Some Definitions
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
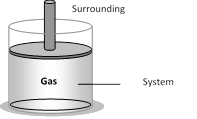
(1) Thermodynamic system
(i) It is a collection of an extremely large number of atoms or molecules
(ii) It is confined with in certain boundaries.
(iii) Anything outside the thermodynamic system to which energy or matter is exchanged is called its surroundings.
(iv) Thermodynamic system may be of three types
(a) Open system : It exchange both energy and matter with the surrounding.
(b) Closed system : It exchange only energy (not matter) with the surroundings. (c) Isolated system : It exchange neither energy nor matter with the surrounding. 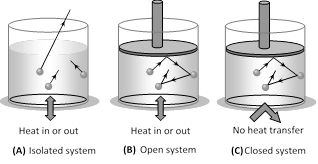
(2) Thermodynamic variables and equation of state : A thermodynamic system can be described by specifying its pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy and the number of moles. These parameters are called thermodynamic variables. The relation between the thermodynamic variables (P, V, T) of the system is called equation of state.
For \[\mu \] moles of an ideal gas, equation of state is \[PV=\mu RT\] and for 1 mole of an it ideal gas is PV = RT
(3) Thermodynamic equilibrium : In steady state thermodynamic variables are independent of time and the system is said to be in the state of thermodynamic equilibrium. For a system to be in thermodynamic equilibrium, the following conditions must be fulfilled.
(i) Mechanical equilibrium : There is no unbalanced force between the system and its surroundings.
(ii) Thermal equilibrium : There is a uniform temperature in all parts of the system and is same as that of surrounding.
(iii) Chemical equilibrium : There is a uniform chemical composition through out the system and the surrounding.
(4) Thermodynamic process : The process of change of state of a system involves change of thermodynamic variables such as pressure P, volume V and temperature T of the system. The process is known as thermodynamic process. Some important processes are
(i) Isothermal process : Temperature remain constant
(ii) Adiabatic process : No transfer of heat
(iii) Isobaric process : Pressure remains constant
(iv) Isochoric (isovolumic process) : Volume remains constant
(v) Cyclic and non-cyclic process : Incyclic process Initial and final states are same while in non-cyclic process these states are different.
(vi) Reversible and irreversible process :
(5) Indicator diagram : Whenever the state of a gas (P, V, T) is changed, we say the gaseous system is undergone a thermodynamic process. The graphical representation of the change in state of a gas by a thermodynamic process is called indicator diagram. Indicator diagram is plotted generally in pressure and volume of gas.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
