Light, Shadows and Reflections
Category : 6th Class
Light, Shadows and Reflection
Synopsis
- Objects which emit light energy by themselves are called luminous bodies.
e.g., the sun, the stars, and glow worms.
- The bodies which do not have light energy of their own but reflect the light energy falling on them and hence are visible to us are called non-luminous bodies.
e.g., the moon, objects around us, books, chairs, buildings, trees, etc.
- The moon appears bright due to the reflection of sunlight falling on it.
- Transparent bodies are substances through which light is propagated easily,
e.g., glass/water/etc.
- Translucent bodies are substances through which light is propagated partially.
e.g., oil, ground glass, etc.
- Opaque bodies are substances through which light is not propagated.
e.g., wood, iron, etc.
- Light travels in straight lines.
- Smooth surfaces like mirrors form images.
- The shadow of an object is formed because of the rectilinear propagation of light. A shadow is the area of darkness formed on the screen, when an opaque body is placed in between the screen and a source of light
- A pin hole camera uses the principle of rectilinear propagation of light. It produces a real image which is much smaller than the object and is inverted (upside down).
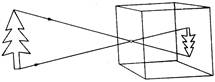
- The returning of a light ray passing through an optical medium into the same medium from the surface of the second medium is called the reflection of light.
- The surfaces which reflect light are called reflecting surfaces.
- Images are different from shadows.

