterment of the people, the indigenous people look upon these changes as a threat to their identity and for the environment as well.
SUB-TROPICAL REGION
THE GANGA-BRAHMAPUTRA BASIN
Location
The Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin is located in the Northern Hemisphere between 10°N and 30°N latitudes. This basin forms the major part of the subtropical Northern Plains.
The Ganga rises from glacier Gangotri in the Greater Himalayas, and the Brahmaputra rises from the Angs glacier the Tibetan Plateau. Although they do not now in the same direction, they join together in Bangladesh and form the largest delta of the world named Sunderbans before merging into the Bay of Bengal.
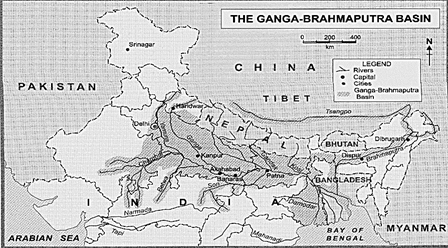
Map No. 9.2 the Ganga Brahmaputra Basin
The Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin includes the plains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers and their tributaries, the Himalayas and the Sunderban delta. In their upper course, the Ganga and its tributaries flow through the rocky Himalayas and deposit coarse soil along the foothills of the Himalayas. Below this level, these rivers spread to form swampy soil and thus forming the Terai region. Beyond this Terai region, lie the huge alluvial plains of the river Ganga. These plains are formed by the depositional work of the river Ganga and its tributaries. In the north-east, particularly in Assam, the Ganga plains merge with the

The Himalayas, the origin of magnificent rivers
Geography Reveals
The Average width of the Brahmaputra is 6 miles in the plains. The Largest riverine island "Majuli" is found in the river Brahmaputra. Its area is 163 sq km. In 2014, China operationalized the Zangmu Dam in Tibet, as part of the hydroelectric power project. It is the first major dam on the Brahmaputra River.
Brahmaputra plains (plains formed by the Brahmaputra river and its tributaries) together forming the Ganga-Brahmaputra plains or the Northern plains.
The Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin includes the states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Assam.
Q. can you tell the various names of the Ganga and the Brahmaputra in different regions from where these rivers flow towards the Bay of Bengal?
Climate
Hot summer, rainy and wet monsoon months and cold winter are the main features of this type of climate. The average rainfall increases from about 650 millimetres in the west to about 2500 millimetres in the east.
Vegetation

Mangrove forests
The humid monsoon type of climate provides scope for the growth of tropical deciduous forests. The plains of the River Ganga are covered with tropical deciduous trees such as peepal, sal and teak. The Tropical deciduous trees yield valuable timber. Besides, bamboos also grow in large numbers which are used for basket making and construction works. However, parts of Sikkim, Uttarakhand and Arunachal Pradesh are covered with coniferous forests as the climate is cooler in these areas. Trees of pine, deodar, chestnut and oak are the main trees found in these forests. In the higher regions of the Himalayas, the temperate forests (coniferous forests) give way to the alpine vegetation. Thick bamboo forests are a common sight in the plains of the Brahmaputra while the deltaic areas of Sunderbans have the mangrove forests where trees have stilt roots. One can easily find such stilt roots in the Sundri trees of Sunderbans. However, forests of Ganga-Brahmaputra basin are being fast depleted for agriculture and settlement purposes.
Wildlife
The forests in the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin have a rich wildlife. Elephant, deer, tiger and one-horned rhinoceros are found in large numbers in the states of West Bengal and Assam. Crocodiles, alligators and other aquatic animals are found in the fresh river waters and lakes. The fresh water dolphins known as 'susu' or the blind dolphins are also found here. A large varieties of fish like rohu, katia and hilsa are found in large numbers in the fresh waters of the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.

Fresh Water Dolphin found in the Ganga and the Tiger Found in Bengal
Geography Reveals
The Ganga is a river where the soul of India thrives and still lives. Researches have revealed some amazing facts about the Ganga:
· Mr. D.S. Bhargava of Roorkee University, has found'? Out that the Ganga is the only river in the world that: decomposes organ wastes at a rate which is 15 to 25 times faster compared to other rivers in the world.
· The New Delhi based Malaria Research Center found that water taken from the Ganga's upper ambits prevent mosquito breeding when the waters was added to any other water taken from different?;: sources.
Q. Despite these amazing attributes, there is a huge outcry for saving the Ganga from the pollution all along its course. What do you think, if the prevailing level of pollution continues will these facts still be true?

Human Activity
Agriculture is the main occupation of the people living in the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin. The main crop is rice or paddy. Rice is a major staple diet in most parts of this basin.
The climate of this basin allows an all year growing season. During the rainy season, the south-west monsoons help produce kharif crops such as rice, millets, maize, moong (pulse), etc. Cash crops like sugarcane and jute are also grown in the basin of Ganga-Brahmaputra. Rice is planted when the monsoon rains hit the plains and the rivers are flooded. Agriculture is a labour intensive activity and a large number of people are associated with this primary occupation (agriculture). A high rate of agricultural produce has supported the growth of many agro-based industries in this region.
Fishing is yet another important activity in the Ganga-Brahmaputra plains. Both of these rivers and their tributaries have fresh water all through the year teeming with a variety of fish.
The flat land of the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin has supported the growth of settlements and land transport routes. Many villages are found along the tributaries of the Ganga and the Brahmaputra rivers. Similarly roads, railways and waterways and air routes are well developed in the plains of these two rivers. All this has helped people of this basin develop on all fronts-culturally and economically. The northern part of this basin is hilly area which is occupied by some tribes. These areas are sparsely populated and the tribal people living here practise subsistence agriculture and rear livestock. Terrace farming is carried out in hilly and mountainous areas where rice, wheat, maize, etc. are grown along with the local cereals. Plantations of tea in Assam and West Bengal, orchards of apples, plums and peaches, etc. in the hilly areas have helped the economy of this region to develop.
Oil and Natural Gas exploration is another important activity in the Brahmputra basin. Digboi, Naharkatia, Dibrugarh and Lakhimpur are the main centres.
Tourism plays an important role in the economic development of the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin. The Taj Mahal in Agra, Allahabad at the confluence of Yamuna and Ganga, Varanasi with its ghats and temples, the Buddhist stupas in UP and Bihar, and the city of Lucknow with its Imambaras are all famous tourist places of this region. The North-east with its national parks and wildlife sanctuaries like Kaziranga, Manas, Laokhowa, Pobitora and Orang and distinct tribal culture as well as Uttarakhand with its Char Dhams, namely (i) Gangotri, (ii) Yamunotri, (iii) Badrinath, and (iv) Kedarnath receive a large number of visitors every year. Auli near Joshimath is an important hill station as well as a popular skiing and trekking destination in the Himalayan Mountains of Uttarakhand. Joshimath itself is the base for trekking to the famous Valley of Flowers, Uttarakhand.

Multiple centers of fourism in the Ganga basin
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
