Plants
Category : 5th Class
Plants
Plants are very useful to us. Being a living thing, plants also reproduce to maintain the existence of their species. Plants reproduce in a number of ways:
(i) From their body parts
(ii) From spores
(iii) From seeds
Reproduction through Body Parts
Some new plants grow from the parts of the mother plants. They grow from roots, stem and leaf. Such type of reproduction is known as vegetative propagation.
Root
A sweet potato is a swollen root of the plant. The new plant of sweet potato can be grown from the roots of the original plant.
Stem
Some plants can reproduce by burying a part of stem in the soil. From stem cutting, new shoots grow from buds. For example,
Sugarcane, rose plant
Underground Stem
Underground stems like potato and ginger have buds on them from where new shoots will grow on planting them in the soil.

Potato
Similarly, some plants like onions and lilies grow from their bulb shaped stems.
Leaves
In Bryophyllum, new plant grows from their leaves.

Bryophyllum
Reproduction Through Spores
The plants like ferns, mushrooms or mosses, which do not have flowers, produce spores which can be grown into a new plant.

Mushroom
Reproduction Through Spores
The fruit bearing plants have seeds inside fruit. When these seeds fall on the soil, new plants grow from them. For example,
Mango, rice, wheat and tomato, etc.

Tomato
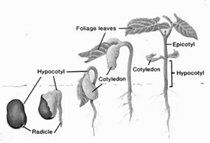
Parts of Seed
Seed has an upper covering which is called seed coat. Inside the seed coat/there may be one or two seed leaves called cotyledons. Between them, baby plant grows called seedling. Seedling has radicle growing downwards that develops into root and plumule growing upwards towards the sunlight that develops into shoot. Food for the baby plant wheat and rice have only one cotyledon and are monocot plants. Pea and beans have two cotyledons and are dicot plants.
The process by which baby plant grows from a seed is called germination.
A seed needs water, sunlight and air. A seedling grows into a plant when it gets sufficient water and food from soil, sunlight and air.
Germination of seed
Dispersal of Seeds
Plants have to disperse their seeds with the help of nature so that all seeds would not fall on one place causing lack of sunlight, water and space to grow Seeds are dispersed by wind, water, animals and explosion of fruits. These all are agents of dispersal.
Wind
The seeds which are light and have wings or hairs on them are easily carried by wind. Seeds of cotton and madar have hairs.

Cotton seed
Water
Seeds are carried to different places by flowing water.
Coconut is very light in weight as it is hallow from inside so that it does not sink when it falls into water. It floats for several months in sea before reaching land.

Coconut
Animals
Seeds of mango, apple, etc. are thrown by human beings and animals after eating. Some seeds have stiff hair which cling to bodies of animals or feathers of birds or our clothes and carried away from one place to another.


Mango seed Apple seed
Explosion
The fruits of some plants, like pea on drying explode suddenly. This explosion causes the seeds to scatter away from the mother plant. For example, pea plant and bean plant.


Pea seeds Bean seeds
Food from Plants
The growth of different crops depends on different seasons, climate and soil. The crops which grow in winter from november to april are called rabi crops. Examples of rabi crops are wheat and gram.


Wheat Gram
The crops which grow in summer from June to October are called kharif crops. Rice, maize and bajra are examples of kharif crops.


Rice Maize
Protection of Crops
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
