Networking
Category : 5th Class
Networking
Introduction
Do you know every person has its own network? Network are everywhere or so it seems. You can hardly do anything with data that does not involve a network. Like the human networks that we are all part of computer network let us share information and resources. Networks help individuals and business alike save money, but they also help create income. A computer network is a network of computers that are geographically distributed, but connected in a manner to enable meaningful transmission and exchange of data among them.
The purpose of networking
v Get the information you need to develop yourself and your career or business.
v To let people know what you are doing and what you are interested in.
Also networking in increasingly viewed as important to the achievement of personal and work-related goals. For example personal network include with family, friends and everyone we know.
Today's, information technology provides us with one of our most important sources of information for networking.
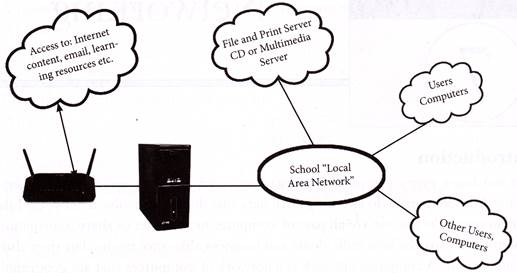
A computer network consists of a collection of computers, printers and other equipment that is connected together so that they can communicate with each other. An example of a network in a school comprising of a local area network or LAN connecting computers with each other.
Different Types of Networks
The network is divided into 3 main categories:
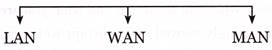
LAN
A LAN is used to connect the computers and other network devices so that the devices can communicate with each other to share the resources. The resources to be shared can be a hardware device like printer, software like an application program or data. The size of LAN is usually small. The various devices in LAN are connected to central devices called Hub or switch using a cable. If the network is contained with a relatively small area, such as a classroom, school, or single, building as shown in the figure, it is commonly referred to as a local area network (LAN). This type of network has the lowest cost.
Advantages of LAN
v Ability to share hardware and software resources.
v Individual workstation might survive network failure.
v Components and system evolution are possible.
v Support for heterogeneous forms hardware and software.
v Access to other LAN's and WAN's.
v Private ownership.
v Secure transfers at high speeds with low error rates.
Disadvantages of LAN
v Equipment and support can be costly.
v Some types of hardware may not interoperate.
v Power - a good LAN is required to be on all the times.
v A lot of times a network shares one internet connection if all computers running at once, can reduce speed for each.
v Area covered is limited.

WAN
A WAN is term as Wide Area Network. A WAN is a telecommunication network. A Wide Area Network is simply a LAN of LAN's or Network of Networks. WAN connect LAN's that may be on opposite sides of a building, across the country or around the world. WAN's are characterized by the slowest data communication rates and the largest distances. Computer connected to a WAN are often connected through public networks, such as telephone system. The largest WAN in existence is the Internet.
Advantages of WAN
v It covers a very large geographic area, like country or long distance businesses can connect on the one network.
v The speed of WAN is very high.
v The largest WAN in existence is the Internet.
v Message can be sent very quickly to anyone else on the network.
Disadvantages of WAN
v The bigger the network the more expensive it is
v The cost for equipment and technology is very expensive. '
MAN
MAN is term as Metropolitan Area Network, a data network is designed for a home or city. In terms of geographic breadth, man's are larger than local-area networks (LAN's), but smaller than wide area network (WAN's). Man's are usually characterized by very high speed connections using cable or digital media.
Comparison between LAN, MAN & WAN.
|
Inter processor Distance |
Processors Located in Same |
Example |
|
1m |
Square meter |
LAN |
|
10 m |
Room |
LAN |
|
100 m |
Building |
LAN |
|
1 km |
Campus |
LAN |
|
10 km |
City |
MAN |
|
100 km |
Country |
WAN |
|
1000 km |
Continent |
WAN |
|
10,000 km |
Planet |
Internet |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
