Living Organisms Habitats
Category : 6th Class
Living Organisms and their Habitats
Plants
There are a large number of plants in our surroundings. Plants are living things which can make their own food. They are vital for the survival of animals including us. Let's study about the plants in some detail.
Classification of Plants on the Basis of Bearing Flowers
All the plants has been divided into two groups on the basis that either they bear flower or not.
Flowering Plants: The plants, which bear flowers, are called flowering plants. For example, rose, mango, sunflower, grass, lemon, tulsi, peepal, etc.
Non-Flowering Plants: The plants, which do not bear flowers, are called non-flowering plants. For example, ferns, mosses, algae, fungi, etc.
Classification of Plants on the Basis of Size, Nature of Stem and Life-span
Herbs
Herbs are small plants which have a soft and delicate stem. They have short life-spat. They live for only one or two season. For example, grass, tomato, wheat, paddy, cabbage etc. Banana plant is a herb.
Shrubs
Shrubs are medium sized plants which have hard but not very thick stem. Their lifespan is for many years but less than that of trees. For example, rose, lemon, jasmine, etc.
Trees
Trees are tall and big plants which have hard brown thick stem. Their life-span is for many years. For example, mango, neem, palm, coconut, etc.
Climbers
Climber plants have long, thin and weak stem so they cannot stand upright. They climb up with the help of a support. For example, pea plants, grape vine, glory lily, jasmine, etc.
Creepers
Creeper plants also have long, thin, and weak stem. Creeper plants do not have special organ for climbing up so they spread out on the ground. For example, strawberry, pumpkin, cucumber, etc.
Parts of a Plant
Root stem, leaves, flowers and fruits are the main parts of plants.
Root
This part of a plant grows below the ground. Root fixes the plant firmly to the soil. It absorbs water and minerals from the soil which are essential for the photosynthesis.
Types of Roots
There are mainly two types of roots: tap root and fibrous root.
Tip root: It consists of a main root called tap root from which a number of branching
Roots arise called lateral roots. For example, mango, radish, mustard, etc.

Fibrous root: It consists of many thin, fibre like roots arising from the base of the stem. For example, grass, wheat, paddy, maize, etc.

Functions of Stem:
Leaf
It is the thin, broad, flat and green part of plants which is attached to stem. Flat green portion of leaf is called are called stomata.
Functions of leaf:
Flower
It is a beautiful part of a plant which helps in reproduction. The main parts of a flower are sepals, petals, stamen and pistil.
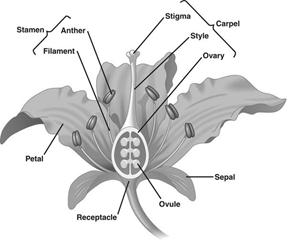
Sepals: They are the green leaf-like structures which protect the bud.
Petals: They are the most attractive parts of flowers which protect stamen and pistil.
Stamen: It is the male part of a flower consisting of filament and anther. Anther contains pollen grains and pollen grains contain male sex cells.
Pistil: It is the female part of the flower consisting of stigma, style and ovary. Ovary contains ovules and ovules contain female sex cells.
Fruit
When male sex cells fuses with the female sex cells of a flower, ovary of the flower grow into fruits and ovules changes into seeds.
Living Organisms and their Surroundings
The environment consists of both living things and nonliving things. Living things are known as biotic components whereas nonliving things are known as abiotic components of the environment.
All the living things have been classified into three groups: producers, consumers and decomposers.
Producers
Producers are the living organisms which can make their own food with the help of photosynthesis. They include all the green plants like mango, peepal, grass etc.
Consumers
Consumers are the living organisms which consume the food prepared by the green plants. They includes all the animals like tiger, elephant, human, etc.
Decomposers
It includes the microorganisms which decomposes dead bodies of plants and animals.
Habitats
The place where an organism lives is called its habitat. There are various types of habitats.
Types of Habitats
There are mainly two types of habitats:
(i) Aquatic habitat
(ii) Terrestrial habitat
Aquatic Habitats
A water based habitat is known as aquatic habitat.
Hydrophytes: Plants which live in water.
Hhrdrocoles: Animals which live in water.
Phytoplanktons: The microscopic plants which live in water.
Zooplanktons: The microscopic animals which live in water.
Aquatic habitat has been divided into three groups:
Terrestrial Habitats
Land based habitats are known as the terrestrial habitats. Terrestrial habitats have been divided into five groups:
Desert habitats
It is the region of land habitat with very low rainfall.
Xerophytes: The plants which live in desert.
Xerocoles: The animals which live in desert.
Grassland Habitats
This is the region of terrestrial habitat of moderate rainfall.
Rainforest Habitats
This is the region of hot and wet weather with high rainfall.
Tundra Habitats
This is very cold region of terrestrial habitat which is covered by snow throughout the year.
Mountainous Habitats
This is the region of landform that rises high above the surrounding terrain.
Adaptations in Desert Organisms
Desert Plants
Desert plants have long and extensive root system, with which they go deep in the soil in search of water. The leaves and stems of some plants become thick and store water for example, agave, opuntia. The desert plants are called succulent plants.
Desert Animals
Desert animals like rats, snakes, etc. dig deep burrows to live which protects them from extreme heat during the day.
Adaptations in Water Organisms
Aquatic Plants
Aquatic plants have very short and small roots. Their stems are soft, hollow and having large spaces filled with air.
Submerged leaves are long and narrow whereas floating leaves are large and flat have waxy upper surface.
Aquatic Animals
Body of water animals are streamlined which are covered by scales and mucous. They have fins and tail to swim in water and gills for breathing.
Adaptations for Cold Weather
Tundra Animals
The animals which live in very cold region have thick fur on their bodies to protect them from cold. They have thick layer of fat under the skin to regulate their body temperature. Sometimes they go for long winter sleep called hibernation.
Adaptations in Grassland Organisms
Predators have long, strong and sharp claws in their front legs. Eyes in front of head enables them to find the exact location of their prey and light brown colour of their skin help them in hiding in the grassland.
Prey have eyes in sides of their head to see in all direction. They have big ear for good hearing. They can run fast and their strong teeth enables them to eat hard plant stems.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
