Fun with Numbers
Category : 3rd Class
Learning Objectives
This lesson will help you to read:—
Amazing Facts
Zero (0) is the only number which cannot be represented by Roman numerals.
Abacus is considered the origin of the calculator.
While writing number names from 0 to 1,000 the letter “A” only appears in 1,000 (‘’ one thousand ’)
Quick Concept Review
Even and odd Numbers
Ascending and Descending Numbers
Place Value
The value of a digit due to its position in a number is called its place value.
|
Ten thousands |
Thousands |
Hundreds |
Tens |
Ones |
|
10000 |
1000 |
100 |
10 |
1 |
For example if we have to place 87654 we will show it
|
Ten thousands |
Thousands |
Hundreds |
Tens |
Ones |
|
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
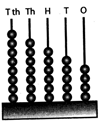
Face Value
Face value of a digit in a number is the digit itself. For example- Face value of 9 in 1892 is 9.
Let's understand the concept of place value and face value with few more examples.
Expanded Form of Number
We find that when we add the place values of all the digits in a number we get the number. For example:-
300 +80+6 is the expanded form of 386.
Let's get it clear with few more examples:
(a) 819 = 800+10+9
(b) 206 =200+6
(c) 467 = 400 +60+7
Number Names
We know that a number's name is derived from where the digits are placed in the number. For example: The number name of 87654 is Eighty seven thousand six hundred and fifty four.
Few more examples for you:
(a) 32436 –Thirty two thousand four hundred and thirty six.
(b) 126252 – Twelve thousand six hundred and fifty two
Historical preview
Smallest and Largest Number
Let's take another example.
Also look at these examples of greater than and less than.
(a) Greater than: 43 > 34
(b) Less than: 57 < 69
(c) Equal to: 197 = 197
Skip Counting
2, 4, 6, 8, 10....
(b) skip counting of 3 can be done as - 3,6,9,12,15....
(c) Skip count in fives following 50 can be done as 55, 60, 65, 70....
Here, every number is five number more than the previous number
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
