Notes - Human Environment-Settlements, Transport And Communication
Category : 7th Class
Human Environment - Settlements, Transport and Communication
We have learned about the environment in the first chapter followed by four realms of the physical environment in subsequent chapters. After discussing the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere in detail, we need to learn about the human environment as well because man is responsible for many changes on the earth. In the process of fulfilling his basic and higher needs, man has changed the face of the earth and what we see today around us is all, the man-made environment.
The settlements, transport mediums and the communication system together build up a complete human environment for the people living therein to turn into a civilization.
SETTLEMENTS
Human Environment as we discussed in the initial chapters, refers to the man-made surroundings that include the
Physical, social and economic components that determine the state, condition and quality of living of a person. These components vary from one place to another and have evolved overtime with the advancements and changes in the society.
Early humans lived on trees and in caves. When they began to grow crops, they started settling at one place and these settlements grew near the river valleys. With the development of trade and commerce human settlements became larger. A settlement is a place where people live and they are of various types.
TYPES OF SETTLEMENTS
On the basis of stability, a settlement can either be temporary type or permanent type. Nomadic people usually build temporary settlements. These settlements include tents or temporary huts. In fact, nomads have to build settlements in deserts or in areas where there is shortage of food, water and fuel supply. Therefore, they have to shift their settlements from time to time. Such lifestyle, in which people keep migrating from one place to another in search of food and water, is called transhumance.
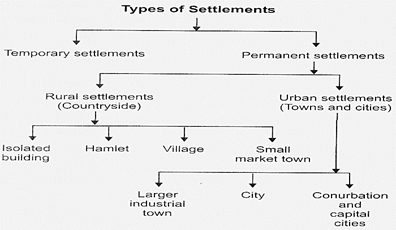
However, more and more people today live in permanent settlements. Villages, towns and cities are the permanent settlements. On the basis of lifestyle and other prominent features, permanent settlements can be divided into two categories: (i) Rural settlement, and (ii) Urban settlement. We can get a brief idea of them from the pictures given above.

A view of the rural settlement in India
Rural settlement
Rural settlements are the settlements where people are occupied with primary activities such as agriculture, fishing, forestry, rearing of animals, weaving, pottery and mining, etc. A village is an example of rural settlement. Large open spaces and pasture lands are the usual characteristics of such settlement.
Urban settlement
Urban settlements are compact and comparatively larger (in area) than the rural ones. Towns and cities come under this category of settlement. Urban settlements can be classified on the basis of size of population, density of population, administrative status, land-use pattern and economic activities.
People of the urban settlements are usually occupied with non-farming activities such as manufacturing, processing, trading of finished products, etc. All these activities are known as the secondary activities. They are also involved in tertiary activities like transportation, administration, education and in providing various services. People here enjoy the modern amenities like?big schools, colleges, hospitals, well linked transportation facilities, etc.

A view of the urban settlement in India
The classification of the urban settlements is always based on the number of people or population size. This criteria vary from one country to another. Different cities are sometimes named as simply class I, II, III or IV level city.
At many places different names are given for different cities.
SETTLEMENT PATTERNS
In the process of development, settlements usually change their shapes and sizes. Thus, settlements grow in different forms called settlement patterns. Settlement patterns are determined by the arrangement or layout of buildings within a settlement. There can be different types of settlement pattern. They are as follows:
1. Compact or Nucleated settlement pattern
2. Linear settlement pattern
3. Dispersed settlement pattern
Compact or nucleated settlements
A nucleated pattern of settlement occurs where buildings cluster together for economic and social purposes. In ancient times, people used to stay close to each other for security purposes, hence the nucleated pattern of settlements developed. The nucleated settlements can be seen along the river confluences, major crossroads and along the major transport routes.
Linear settlements
When settlements are built along the main line? Of communication such as highways, roads and Railways, a linear settlement pattern is formed. Such pattern of settlements can also be found in narrow river valleys and along main roads.
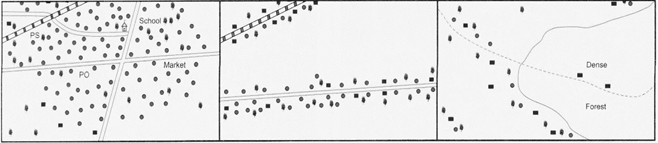
Nucleated, Linear and scattered settlement patterns
Dispersed settlements
Dispersed pattern of settlements is built in a scattered way. Therefore, this pattern is also known as the scattered pattern of settlements. Such pattern of settlements can be found in a difficult terrain or at a place which has harsh climate and poor soil. Forests, mountainous areas or less fertile areas can have such type of settlement patterns. Usually these settlements are not very large.
TRANSPORT
The human environment includes the transportation system also. Transportation is the "movement of goods and persons from one place to another." A good transportation system and a well-knit transportation network are important for the promotion of trade and commerce of an area. As scientific and technological knowledge progressed, new modes of transport developed over land, water and air.
TYPES OF TRANSPORT
The transport medium are categorised as follows in three parts, (i) Land Transport (ii)
Air Transport (iii) Water Transport (iv) Other modes of transport?(Pipeline, Canal, Tunnel).
Road transport
Roads are the easiest and the most common means of transportation for short distances. Roads built underground are called subways or under path. Automobiles need metalled roads to move on. Highways and expressways are constructed for speedy transportation. As per the government plan in India, major cities (Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai- Mumbai) are being linked through a six-lane Super Express Highway called the Golden Quadrilateral. Besides, North-South Corridor is to link Kashmir with Kanyakumari and East-West Corridor is to link Silchar in the east to Porbandar in the west. India ranks second in the world for having the largest road network; United States of America has the densest road network.

Latest development in road network is Yamuna Expressway that connects Noida to Agra
Geography Reveals
Khardung La in Leh (India) is the highest motorable road in the world, located at a height of 18,380 feet.
Rail transport
Railways provide the fastest and cheapest portage on land. In industrial regions, railways serve an important channel for receiving raw materials and sending finished products to distant places. Railways not only facilitate people travelling long distances in less time but also provide the best means for carrying bulky goods efficiently. With advancement in technology, tunnels and bridges are built in hilly and mountainous areas and railway services are being provided in the rugged terrain of mountainous areas also. The Konkan railways in the Western Chats (India), Trans-Montane railways in Europe and the Trans-Andean railways in South America are the best examples of this.
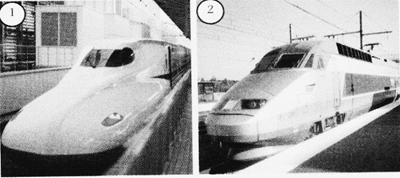
1. Bullet Train of Japan, and 2. TGV of France
Geography Reveals
The Trans-Siberian railway is the world's longest railway line; it connects Moscow in European Russia to Vladivostok on the east coast of Asian Russia making it the longest train trip in the world. It covers the distance of 5,778 miles with 91 stations in 9 days'!
With the advancement of technology, electric engines are now being used. This has enabled trains to move at a greater speed. The Bullet Train of Japan and Train of Grande Vitesse (TGV), France are the finest examples of fast moving electric trains. TGV of France moves at a speed of 300 kilometres per hour.
In cities like London, Paris, Delhi and Kolkata, people enjoy city services called Metro Rails. India has the largest network of railways in the world. However, the densest railway networks exist in the urbanised and industrial areas of Western Europe and East-Central United States of America (USA).
Water Transport
Water transport was the first to be used for the transportation of both people and goods. The water transport can carry bulky materials in large quantity to distant lands. It is the cheapest mode of transport as nature itself provides for waterways in the form of rivers, lakes, seas and oceans.

Map No. 8.1 sec and ocean routes of the world
Ships nowadays, are better designed and can move efficiently. For example, an ice-breaker (ship) can travel in the frozen ocean around poles and in Antarctica as well. Waterways, can be categorised as: (i) Inland waterways and
(ii) Ocean and Sea routes.
Inland waterways: Rivers, lakes and canals are the inland waterways. They can be navigated easily. Transportation takes place in these inland waterways through boats and steamers. Some important inland waterways in the world are the Ganga-Brahmaputra river system (India), the Great Lakes (USA, Canada), the Mississippi and Missouri rivers (Southern USA), Rivers Seine and Loire (France), River Rhine (Germany), River Nile (Egypt, Africa) and River Yangtze Kiang (China)
Q. Locate the major sea ports of the world on a map.
Ocean and Sea routes: Seas and oceans provide much important routes for the international trade and commerce since ancient times. Some important sea routes of the world are as follows:
· The Indian Ocean?Mediterranean Sea Route (via-Suez canal) connects East Asian countries with Australia and the West European countries as well.
· The North Atlantic Route connects the eastern parts of North America with the Western European countries.
· The South Atlantic Route connects the South American countries with the West African countries.
· The Cape of Good Hope Route (on the tip of South Africa) connects the Asian countries with the European countries.
· The North and South Pacific Route connects Australia, East Asia, Western Europe and North America through Panama Canal.
Air Transport
Air transport is the fastest mode of transports, developed in the twentieth century. Big aircrafts are used to carry loads and travel to distant places. Airports are established all across the world that provide base for air transportation.
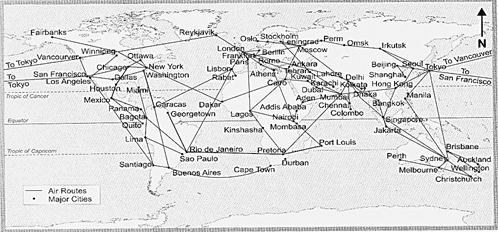
Map No. 8.2 Major air routes of the word
These airports are equipped with the advanced system to monitor the takeoff, movement and landing of aircraft. With 7000 civil airports, USA has one of the most advanced and frequently used airways in the world. Domestic airways give air services within a country. The international airways provide international services and link major cities of the world. Helicopters are used for faster services in most inaccessible locations.
Geography Reveals
· The airport at Bangda in Tibet is the highest airport in the world.
· London to New York is the busiest international air route.
Other Transportation Structures
Besides roadways, railways, waterways and airways, there are some other structures like tunnels, canals, bridges and pipelines that facilitate transportation.
Canals are the especially constructed channels for the free movement of inland as well as open sea vessels. Canals are constructed at a place where the natural water is not navigable. Some canals link the North Sea with the Mediterranean sea. The St. Lawrence Seaway (canal) links all the five lakes of the Great Lakes (on the Canada-US border) to the St. Lawrence River, which ultimately flows into the Atlantic Ocean. The Suez Canal links the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea and the Panama Canal links the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean.
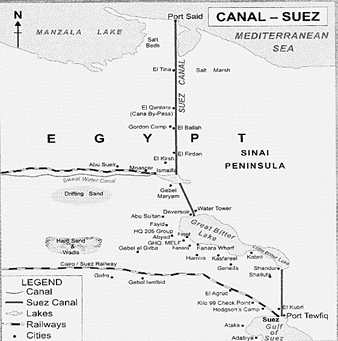
Mop No. 8.3 Suez Canal
Tunnels help to make movement or transportation easier by providing a direct route in the mountainous regions. Tunnels under the sea overlook the water barrier. Tunnels also help making journey shorter and easier. The Channel
Tunnel under the English Channel links London (UK) with Paris (France).
Bridges also facilitate movement or transportation of goods and people. Bridges are constructed over the water bodies to overcome water barriers and to shorten travelling distances caused by such barriers.
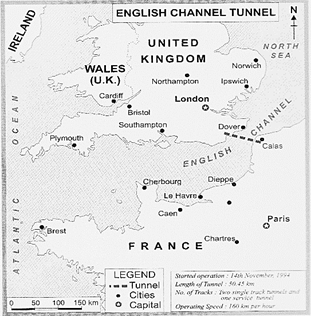
Map No. 8.4 English Channel Tunnel
Geography Reveals
· The longest railway tunnel in the world is the Seikan Tunnel in Japan which is 53.9 km long.
· The longest highway tunnel in the world is the Saint Got [hard Tunnel in Switzerland which is 16.3 km long.
· Hangzhou Bay Bridge in China is the world's longest cross-sea bridge in the world. It is 35.6 kilometers long with a six lane highway in both directions. It connects Shanghai with Ningbo.

· Millau Viaduct in France is the world?s highest bridge, i.e. about 1125 feet above the Tarn Valley in Southern France.

· Akashi Bridge in Japan is the longest suspension bridge in the world with a length of about 3,911 kilometres. It contains a six-lane highway.

The Alaska Oil Pipeline is the longest oil pipeline in the world with a length of about 1242 kilometres. It pumps out crude oil from America''s largest oil field at Prudhoe Bay.
Pipelines are constructed mainly for the transportation of oil and natural gas.
COMMUNICATION
Communication means transmission of a message by speaking or writing or sending a message. Important components of communication are sender, receiver and mode for transmitting the message. The modes of communication are many and are chosen depending upon the type of communication. The history of communication dates back to early historic times. Human communication was revolutionised with the origin of language and speech approximately 500,000 years ago. Symbols were developed about 30,000 years ago.
Oldest known symbols created with the purpose of communication through time are cave paintings. The connection between drawing and writing is further shown by linguistics. The concept and words of drawing were one and same in Ancient Egypt and Greece. The communication can be verbal, non-verbal and written. When communication is between two people, it is personal communication. When the sender wants to communicate something to more than one person or group of people; he uses the mediums of Mass Communication Like - newspaper, radio and television.
MODES OF COMMUNICATION
Postal Communication
The Department of Posts is a government operated postal system in India operated through the network of Post Offices. The Indian postal system is the most widely distributed postal system in the world. As of March 2011, there were 15,4866 post offices in India with each post office serving an area of about 21 sq km and a population of 7114. The post offices also offer other financial and banking services. You are familiar with the PIN Code. It stands for Postal Index Number and is a six-digit code introduced on 15 August, 1972. There are 9 such regions in the country. The first eight belong to different geographical regions and the last one is for the Army Postal Service
Telecommunication
Telecommunication occurs when the exchange of information between two or more entities includes the use of technology. Earlier, for long distance communication means used were visual signals such as?beacons, smoke signals, signal flags, telegraphy and optical heliography. Now with the changing technology, electrical means like telephones, teleprinters, radio network, and internet telephony, etc., are being used. Developments in technology have helped in increasing the number of mobile devices. They enable people to communicate anytime, any Place, anywhere. There is a wealth of information available to society that can be accessed on demand. With the rapid advancement in the field of information technology, the communication system has been thoroughly revolutionised. The use of computers and the Internet and transmission of messages through undersea cables and radio waves have made communication fast and effective. Now,? electronic mails (e-mails) and SMS through the Internet and cellular phones have all made our lives comfortable Satellite pictures help us explore mineral- and oils, understand underground water movement, and forecast weather phenomenal' as well. Thus, telecommunication has improves communication and though the physical distances are the same, the world has shrunk into a global village.

Use of Internet, laptop and Smart phones the revolutionized the communication
Activity
There are ethical and health issues related to the technologies that you use today for communication. The adversities include health implications of mobile devices, unauthorized access to wireless networks, etc. Your class can make a chart for the display board on the topic "Ethical and health issues related to modern technologies".
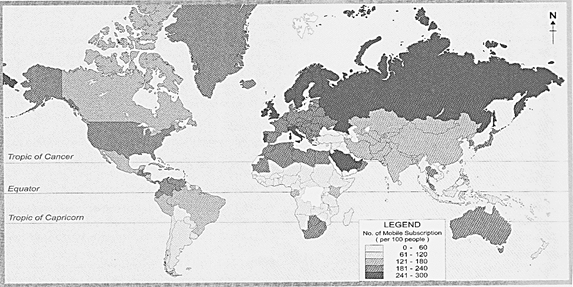
Mop No. 8.3 the Status of mobile phone users in the World
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
