More About Networking and Internet
Category : 6th Class
More About Networking and Internet
A network is a set of inter connected devices, such as computers and printers. These novices are connected with transmission media or communication channel. Using network you can send and receive data from one computer to another computer. You can also-hare printer and scanner with other users.
Internet is the technology that is used to connect different computer systems located in different geographic locations.
The internet interconnects millions of computers, providing a global communication, storage, and computation infrastructure. Moreover, the Internet is currently being integrated with mobile and wireless technology.
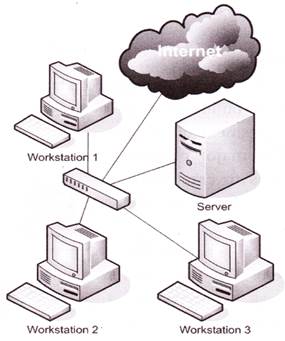
The Purpose of Networking
File and Data Sharing
It allows files to be shared instantaneously across the network with hundreds of users.
Resource Sharing
It allows the sharing of network resources such as printers, dedicated services, input devices and internet connections without being relocated.
Internal Communications
It allows organizations to maintain internal communication system. It enables employees to co-ordinate meetings and work activities which intern increases productivity.
Provides Reliability
Computer network is a very reliable network. If one of the systems in a network collapse, data can be collected from another system in the same network.
Different Types of Networks
Computer networks are classified on the basis of various factors. They include geographical span, inter-connectivity, administration, architecture etc.
The three main types of computer networks are:-
v LAN
v WAN
v MAN
Local Area Network (LAN)
This type of network is usually a small network constrained to a small geographic area like a home, office, or group of buildings. It is normally used for a single business office or a residential apartment. The major purpose of such inter connectivity is to establish a communication system in order to make the work easier.
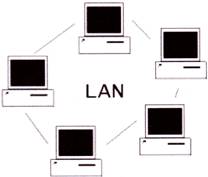
LAN provides a useful way of sharing the resources between end users. The resources such as printers, file servers, scanners and internet are easily sharable among other computers.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network is a network that connects two or more Local Area Network or Campus Area Network together but does not extend beyond the boundaries of the immediate town, city, or metropolitan area. Multiple routers and switches are connected to create a MAN. It provides high speed internet services throughout the area covered within the network.
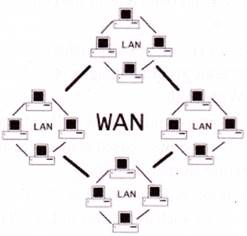
Wide Area Network (WAN)
WAN is a system of network that covers a large geographical area across the world. WAN is used to connect LANs and other types of networks together, so that users and computers in one location can communicate with users and computers in other locations.
The services of WAN are provided by public or government agencies as well as private agencies. This network also provides the facility to access databases located remotely WAN may be managed by multiple administrations.
Network Protocol
Protocol is a set of rules that allows two computers on a network to communicate and transfer data between them. Protocols are generally implemented by software, hardware, or a combination of both. It may have signalling error detection or correction and authentication capabilities.
The network protocol plays the following roles
v Identify the corrupt messages using error checker.
v While receiving messages, indicates the receiving devices.
v While sending messages, indicates the sending devices.
v To compress the data transmitted through the network, the method data compression is used.
Some of the important networking protocols are:
v Ethernet: Ethernet is the most popular LAN technology in the world. It is a fast and reliable network solution that is still widely used today. It is a network protocol that controls how data is transmitted over a LAN. Technically it is referred to as the IEEE 802.3 Protocol.
v TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the language a computer uses to access the internet. It consists of a set of protocols designed to establish a network of networks to provide a host with access to the internet.
v FTP: File Transfer Protocol is a standard Internet protocol for transmitting files between computers on the internet over TCP/IP connections.
v Telnet: Telnet is a program that runs on the computer and connects your PC to a server on the network.
v HTTP: HTTP stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol. HTTP is the set of rules for transferring files (text, graphics images, sound, videos and other multimedia files) on the World Wide Web.
v Apple Talk: It is used to communicate with Apple macintosh computers.
v New Link: It connects windows ?based computers and computers running MS client on Disk Operating System (DOS).
v Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi is stands for Wireless Fidelity. Wi-Fi was developed to be used for mobile computing devices, such as laptops in LAN, but is now increasingly used for more applications including Internet and VOIP phone access, gaming and basic connectivity of consumer electronics such as televisions and DVD players or digital cameras.
IP Addressing
The IP address is a 32 bit unique number that is assigned to a computer. An IP (Internet Protocol) address is similar to the address of your home, IP address basically consists of two IDs, one is the network ID and other is the host ID. The unique number which is used by your network is the Network ID and the host ID portion uniquely identifies the system on your network.
Basically the IP address format is known as dotted decimal notation format and contains a set of four numbers separated by periods. For example, 192.178.2.200 is an IP address mentioned in four numbers in a dotted decimal notation form. In the given IP address, first two numbers (192.178) are the Network ID and last two numbers (2.200) are host ID. The Network ID is same for all the systems on the same network. Basically there are five major classes of IP address. They are as follows:
Class A
The range of Class A IP address is from 1.0.0.1 to 126.255.255.254 and this supports 16 million hosts on each of 127 networks.
Class B
The range of Class B IP address is range as 128.1.0.1 to 191.255.255.254 and it supports 65,000 hosts on each of 16,000 networks.
Class C
The range of Class C IP address is range as 192.0.1.1 to 223.255.254.254 and it supports -254 hosts on each of 2 million networks.
Class D
The range of Class D IP address is range as 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 and it is reserved for multicast groups.
Class E
The range of Class E IP address is range for Class E is 240.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.254 and this is reserved for the future use.
Internet
The Internet is a network of networks. Through Internet you can connect to any computer throughout the world. Internet is the best example of WAN (Wide Area Network). Internet is worldwide global system of interconnected computer networks. It uses standard Internet Protocol TCP/IP. Every computer has a unique IP address. A special computer server Domain Name Server (DNS) is used to give name to the IP address so that user can locate a computer by a name.
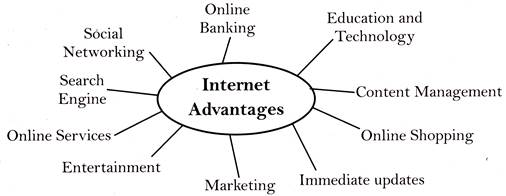
Some of the advantages of Internet:
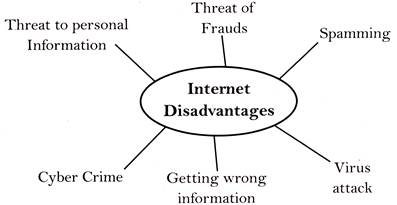
Some of the disadvantages of Internet
Network Devices
Network devices are also known as network equipment or networking hardware. They are required for communication and interaction between devices on a computer so that they can share files or resources like printers or fax machines.
Types of Network Devices
Modem
Modem is one of the most important part for using internet services. This works as a key because it receives the packet of data or signals through the service provider and thus after receiving it, it allows user to use the packet of data for surfing. Without modem, surfing is unable to proceed. Modems are generally categorized by the amount of data to be transferred in a given time. It is measured in bits per second.
Hub
Hub is a networking device which is used to connect multiple network hosts. It is also used to transfer data. The data is transferred in terms of packets. When a host sends a packet to a network hub, it copies the data packet to all of its ports connected to it.
Switch
While hub just does the work of data forwarding, a switch filters and then do forwarding which is more intelligent way of dealing with the data packets.
Router
A router is responsible for routing traffic from one network to another. These two networks could be a private company network or a public network. You can think of a router as a traffic police who directs different network traffic to different directions.
Bridge
If a router connects two different types of networks, then a bridge connects two sub- networks as a part of the same network. You can think of labs or two different floors connected by a bridge.
Repeater
A repeater is an electronic device that amplifies the signal it receives. In other terms, you can think of repeater as a device which receives a signal and retransmits it at a higher level or higher power so that the signal can cover longer distances.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
